
Boodjamulla National Park, formerly known as Lawn Hill National Park, is a national park in the Shire of Burke, Queensland, Australia. The Riversleigh World Heritage Area is a World Heritage Site within the park.
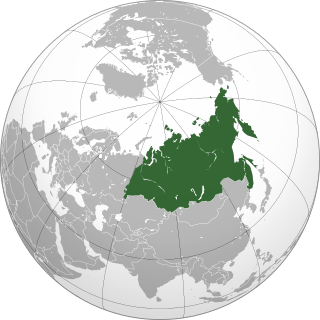
North Asia or Northern Asia, also referred to pars pro toto as Siberia, is the northern region of Asia. North Asia is administrated primarily as part of Russia, albeit Northern Kazakhstan and Mongolia may also come under the definition. Typically the region consists of the Russian regions east of the Ural Mountains: Ural, Siberia and the Russian Far East. North Asia is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to its north, by Eastern Europe to its west, by Central and East Asia to its south, and by the Pacific Ocean and North America to its east. The region covers an area of approximately 13,100,000 square kilometres (5,100,000 sq mi), or 8.8% of Earth's total land area. It is the largest subregion of Asia by area, but also the least populated with an approximate population of only 33 million people, or 0.74% of Asia's population.

The Mendip Hills is a range of limestone hills to the south of Bristol and Bath in Somerset, England. Running east to west between Weston-super-Mare and Frome, the hills overlook the Somerset Levels to the south and the Chew Valley and other tributaries of the Avon to the north. The hills give their name to the local government district of Mendip, which administers most of the area. The higher, western part of the hills, covering 198 km2 (76 sq mi) has been designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), which gives it a level of protection comparable to a national park.

The Vercors Massif is a range in France consisting of rugged plateaux and mountains straddling the départements of Isère and Drôme in the French Prealps. It lies west of the Dauphiné Alps, from which it is separated by the rivers Drac and Isère. The cliffs at the massif's eastern limit face the city of Grenoble.

The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia, South Asia, and East Asia, at the junction of the Himalayas with the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun,and Hindu Kush. They are among the world's highest mountains.

In geology and physical geography, a plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain, that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones.

The Vindhya Range is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.

The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Odisha, West Bengal and Chhattisgarh. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi River lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).

The Ken River, is one of the major rivers of the Bundelkhand region of central India, and flows through two states, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. It is a tributary of the Yamuna.

The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in central India, and thus forms part of the greater Gangetic drainage system. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan, then forming the boundary between Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh before turning southeast to join the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh state.
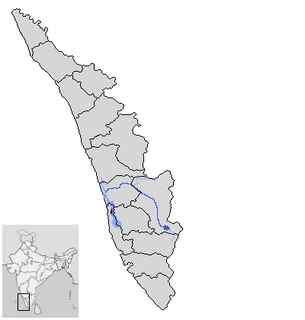
Periyar is the longest river and the river with the largest discharge potential in the Indian state of Kerala. It is one of the few perennial rivers in the region and provides drinking water for several major towns. The Periyar is of utmost significance to the economy of Kerala. It generates a significant proportion of Kerala's electrical power via the Idukki Dam and flows along a region of industrial and commercial activity. The river also provides water for irrigation and domestic use throughout its course besides supporting a rich fishery. Due to these reasons, the river has been named the "Lifeline of Kerala". Kochi city, in the vicinity of the river mouth draws its water supply from Aluva, an upstream site sufficiently free of seawater intrusion. Twenty five percent of Kerala's industries are along the banks of river Periyar. These are mostly crowded within a stretch of 5 kilometres (3 mi) in the Eloor-Edayar region (Udhyogamandal), about 10 kilometres (6 mi) north of Kochi harbor.
The Bhander Plateau is a plateau in the state of Madhya Pradesh in India. It has an area of 10,000 square kilometres (3,900 sq mi). It links the Deccan Plateau to the south with the Indo-Gangetic Plains and the Chota Nagpur Plateau to the north and east respectively. The plateau is part of the Vindhya Range in central India.
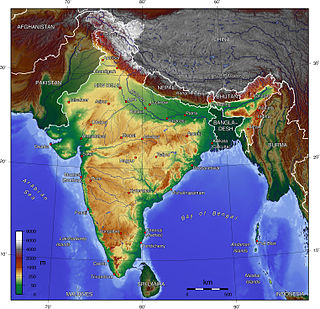
The Indian Himalayan Region'(IHR) is the section of the Himalayas within India, spanning 11 Indian states and union territories namely UTs of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, and States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam and West Bengal. The region is responsible for providing water to a large part of the Indian subcontinent and contains various flora and fauna.

Odisha is one of the 28 states in the Republic of India. Odisha is located in the eastern part of the Indian peninsula and the Bay of Bengal lies to its East while Chhattisgarh shares its border in the west and north-west. The state also shares geographic boundaries with West Bengal in the north-east, Jharkhand in the north and Andhra Pradesh in the south. The state is spread over an area of 155,707 km2 and extends for 1030 km from north to south and 500 kilometres from east to west. Its coastline is 480 km long. The state is divided into 30 districts which are further subdivided into 314 blocks.

Kaimur Range is the eastern portion of the Vindhya Range, about 483 kilometres (300 mi) long, extending from around Katangi in Jabalpur district of Madhya Pradesh to around Sasaram in Rohtas district of Bihar. It passes through the Rewa and Mirzapur divisions. The range never rises more than a few hundred metres above the surrounding plains and has a maximum width of around 80 km.

The Rewa Plateau covers a portion of Rewa district in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.

The Rohtas Plateau is a plateau that lies in the south-western part of the Indian state of Bihar.

Sigur Plateau is a plateau in the north and east of Nilgiri District in the Nilgiri Hills of Tamil Nadu, South India. It covers the 778.8 square kilometres (300.7 sq mi) portion of the Moyar River drainage basin on the northern slopes of the Nilgiri Hills, south of the Moyar River.

The Garhjat Hills is a mountain range formed by a series low lying hills, plateaux, ridges and meadows that stretch into Odisha from the Utkal Plains in the Chotanagpur region of Jharkhand and the Chhattisgarh Plains. The range, also known as the Odisha Highlands, runs in a north east to south west direction for about 382 km along the Odisha coast, covering 76,800 km2.

Bijawar State was a princely state of colonial India, located in modern Chhatarpur district of Madhya Pradesh.


















