
Vindhya Pradesh was a former state of India. It occupied an area of 61,131.5 km2. It was created in 1948 as Union of Baghelkhand and Bundelkhand States, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named as Vindhya Pradesh on 25 January 1950 after the Vindhya Range, which runs through the centre of the province. The capital of the state was the former princely state of Rewa. It lay between Uttar Pradesh to the north and Madhya Pradesh to the south, and the enclave of Datia, which lay a short distance to the west, was surrounded by the state of Madhya Bharat.

Panna is a city and a municipality in Panna district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is known for its diamond mines and temples. It is the administrative centre of Panna District.

Satna is a city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of Satna district. It is 7th largest city and 8th most populous city of the state. The city is 500 km east of the state capital Bhopal. The city is distributed over a land area of 111.9 square kilometres.
Bijawar is a city the state of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Bijawar Taluk, and was formerly the capital of a princely state of British India of the same name. The people of Bijawar are demanding the district status from their state government. It is the 53rd proposed district of Madhya Pradesh

The Bundelkhand Agency was a political agency of the British Raj, managing the relations of the British government with the protected princely states of the Bundelkhand region.

Rewa State, also known as Rewah, was a kingdom and later princely state of India, surrounding its eponymous capital, the town of Rewa.

Alipura was a princely state in what is today the Chhatarpur District in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.

Baraundha was a princely state of colonial India, located in modern Satna district of Madhya Pradesh. Although historically far larger, at the time of Indian independence in 1950, it was a saluted state of 9 guns.

Datia State was a princely state in subsidiary alliance with British India.

Orchha State was a kingdom situated in the Bundelkhand region and later a princely state in British India. The state was ruled by Bundela clan of Rajputs. It was located within what is now the state of Madhya Pradesh.

Alirajpur State was formerly a princely state of India, administratively under the Bhopawar Agency subdivision of the Central India Agency. The state covered an area of 2165 square kilometres, with a population of 50,185 in 1901 and its capital at Alirajpur. The average revenue of the state was Rs.100,000 in 1901.

Chhatarpur Assembly constituency is one of the 230 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. This constituency came into existence in 1951, as one of the 48 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of the erstwhile Vindhya Pradesh state.

Bijawar Assembly constituency is one of the 230 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of Madhya Pradesh state in central India. This constituency came into existence in 1951, as one of the 48 Vidhan Sabha constituencies of the erstwhile Vindhya Pradesh state.

Ajaigarh State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The state was ruled by Bundela clan of Rajput But later on this place was ruled by Yadav (Dauwa) kings.. The state was founded in 1765 by Guman Singh and its capital was located in Ajaigarh, Madhya Pradesh. Sawai Maharaja Punya Pratap Singh signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1950.

Udaipur State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. The town of Dharamjaigarh was the former state's capital.

Gaurihar State was a princely state in India, ruling a territory that is now in Madhya Pradesh.

Panna State was a kingdom and later princely state of colonial India, located in modern Panna district of Madhya Pradesh.
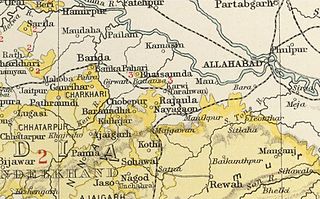
Kothi State was a princely state of the British Raj. It belonged to the Bagelkhand Agency of Central India. Its capital was at Kothi, in modern Satna district of Madhya Pradesh.

















