
The United States courts of appeals or circuit courts are the intermediate appellate courts of the United States federal court system. The courts are divided into 13 circuits, and each hears appeals from the district courts within its borders, or in some instances from other designated federal courts and administrative agencies. Appeals from the courts of appeals are taken to the U.S. Supreme Court.

The United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit is a court of appeal that has appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts:

The United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit is a United States federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the following United States district courts:

The United States Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts for the following districts:

The United States Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following federal judicial districts:

The United States Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the courts in the following districts:

In the United States, the title of federal judge means a judge nominated by the president of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate pursuant to the Appointments Clause in Article II of the United States Constitution.

Judiciary of Malaysia is largely centralised despite Malaysia's federal constitution, heavily influenced by the English common law, as well as Islamic jurisprudence.
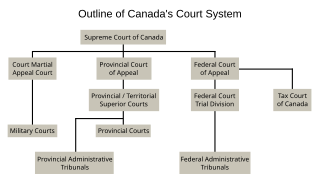
The court system of Canada forms the judicial branch of government, formally known as "The Queen on the Bench", which interprets the law and is made up of many courts differing in levels of legal superiority and separated by jurisdiction. Some of the courts are federal in nature, while others are provincial or territorial.

The United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit is a United States court of appeals headquartered in Washington, D.C. The court was created by Congress with passage of the Federal Courts Improvement Act of 1982, which merged the United States Court of Customs and Patent Appeals and the appellate division of the United States Court of Claims, making the judges of the former courts into circuit judges. The Federal Circuit is particularly known for its decisions on patent law, as it is the only appellate-level court with the jurisdiction to hear patent case appeals.
The Federal Court of Appeal is a Canadian appellate court that hears cases concerning federal matters.

The federal judiciary of the United States is one of the three branches of the federal government of the United States organized under the United States Constitution and laws of the federal government. Article III of the Constitution requires the establishment of a Supreme Court and permits the Congress to create other federal courts, and place limitations on their jurisdiction. Article III federal judges are appointed by the president with the consent of the Senate to serve until they resign, are impeached and convicted, retire, or die.

The judiciary of Australia comprises judges who sit in federal courts and courts of the States and Territories of Australia. The High Court of Australia sits at the apex of the Australian court hierarchy as the ultimate court of appeal on matters of both federal and State law.

The Judiciary of Brazil is the judiciary branch of the Brazilian government. The structure and the division of jurisdiction between the divisions of the Brazilian judiciary is defined in the Brazilian Constitution.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











