A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.

Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R–O–R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (CH3–CH2–O–CH2–CH3). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.
In chemistry, the empirical formula of a chemical compound is the simplest positive integer ratio of atoms present in a compound. A simple example of this concept is that the empirical formula of sulfur monoxide, or SO, would simply be SO, as is the empirical formula of disulfur dioxide, S2O2. Thus, sulfur monoxide and disulfur dioxide, both compounds of sulphur and oxygen, have the same empirical formula. However, their molecular formulas, which express the number of atoms in each molecule of a chemical compound, are not the same.

Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3 (also represented by the pseudoelement symbols PhAc or BzMe). It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphic representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are possibly arranged in the real three-dimensional space. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly. Unlike chemical formulas, which have a limited number of symbols and are capable of only limited descriptive power, structural formulas provide a more complete geometric representation of the molecular structure. For example, many chemical compounds exist in different isomeric forms, which have different enantiomeric structures but the same chemical formula.

An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base. "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula C
2H
3O−
2. The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a positive ion are also commonly called "acetates". The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion CH
3CO−
2, or CH
3COO−
.

In the context of organic molecules, aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as a placeholder for the aryl group in chemical structure diagrams, analogous to “R” used for any organic substituent. “Ar” is not to be confused with the elemental symbol for argon.
Lewis structures, also known as Lewis dot formulas,Lewis dot structures, electron dot structures, or Lewis electron dot structures (LEDS), are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, as well as the lone pairs of electrons that may exist in the molecule. A Lewis structure can be drawn for any covalently bonded molecule, as well as coordination compounds. The Lewis structure was named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced it in his 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule. Lewis structures extend the concept of the electron dot diagram by adding lines between atoms to represent shared pairs in a chemical bond.
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula –CH
2CH
2CH
3 for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr.
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula −C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers (n-butane and isobutane) of butane.
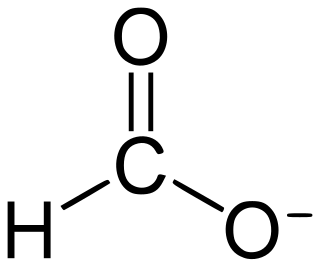
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the anion derived from formic acid. Its formula is represented in various equivalent ways: HCOO− or CHOO− or HCO2−. It is the product of deprotonation of formic acid. It is the simplest carboxylate anion. A formate (compound) is a salt or ester of formic acid.
The IUPAC International Chemical Identifier is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by IUPAC and NIST from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary.

tert-Butyl alcohol is the simplest tertiary alcohol, with a formula of (CH3)3COH (sometimes represented as t-BuOH). It is one of the four isomers of butanol. tert-Butyl alcohol is a colorless solid, which melts near room temperature and has a camphor-like odor. It is miscible with water, ethanol and diethyl ether.

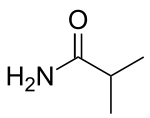
Butyramide is the amide of butyric acid. It has the molecular formula C3H7CONH2. It is a white solid that is freely soluble in water and ethanol, but slightly soluble in diethyl ether. At room temperature, butyramide is a crystalline solid and in contrast to butyric acid, it is devoid of an unpleasant, rancid smell.
In mathematics, the Weyl character formula in representation theory describes the characters of irreducible representations of compact Lie groups in terms of their highest weights. It was proved by Hermann Weyl. There is a closely related formula for the character of an irreducible representation of a semisimple Lie algebra. In Weyl's approach to the representation theory of connected compact Lie groups, the proof of the character formula is a key step in proving that every dominant integral element actually arises as the highest weight of some irreducible representation. Important consequences of the character formula are the Weyl dimension formula and the Kostant multiplicity formula.

The hydroxymethyl group is the name for a substituent with the structural formula −CH2−OH. It consists of a methylene bridge (−CH2− unit) bonded to a hydroxyl group (−OH). This makes the hydroxymethyl group an alcohol. It has the identical chemical formula with the methoxy group (−O−CH3) that differs only in the attachment site and orientation to the rest of the molecule. However, their chemical properties are different.
![Enterodiol Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)
Enterodiol is an organic compound with the formula [HOC6H4CH2CH(CH2OH)]2.
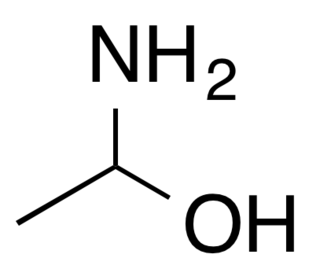
1-Aminoethanol is an organic compound with the formula CH3CH(NH2)OH. It is classified as an alkanolamine. Specifically, it is a structural isomer of 2-aminoethanol (ethanolamine). These two compounds differ in the position of the amino group. Since the central carbon atom in 1-aminoethanol has four different substituents, the compound has two stereoisomers. Unlike 2-aminoethanol, which is of considerable importance in commerce, 1-aminoethanol is not encountered as a pure material and is mainly of theoretical interest.
Sodium bromite is a sodium salt of bromous acid. Its trihydrous form has been isolated in crystal form. It is used by the textile refining industry as a desizing agent for oxidative starch removal.

The CompTox Chemicals Dashboard is a freely accessible online database created and maintained by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The database provides access to multiple types of data including physicochemical properties, environmental fate and transport, exposure, usage, in vivo toxicity, and in vitro bioassay. EPA and other scientists use the data and models contained within the dashboard to help identify chemicals that require further testing and reduce the use of animals in chemical testing. The Dashboard is also used to provide public access to information from EPA Action Plans, e.g. around perfluorinated alkylated substances.,











![Enterodiol Lignan formed by the action of intestinal bacteria on lignan precursors found in plants.[1]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/e/eb/Enterodiol.png/320px-Enterodiol.png)

