
The Continental Divide of the Americas is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and Arctic Ocean, including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and Hudson Bay.

A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.
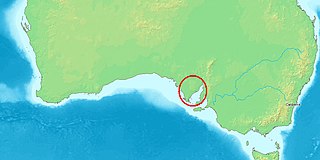
The Spencer Gulf is the westernmost and larger of two large inlets on the southern coast of Australia, in the state of South Australia, facing the Great Australian Bight. It spans from the Cape Catastrophe and Eyre Peninsula in the west to Cape Spencer and Yorke Peninsula in the east.

The Lake Eyre basin is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia. It is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi), including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales. The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with a high degree of variability anywhere. It supports only about 60,000 people and has no major irrigation, diversions or flood-plain developments. Low density grazing that sustains a large amount of wildlife is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin. The Lake Eyre basin of precipitation to a great extent geographically overlaps the Great Artesian Basin underneath.

The Gulf of Carpentaria is a sea off the northern coast of Australia. It is enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea, which separates Australia and New Guinea. The northern boundary is generally defined as a line from Slade Point, Queensland in the northeast, to Cape Arnhem on the Gove Peninsula, Northern Territory in the west.

The Timor Sea is a relatively shallow sea in the Indian Ocean bounded to the north by the island of Timor with Timor-Leste to the north, Indonesia to the northwest, Arafura Sea to the east, and to the south by Australia. The Sunda Trench marks the deepest point of the Timor Sea with a depth of more than 3300 metres, separating the continents of Oceania in the southeast and Asia to the northwest and north. The Timor sea is prone to earthquakes and tsunamis north of the Sunda Trench, due to its location on the Ring of Fire as well as volcanic activity and can experience major cyclones, due to the proximity from the Equator.

The Ord River is a 651-kilometre long (405 mi) river in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. The river's catchment covers 55,100 square kilometres (21,274 sq mi).

The Victoria River is a river in the bioregion of Victoria Bonaparte in the Northern Territory of Australia. It flows for 560 kilometres (350 mi) from its source south of the Judbarra / Gregory National Park to the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf in the Timor Sea.

The Northern Territory (NT) occupies the north central part of the continent of Australia. The Northern Territory borders are to the west with Western Australia, the Western Australia border being near the 129° east longitude. The NT to the south with the South Australian border being the 26th parallel south latitude. To the east the NT with the Queensland border along the 138° east longitude.

The Northwest Shelf Transition, also known as Bonaparte Coast, is a biogeographic region of Australia's continental shelf. It adjoins the Kimberley region of Western Australia and the adjacent coast of the Northern Territory.

A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not connected to the open sea. Every continent on earth except Antarctica has at least one continental drainage divide; islands, even small ones like Killiniq Island on the Labrador Sea in Canada, may also host part of a continental divide or have their own island-spanning divide. The endpoints of a continental divide may be coastlines of gulfs, seas or oceans, the boundary of an endorheic basin, or another continental divide. One case, the Great Basin Divide, is a closed loop around an endorheic basin. The endpoints where a continental divide meets the coast are not always definite since the exact border between adjacent bodies of water is usually not clearly defined. The International Hydrographic Organization's publication Limits of Oceans and Seas defines exact boundaries of oceans, but it is not universally recognized. Where a continental divide meets an endorheic basin, such as the Great Divide Basin of Wyoming, the continental divide splits and encircles the basin. Where two divides intersect, they form a triple divide, or a tripoint, a junction where three watersheds meet.
Western Australia has the longest coastline of any state or territory in Australia, at 10,194 km or 12,889 km. It is a significant portion of the coastline of Australia, which is 35,877 km.

Cambridge Gulf is a gulf on the north coast of the Kimberley region of Western Australia. Many rivers flow into the gulf, including the Ord River, Pentecost River, Durack River, King River and the Forrest River, making the environment an estuarine one.
Bonaparte is a French and Italian surname. It derives from Italian bona (buona) 'good' and parte 'solution' or 'match'.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.
The Fitzmaurice River is a river in the Northern Territory of Australia.

The Legune Important Bird Area comprises a low-lying, swampy, floodplain peninsula at the south-eastern end of the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf in the Top End of the Northern Territory of Australia. The land is part of the Legune Station, a cattle station and pastoral lease.

The Anson Bay, Daly and Reynolds River Floodplains comprise some 2,656 square kilometres (1,025 sq mi) of seasonally inundated floodplains around Anson Bay, and the lower reaches of the Daly, Reynolds and Docherty Rivers entering the bay, on the west coast of the Top End of the Northern Territory of Australia. Anson's Bay lies about 120 kilometres (75 mi) south-west of Darwin, on the eastern side of the Joseph Bonaparte Gulf, opening on to the Timor Sea. The site is important for large numbers, and a wide variety, of waterbirds.

The Bonaparte Basin is a sedimentary basin in Western Australia and the Northern Territory of Australia. Its total area is approximately 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi), most of which is offshore.
















