
John Cleves Symmes Jr. was an American Army officer, trader, and lecturer. Symmes is best known for his 1818 variant of the Hollow Earth Theory, which introduced the concept of openings to the inner world at the poles.

The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-foot (411 m)-long, three-foot-high prehistoric effigy mound on a plateau of the Serpent Mound crater along Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. Maintained within a park by Ohio History Connection, it has been designated a National Historic Landmark by the United States Department of Interior. The Serpent Mound of Ohio was first reported from surveys by Ephraim Squire and Edwin Davis in their historic volume Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley, published in 1848 by the newly founded Smithsonian Museum.

Fort Ancient is a Native American earthworks complex located in Washington Township, Warren County, Ohio, along the eastern shore of the Little Miami River about seven miles (11 km) southeast of Lebanon on State Route 350. The site is the largest prehistoric hilltop enclosure in the United States with three and one-half miles (18,000 ft) of walls in a 100-acre (0.40 km2) complex. Built by the Hopewell culture, who lived in the area from the 200 BC to AD 400, the site is situated on a wooded bluff 270 feet (82 m) above the Little Miami. It is the namesake of a culture known as Fort Ancient who lived near the complex long after it was constructed.

The various cultures collectively termed "Mound Builders" were inhabitants of North America who, during a circa 5,000-year period, constructed various styles of earthen mounds for religious, ceremonial, burial, and elite residential purposes. These included the pre-Columbian cultures of the Archaic period, Woodland period, and Mississippian period; dating from roughly 3500 BCE to the 16th century CE, and living in regions of the Great Lakes, the Ohio River Valley, and the Mississippi River valley and its tributary waters.

Hopewell Culture National Historical Park is a United States national historical park with earthworks and burial mounds from the Hopewell culture, indigenous peoples who flourished from about 200 BC to AD 500. The park is composed of six separate sites in Ross County, Ohio, including the former Mound City Group National Monument. The park includes archaeological resources of the Hopewell culture. It is administered by the United States Department of the Interior's National Park Service.

Caleb Atwater was an American politician, historian, and early archaeologist in the state of Ohio. He served several terms as a state politician and was appointed as United States postmaster of Circleville, Ohio. He was known best during the 19th century for his publication History of the State of Ohio (1838), the first book-length history of the new state. It also included much natural lore.

Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley (1848) by the Americans Ephraim George Squier and Edwin Hamilton Davis is a landmark in American scientific research, the study of the prehistoric indigenous mound builders of North America, and the early development of archaeology as a scientific discipline. Published in 1848, it was the Smithsonian Institution's first publication and the first volume in its Contributions to Knowledge series. The book had 306 pages, 48 lithographed maps and plates, and 207 wood engravings.
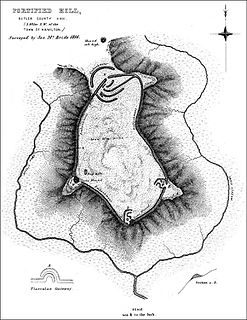
Fortified Hill Works is a registered historic site near Hamilton, Ohio, listed in the National Register on July 12, 1974.

The Hopeton Earthworks are Hopewell culture mounds and earthworks located about a mile east of the Mound City group on a terrace of the Scioto River. The walls have been damaged by cultivation. They are contained in a detached portion of Hopewell Culture National Historic Park, east of the main Mound City Group. The Hopeton Earthworks are open to the public.
The Portsmouth Earthworks are a large prehistoric mound complex constructed by the Ohio Hopewell culture mound builder indigenous peoples of eastern North America. The site was one of the largest earthwork ceremonial centers constructed by the Hopewell and is located at the confluence of the Scioto and Ohio Rivers, in present-day Ohio.
Edwin Hamilton Davis was an American archaeologist and physician who completed pioneering investigations of the mound builders in the Mississippi Valley. Davis gathered the largest collection of prehistoric Indian collections in the United States.

The Wolf Plains Group is a Late Adena culture group of 30 earthworks including 22 conical mounds and nine circular enclosures. The Plains, originally known as Wolf's Plains, located a few miles to the northwest of Athens, is a relatively flat terrace in an area of hilly terrain in southeastern Ohio's Hocking River valley. The terrace was formed by glacial outwash coming down the Hocking River, which became dammed at The Plains and found a new outlet to the northeast, leaving the terrace in place.

The Mount Horeb Earthworks Complex is an Adena culture group of earthworks in Fayette County, Kentucky. It consists of two major components, the Mount Horeb Site 1 and the Peter Village enclosure, and several smaller features including the Grimes Village site, Tarleton Mound, and Fisher Mound. The Peter Village and Grimes Village enclosures were mapped by Rafinesque and featured in Squier and Davis's landmark publication Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley in 1848 as Plate XIV Figures 3 and 4.

The Biggs Site (15Gp8), also known as the Portsmouth Earthworks Group C, is an Adena culture archaeological site located near South Shore in Greenup County, Kentucky. Group C was originally a large series of concentric circular embankments and ditches surrounding a central conical burial mound. It was part of a larger complex, the Portsmouth Earthworks located across the Ohio River, now mostly obliterated by agriculture and the developing city of Portsmouth, Ohio. The site was surveyed and mapped by E. G. Squier in 1847 for inclusion in the seminal archaeological and anthrolopological work Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley.

Indian Mound Reserve is a public country park near the village of Cedarville, Ohio, United States. Named for two different earthworks within its bounds — the Williamson Mound and the Pollock Works — the park straddles Massies Creek as it flows through a small canyon.
Fort Hill State Memorial is a Native American earthwork located in Highland County, Ohio, United States. Built by the Hopewell culture, it is maintained by the Arc of Appalachia Preserve System and the Ohio History Connection.
The Junction Group is a site of earthworks located two miles southwest of Chillicothe, Ohio in the United States. The earthworks are associated with the Hopewell tradition. The site has been described as "unusual" by contemporary archaeologists. Excavations in the early 19th-century state that the site was not for fortification, but was used for religious purposes, including for burials.
The Dunlap Works are a group of Hopewell tradition earthworks located in Ross County, Ohio in the United States. It is located approximately 6 miles (9.7 km) north of the city of Chillicothe, Ohio on the left bank of the Scioto River. The site should not be confused with the earthworks in Hamilton County on the Great Miami River near Dunlap's Station, the former site of a pioneer fort.

The Piketon Mounds are a group of earthworks located in Piketon, Ohio in the United States. The site is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The specific age of the site is unknown. Some mounds were created by the Adena culture, while other mounds were built by the Hopewell culture.

The Stubbs Earthworks was a massive Ohio Hopewell culture archaeological site located in Morrow in Warren County, Ohio.




















