Wadhwan State | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1630–1948 | |||||||||
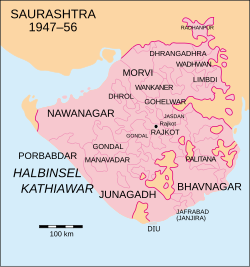 Location of Wadhwan State in Saurashtra | |||||||||
| Capital | Wadhwan | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1630 | ||||||||
• Accession to the Indian Union | 1948 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1931 | 627 km2 (242 sq mi) | ||||||||
| 1943 | 1,202 km2 (464 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1931 | 42,602 | ||||||||
• 1943 | 69,245 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Wadhwan State was an offshoot of Jhalavad, later became 9-guns Salute princely state during the British Raj. It ruled by the Jhala clan of Rajputs [1]
Contents
The town of Wadhwan in the Saurashtra region of Gujarat was its capital. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 15 February 1948. [2] [3]

