The Vaghela dynasty ruled the Kingdom of Gujarat in India in the 13th century CE, with their capital at Dholka. They were the last Hindu dynasty to rule Gujarat before the Muslim conquest of the region. They belonged to the Vaghela clan of Rajputs.

Surendranagar is an administrative district in Saurashtra region of Gujarat state in India. It has a population of approximately 1.7 million people. Surendranagar, along with the twin city of Wadhwan, has a total of 400,000 inhabitants, and is known as "Camp".
Parmar, also known as Panwar or Pawar, is a Rajput clan found in Northern and Central India, especially in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and North Maharashtra. The Panwar ruled in Ujjain and later in Dhar.
The Khasia, or Khasiya is a clan (Gotra) of the Koli caste found in the Indian state of Gujarat. The Mahuva was the stronghold or controlled by Khasia Kolis but they were defeated by the Thakur Wakhatsinhji of Bhavnagar State and their controlled Territories of Mahuva, Kundla, Rajula, Gadhada and Botad. Khasiya Kolis were pirates in Gujarat ocean and lived by piracy.
Guhila is a clan of Rajputs. They ruled a number of kingdoms and principalities including Mitaron, Mewar, Banswara, Dungarpur, Pratapgarh, Shahpura, Bhavnagar, Palitana, Lathi and Vala.

The Maukhari dynasty was the ruling house of the Kingdom of Kannauj and controlled the vast plains of Ganga-Yamuna for over six generations from their capital at Kannauj. They earlier served as vassals of the Guptas. The Maukharis established their independence during the mid 6th century. The dynasty ruled over much of Uttar Pradesh and Magadha. Around 606 CE, a large area of their empire was reconquered by the Later Guptas of Magadha. According to Xuanzang, the territory may have been lost to King Shashanka of the Gauda Kingdom, who declared independence circa 600CE.
Ranpur is a town located on the bank of the river Bhadar in Botad district, Gujarat, India. Ranpur is little city of botad district.
Jhala is a Rajput clan. They are found in Rajasthan and Gujarat state of India. The clan is also found among Koli castes as Jala.
The Vala, or Wala is a Gujarati clan (Gotra) mostly found among Koli, Rajput and Kathi castes of Gujarat.
The Dabhi is a Rajput clan of Gujarat in India. The name is also found among the Indian Kolis.
Mahyavanshi are a scheduled caste of India, who were originally identified with Vankars but started a successful movement in the 20th century to establish their identity as a branch of Mayavat rulers.
The Sarvaiya also spelled Sarvaiyya, Sarvia, Sarwia, SavariaSawaria are a social group of India, mainly found in Gujarat. They are offshoot of the Chudasama clan. Sarvaiya Rajputs were jagirdars of many estate, like Vasavad, Bhadli, Chital, Bhakhalka till Independence of India, when jagirdari was abolished.
Raijada or Raizada are one of the Rajput clans .They are off-shoot of Chudasama Rajputs.The name Raijada was adopted by one Bhupatsinh, son of Ra' Mandlik, who was given jagir of Sorath The Raijada, Rana, Sarvaiya and Chudasama consider themselves brothers, they off-shoot branches from Chudasama, so they do not intermarry, as per their Rajput traditions. Until independence of India, they held extensive Jagirs near Keshod and Chorwad in Sorath.

Dhrangadhra State was a princely state during the British Raj in India. The town of Dhrangadhra served as its capital. It was also known as Halvad-Dhrangadhra State. Halvad once had been the capital of this state. In 1735, Dhrangadhra was founded as its new capital.
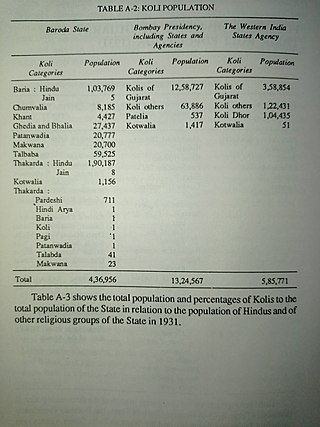
The Baria Koli, or Baraiya Koli, Bareeya Koli and Bariya Koli is a clan (Gotra) of the Koli caste found in the Indian State of Gujarat and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. the Devgad Baria was their Stronghold or given their name to Baria State in Gujarat.
The Gohil dynasty or Gohil or Guhilas of Saurashtra ruled parts of Saurashtra region of present-day Gujarat state of India as subordinates or independents starting 12th century. Their origin is traced to Guhila dynasty of Gujarat and they had migrated to Saurashtra in 12th century. The earliest known inscription of Gohils is found from Mangrol. They later moved to the east coast where they established themselves and the region came to be known as Gohilwar and ruled till the independence of India in 1947. The erstwhile princely states of Bhavnagar, Palitana, Lathi, Vala and Rajpipla belonged to Gohil rulers.
Tumbel is a clan and division of the Charanas of Gujarat, Sindh, and Balochistan. Historically, they were known for their military services in the kingdoms of Kutch and Nawanagar.
The Rajputs in Gujarat, or Gujarati Rajputs are members of the Rajput community living in the western Indian state of Gujarat. They ruled several dynasties and princely states during the British era. Some Rajput clans of Gujarat have origins from outside regions such as Rajasthan, while others are native to the region.

Raj Jhalleshvar Maharaj Rana Ajay Singh Jhala, known as Ajja Jhala or Ajoji, was the 25th ruler of Jhalavad (Dhrangadhra). He was an important vassal of Mewar during Rana Sanga's period. He played a crucial role in the battles of Bayana, Dholpur and Khanwa. He wore the royal insignia of Rana Sanga and was reputed to have saved Sanga's life in battle of Khanwa.
Jhala is a surname of Gujarati and Rajasthani Rajputs based in Indian states of Gujarat and southern Rajasthan.











