| Raqqa Revolutionaries Front Jabhat Thūwwār ar-Raqqah | |
|---|---|
جبهة ثوار الرقة Participant in the Syrian Civil War | |
 Logo of Liwa Thuwar al-Raqqa  Flag of Jabhat Thuwar al-Raqqa | |
| Active | September 2012 – present |
| Ideology | Sunni Islamism (2012–14) [1] |
| Groups |
Former:
|
| Leaders | |
| Headquarters | Ayn Issa |
| Area of operations | Raqqa Governorate, Syria [13] Aleppo Governorate, Syria [9] |
| Size | +800 [14] |
| Part of |
|
| Originated as | Raqqa Revolutionaries Brigade (Liwa Thuwar al-Raqqa) |
| Allies | |
| Opponents | |
| Battles and wars | |
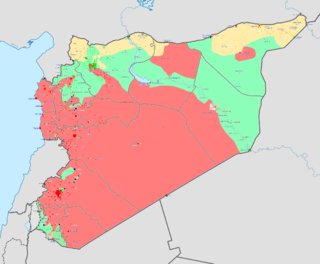
Jabhat Thuwar al-Raqqa (Arabic : جبهة ثوار الرقة, translit. Jabhat Thūwwār ar-Raqqah), or the Front of Raqqa Revolutionaries, is a rebel group that has been active during the Syrian Civil War. [19] It is currently part of the Syrian Democratic Forces, the group which is backed by the American-led intervention in Syria. During an interview by Aymenn Jawad Al-Tamimi in 2015, Liwa Thuwar al-Raqqa's media director stated that the group wants a "civil democratic state". He also claimed that the group had no relations with the Syrian National Coalition based in Turkey. [1]
The romanization of Arabic writes written and spoken Arabic in the Latin script in one of various systematic ways. Romanized Arabic is used for a number of different purposes, among them transcription of names and titles, cataloging Arabic language works, language education when used in lieu of or alongside the Arabic script, and representation of the language in scientific publications by linguists. These formal systems, which often make use of diacritics and non-standard Latin characters and are used in academic settings or for the benefit of non-speakers, contrast with informal means of written communication used by speakers such as the Latin-based Arabic chat alphabet.

The Syrian Civil War is an ongoing multi-sided armed conflict in Syria fought between the Ba'athist Syrian Arab Republic led by President Bashar al-Assad, along with domestic and foreign allies, and various domestic and foreign forces opposing both the Syrian government and each other in varying combinations.

The Syrian Democratic Forces, commonly abbreviated to SDF, HSD, and QSD, is an alliance in the Syrian Civil War comprised primarily of Kurdish, Arab, and Assyrian/Syriac militias, as well as some smaller Turkmen and Chechen forces. The SDF is militarily led by the People's Protection Units (YPG), a mostly Kurdish militia. Founded in October 2015, the SDF states its mission as fighting to create a secular, democratic and federal Syria. The updated December 2016 constitution of the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (NES) names the SDF as its official defence force.
Contents
It was formed in the Raqqa Governorate in September 2012, under its original name Liwa Thuwar al-Raqqa (Arabic: لواء ثوار الرقة, translit. Liwā' Thūwwār ar-Raqqah, lit. 'Raqqa Revolutionaries' Brigade'). [1]
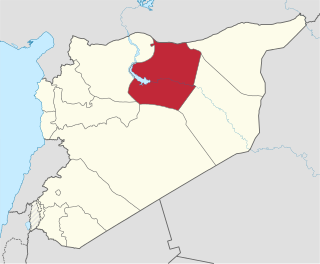
Raqqa Governorate is one of the fourteen governorates (provinces) of Syria. It is situated in the north of the country and covers an area of 19,616 km². The governorate has a population of 921,000. The capital is Raqqa. The Islamic State of Iraq and Levant claimed full control of this province as of August 24, 2014 when its fighters captured Tabqa Airbase in the southwest part of the province. However, the Syrian Democratic Forces now control much of the province; all of the area north of the Euphrates River including the provincial capital of Raqqa and the city of al-Thawrah are under SDF control, with the government holding the southern part of the governorate after a successful offensive was launched with the aid of Liwa al-Quds, tribal militias and Russian air support, which resulted in the recapture of the city of Resafa, and the capture of many oil fields in Ar-Raqqah province, including various oil and gas stations.