| Jafarabad State Jafrabad State જાફરાબાદ રિયાસત | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Princely State of British India In union with Janjira (1759–1948) | |||||||
| c. 1650–1948 | |||||||
Flag | |||||||
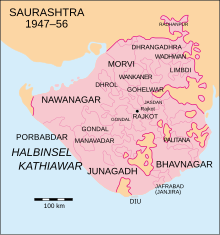 Location of Jafrabad State in Saurashtra | |||||||
| Area | |||||||
• 1901 | 68 km2 (26 sq mi) | ||||||
| Population | |||||||
• 1901 | 12,097 | ||||||
| History | |||||||
• Established | 4 March | ||||||
| 1948 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Gujarat, India | ||||||
Jafarabad, or Jafrabad State, [1] was a tributary princely state in India during the British Raj. It was located in the Kathiawar Peninsula on the Gujarat coast. The state had formerly been part of the Baroda Agency and later of the Kathiawar Agency of the Bombay Presidency.
Contents
Jafrabad State was a dependency of the Nawab of Janjira State, [2] located 320 km to the south-southeast on the Konkan coast.
Jafrabad town, the capital and only municipality, is located 275 km south of Ahmedabad and 240 southwest of Baroda. The state was formed by the city and 11 villages and initially consisted of two districts located on both sides of the estuary of the Ranai river. Jafrabad state had an area of 68 km2 and a population in 1881 of 4,746 and in 1901 of 6,038 inhabitants. The majority of the population were Muslims (80%) and the rest Hindus. The state and the town took their name from Sultan Muzaffar Jafar from Gujarat who built fortifications.[ citation needed ]
