Related Research Articles

Helena is the capital city of the U.S. state of Montana and the seat of Lewis and Clark County.

Page County is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 15,211. The county seat is Clarinda. The county is named in honor of Captain John Page of the 4th U.S. Infantry, who was mortally wounded in the Battle of Palo Alto.

Clarinda is a city in and the county seat of Page County, Iowa. It is located in Nodaway Township. The population was 5,369 at the time of the 2020 census.

Shenandoah is a city in Page and Fremont counties in Iowa, United States. The population was 4,925 at the time of the 2020 U.S. Census. Once referred to as the "seed and nursery center of the world," Shenandoah is the home to Earl May Seed Company and the radio station KMA, founded by Earl E. May. The early live radio stations gave many performers their start, including The Everly Brothers and Charlie Haden.

4-H is a U.S.-based network of youth organizations whose mission is "engaging youth to reach their fullest potential while advancing the field of youth development". Its name is a reference to the occurrence of the initial letter H four times in the organization's original motto "head, heart, hands, and health", which was later incorporated into the fuller pledge officially adopted in 1927. In the United States, the organization is administered by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). 4-H Canada is an independent non-profit organization overseeing the operation of branches throughout Canada. There are 4-H organizations in over 50 countries; the organization and administration varies from country to country.

Georgia 4-H was founded in 1904 by G.C. Adams in Newton County, Georgia, United States, as the Girls Canning, and Boys Corn Clubs.

Iowa Western Community College is a public community college in Council Bluffs, Iowa. It was founded in 1967 and offers 84 programs in both vocational and technical areas as well as in liberal arts. It is also home to a flight school.

KMA is a radio station licensed to serve Shenandoah, Iowa.
Leanna Field Driftmier (1886–1976) was an American radio personality and writer based in Shenandoah, Iowa. Driftmier’s daily 30-minute show Kitchen-Klatter was broadcast around the midwestern United States for five decades. It was the longest-running homemaker show in US radio history.

Thomas Van Scoy was an American minister and educator in Indiana, Oregon, and Montana. A Methodist, he served as the sixth president of Willamette University and as president of the now defunct Portland University. He was also president of Montana Wesleyan University and served in the militia at the end of the American Civil War.

Willis Allen "Bill" Glassgow graduated from Shenandoah Iowa high school. Willis was an American football player and attorney. He played halfback for the University of Iowa from 1927 to 1929, was selected as a first-team All-American in 1929, and received the 1929 Chicago Tribune Silver Football as the best football player in the Big Ten Conference. He played two seasons of professional football in the National Football League for the Portsmouth Spartans in 1930 and the Chicago Cardinals in 1931. He practiced law in Iowa from 1933 to 1959, including two terms as the Page County Attorney (1935–1939) and three terms as the Linn County Attorney (1951–1957).


The Goldenrod Schoolhouse is a historic building located in Clarinda, Iowa, United States. The 23-by-33-foot one-room school was built in Fremont Township, northern Page County, in 1873. Jessie Field taught in the school at the turn of the 20th century. She initiated a school program here in March 1901 that eventually developed into the 4-H organization. The building served as part of the Page County rural school system until 1960. It was slated for demolition when it was saved and moved to the Page County Fairgrounds in Clarinda in 1965. It was near to the place that Jessie Field had held the first Boys Farm Camp and Camp of the Golden Maids in 1910 and 1911. The former school building was originally listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1975.

Lottie Estelle Granger was an American educator and school officer from the U.S. state of Ohio. She served as county superintendent of public schools of Page County, Iowa, and was the second woman elected president of the Iowa State Teachers' Association.
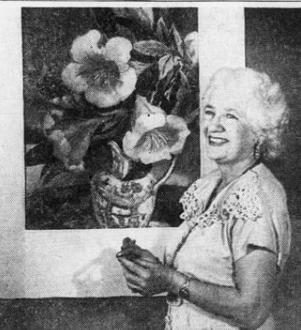
Mildred W. Pelzer was an American art teacher, artist and muralist known for her work in public spaces. In addition to the mural for the post office mural project in Waverly, Iowa, she completed eight murals for the Hotel Jefferson, of Iowa City and a mural for the lobby of the Press-Citizen. In addition to her mural work, Pelzer was known for portraits, floral works and landscapes.
Sara Evans Morse was an American public official in Montana. Morse was the executive secretary of the Montana Tuberculosis Association for three terms.

The Fort Shaw Indian School Girls Basketball Team was made up of seven Native American students from various tribes who attended the Fort Shaw Indian Boarding School in Fort Shaw, Montana, United States. They became World Champions at the 1904 Louisiana Purchase Exposition by defeating basketball teams from across the United States and world.

Agnes Mathilda Samuelson was an American educator and a state superintendent in public schools. She worked to provide equal education for all students in Iowa. She was posthumously inducted into the Iowa Women's Hall of Fame in 1976 and a Des Moines elementary school was named after her.
References
- ↑ Longden, Tom. Famous Iowans: Jessie Field Shambaugh. Des Moines Register
- ↑ Staff report (January 18, 1971). "Jessie Shambaugh Dead; A Founder of 4-H Clubs". New York Times
- ↑ "Bill Announcement". whitehouse.gov – via National Archives.