
Knowledge management (KM) is the collection of methods relating to creating, sharing, using and managing the knowledge and information of an organization. It refers to a multidisciplinary approach to achieve organizational objectives by making the best use of knowledge.

The United States' National Science Digital Library (NSDL) is an open-access online digital library and collaborative network of disciplinary and grade-level focused education providers operated by the Institute for the Study of Knowledge Management in Education. NSDL's mission is to provide quality digital learning collections to the science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education community, both formal and informal, institutional and individual. NSDL's collections are refined by a network of STEM educational and disciplinary professionals. Their work is based on user data, disciplinary knowledge, and participation in the evolution of digital resources as major elements of effective STEM learning.
Media literacy is an expanded conceptualization of literacy that includes the ability to access and analyze media messages as well as create, reflect and take action, using the power of information and communication to make a difference in the world. Media literacy is not restricted to one medium and is understood as a set of competencies that are essential for work, life, and citizenship. Media literacy education is the process used to advance media literacy competencies, and it is intended to promote awareness of media influence and create an active stance towards both consuming and creating media. Media literacy education is part of the curriculum in the United States and some European Union countries, and an interdisciplinary global community of media scholars and educators engages in knowledge and scholarly and professional journals and national membership associations.
The Association of College and Research Libraries defines information literacy as a "set of integrated abilities encompassing the reflective discovery of information, the understanding of how information is produced and valued and the use of information in creating new knowledge and participating ethically in communities of learning". In the United Kingdom, the Chartered Institute of Library and Information Professionals' definition also makes reference to knowing both "when" and "why" information is needed.
M-learning, or mobile learning, is a form of distance education where learners use portable devices such as mobile phones to learn anywhere and anytime. The portability that mobile devices provide allows for learning anywhere, hence the term "mobile" in "mobile learning." M-learning devices include computers, MP3 players, mobile phones, and tablets. M-learning can be an important part of informal learning.

Open educational resources (OER) are teaching, learning, and research materials intentionally created and licensed to be free for the end user to own, share, and in most cases, modify. The term "OER" describes publicly accessible materials and resources for any user to use, re-mix, improve, and redistribute under some licenses. These are designed to reduce accessibility barriers by implementing best practices in teaching and to be adapted for local unique contexts.
Social practice is a theory within psychology that seeks to determine the link between practice and context within social situations. Emphasized as a commitment to change, social practice occurs in two forms: activity and inquiry. Most often applied within the context of human development, social practice involves knowledge production and the theorization and analysis of both institutional and intervention practices.
Digital literacy is an individual's ability to find, evaluate, and communicate information by utilizing typing or digital media platforms. It is a combination of both technical and cognitive abilities in using information and communication technologies to create, evaluate, and share information.

NHS Education for Scotland (NES) is an education and training body and a national (special) health board within NHS Scotland.
The National electronic Library for Health (NeLH) was a digital library service provided by the NHS for healthcare professionals and the public between 1998 and 2006. It briefly became the National Library for Health and elements of it continue to this day as NHS Evidence, managed by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, and a range of services provided by Health Education England's Library and Knowledge Service Leads.
In England, social care is defined as the provision of social work, personal care, protection or social support services to children or adults in need or at risk, or adults with needs arising from illness, disability, old age or poverty. The main legal definitions flow from the National Health Service and Community Care Act 1990, with other provisions covering disability and responsibilities to informal carers. That provision may have one or more of the following aims: to protect people who use care services from abuse or neglect, to prevent deterioration of or promote physical or mental health, to promote independence and social inclusion, to improve opportunities and life chances, to strengthen families and to protect human rights in relation to people's social needs.
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is the British government’s major funder of clinical, public health, social care and translational research. With a budget of over £1.2 billion in 2020–21, its mission is to "improve the health and wealth of the nation through research". The NIHR was established in 2006 under the government's Best Research for Best Health strategy, and is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. As a research funder and research partner of the NHS, public health and social care, the NIHR complements the work of the Medical Research Council. NIHR focuses on translational research, clinical research and applied health and social care research.
The UNESCO Institute for Statistics (UIS) is the statistical office of UNESCO and is the UN depository for cross-nationally comparable statistics on education, science and technology, culture, and communication.

Open educational practices (OEP) are part of the broader open education landscape, including the openness movement in general. It is a term with multiple layers and dimensions and is often used interchangeably with open pedagogy or open practices. OEP represent teaching and learning techniques that draw upon open and participatory technologies and high-quality open educational resources (OER) in order to facilitate collaborative and flexible learning. Because OEP emerged from the study of OER, there is a strong connection between the two concepts. OEP, for example, often, but not always, involve the application of OER to the teaching and learning process. Open educational practices aim to take the focus beyond building further access to OER and consider how in practice, such resources support education and promote quality and innovation in teaching and learning. The focus in OEP is on reproduction/understanding, connecting information, application, competence, and responsibility rather than the availability of good resources. OEP is a broad concept which can be characterised by a range of collaborative pedagogical practices that include the use, reuse, and creation of OER and that often employ social and participatory technologies for interaction, peer-learning, knowledge creation and sharing, empowerment of learners, and open sharing of teaching practices.

OER Commons is a freely accessible online library that allows teachers and others to search and discover open educational resources (OER) and other freely available instructional materials.
CELCIS is the Centre for Excellence for Children's Care and Protection, based at the University of Strathclyde in Glasgow, Scotland and is an organisation that supports the rights and well-being of children and young people and teenagers.
FELTAG is an acronym for Further Education Learning Technology Action Group, based in the United Kingdom. The group was convened by the Minister of State for Skills and Enterprise, Matthew Hancock at the Department of Business, Innovation and Skills.
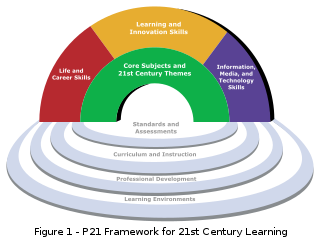
21st century skills comprise skills, abilities, and learning dispositions that have been identified as being required for success in 21st century society and workplaces by educators, business leaders, academics, and governmental agencies. This is part of a growing international movement focusing on the skills required for students to master in preparation for success in a rapidly changing, digital society. Many of these skills are also associated with deeper learning, which is based on mastering skills such as analytic reasoning, complex problem solving, and teamwork. These skills differ from traditional academic skills in that they are not primarily content knowledge-based.
Joyce Lishman the first woman Professor at Robert Gordon University, was a leader in social work education and research.







