Related Research Articles

Atonality in its broadest sense is music that lacks a tonal center, or key. Atonality, in this sense, usually describes compositions written from about the early 20th-century to the present day, where a hierarchy of harmonies focusing on a single, central triad is not used, and the notes of the chromatic scale function independently of one another. More narrowly, the term atonality describes music that does not conform to the system of tonal hierarchies that characterized European classical music between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries. "The repertory of atonal music is characterized by the occurrence of pitches in novel combinations, as well as by the occurrence of familiar pitch combinations in unfamiliar environments".

Milton Byron Babbitt was an American composer, music theorist, mathematician, and teacher. He was a Pulitzer Prize and MacArthur Fellowship recipient, recognized for his serial and electronic music.

Musical analysis is the study of musical structure in either compositions or performances. According to music theorist Ian Bent, music analysis "is the means of answering directly the question 'How does it work?'". The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Bent, "its emergence as an approach and method can be traced back to the 1750s. However it existed as a scholarly tool, albeit an auxiliary one, from the Middle Ages onwards."

Musical set theory provides concepts for categorizing musical objects and describing their relationships. Howard Hanson first elaborated many of the concepts for analyzing tonal music. Other theorists, such as Allen Forte, further developed the theory for analyzing atonal music, drawing on the twelve-tone theory of Milton Babbitt. The concepts of musical set theory are very general and can be applied to tonal and atonal styles in any equal temperament tuning system, and to some extent more generally than that.

In musical set theory, an interval class, also known as unordered pitch-class interval, interval distance, undirected interval, or "(even completely incorrectly) as 'interval mod 6'", is the shortest distance in pitch class space between two unordered pitch classes. For example, the interval class between pitch classes 4 and 9 is 5 because 9 − 4 = 5 is less than 4 − 9 = −5 ≡ 7 (mod 12). See modular arithmetic for more on modulo 12. The largest interval class is 6 since any greater interval n may be reduced to 12 − n.
In music theory, a trichord is a group of three different pitch classes found within a larger group. A trichord is a contiguous three-note set from a musical scale or a twelve-tone row.
In music, a hexachord is a six-note series, as exhibited in a scale or tone row. The term was adopted in this sense during the Middle Ages and adapted in the 20th century in Milton Babbitt's serial theory. The word is taken from the Greek: ἑξάχορδος, compounded from ἕξ and χορδή, and was also the term used in music theory up to the 18th century for the interval of a sixth.

Benjamin Aaron Boretz is an American composer and music theorist.

In music, a permutation (order) of a set is any ordering of the elements of that set. A specific arrangement of a set of discrete entities, or parameters, such as pitch, dynamics, or timbre. Different permutations may be related by transformation, through the application of zero or more operations, such as transposition, inversion, retrogradation, circular permutation, or multiplicative operations. These may produce reorderings of the members of the set, or may simply map the set onto itself.
In music, transposition refers to the process or operation of moving a collection of notes up or down in pitch by a constant interval.
The shifting of a melody, a harmonic progression or an entire musical piece to another key, while maintaining the same tone structure, i.e. the same succession of whole tones and semitones and remaining melodic intervals.
Perspectives of New Music (PNM) is a peer-reviewed academic journal specializing in music theory and analysis. It was established in 1962 by Arthur Berger and Benjamin Boretz.
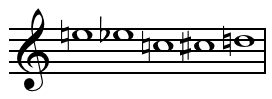
A set in music theory, as in mathematics and general parlance, is a collection of objects. In musical contexts the term is traditionally applied most often to collections of pitches or pitch-classes, but theorists have extended its use to other types of musical entities, so that one may speak of sets of durations or timbres, for example.

In musical set theory, an interval vector is an array of natural numbers which summarize the intervals present in a set of pitch classes. Other names include: ic vector, PIC vector and APIC vector

Drei Klavierstücke, Op. 11, is a set of pieces for solo piano written by the Austrian composer Arnold Schoenberg in 1909. They represent an early example of atonality in the composer's work.
Anton Webern's Concerto for Nine Instruments, Op. 24, written in 1934, is a twelve-tone concerto for nine instruments: flute, oboe, clarinet, horn, trumpet, trombone, violin, viola, and piano. It consists of three movements:

In musical set theory, a Forte number is the pair of numbers Allen Forte assigned to the prime form of each pitch class set of three or more members in The Structure of Atonal Music. The first number indicates the number of pitch classes in the pitch class set and the second number indicates the set's sequence in Forte's ordering of all pitch class sets containing that number of pitches.
In music, the "Ode-to-Napoleon" hexachord is the hexachord named after its use in the twelve-tone piece Ode to Napoleon Buonaparte Op. 41 (1942) by Arnold Schoenberg. Containing the pitch-classes 014589 it is given Forte number 6–20 in Allen Forte's taxonomic system. The primary form of the tone row used in the Ode allows the triads of G minor, E♭ minor, and B minor to easily appear.

In music theory, the chromatic hexachord is the hexachord consisting of a consecutive six-note segment of the chromatic scale. It is the first hexachord as ordered by Forte number, and its complement is the chromatic hexachord at the tritone. For example, zero through five and six through eleven. On C:
References
- ↑ Forte 1973, p. 3.
- ↑ Straus 1990, p. 28.
- ↑ Nelson, Paul (2004). "Two Algorithms for Computing the Prime Form", ComposerTools.com.
- ↑ Tsao, Ming (2007). Abstract Musical Intervals: Group Theory for Composition and Analysis, p.99, n.32. ISBN 9781430308355. Algorithms given in Morris, Robert (1991). Class Notes for Atonal Music Theory, p.103. Frog Peak Music.