
Clozapine is a psychiatric medication and is the first atypical antipsychotic to be discovered. It is primarily used to treat people with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder who have had an inadequate response to two other antipsychotics or who have been unable to tolerate other drugs due to extrapyramidal side effects. It is also used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease.
A psychiatric or psychotropic medication is a psychoactive drug taken to exert an effect on the chemical makeup of the brain and nervous system. Thus, these medications are used to treat mental illnesses. These medications are typically made of synthetic chemical compounds and are usually prescribed in psychiatric settings, potentially involuntarily during commitment. Since the mid-20th century, such medications have been leading treatments for a broad range of mental disorders and have decreased the need for long-term hospitalization, thereby lowering the cost of mental health care. The recidivism or rehospitalization of the mentally ill is at a high rate in many countries, and the reasons for the relapses are under research.
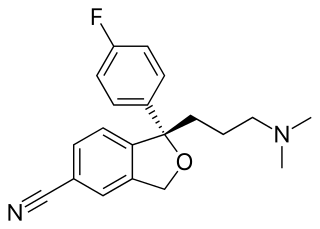
Escitalopram, sold under the brand names Lexapro and Cipralex, among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. Escitalopram is mainly used to treat major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. It is taken by mouth, available commercially as an oxalate salt exclusively.

Citalopram, sold under the brand name Celexa among others, is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, obsessive compulsive disorder, panic disorder, and social phobia. The antidepressant effects may take one to four weeks to occur. It is typically taken orally. In some European countries, it is sometimes given intravenously to initiate treatment, before switching to the oral route of administration for continuation of treatment. It has also been used intravenously in other parts of the world in some other circumstances.

Clonazepam, sold under the brand names Klonopin and Rivotril, is a medication used to prevent and treat anxiety disorders, seizures, bipolar mania, agitation associated with psychosis, OCD and akathisia. It is a long-acting tranquilizer of the benzodiazepine class. It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is typically taken by mouth but is also used intravenously. Effects begin within one hour and last between eight and twelve hours in adults.

Desipramine, sold under the brand name Norpramin among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) used in the treatment of depression. It acts as a relatively selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, though it does also have other activities such as weak serotonin reuptake inhibitory, α1-blocking, antihistamine, and anticholinergic effects. The drug is not considered a first-line treatment for depression since the introduction of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants, which have fewer side effects and are safer in overdose.

Clomipramine, sold under the brand name Anafranil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). It is used in the treatment of various conditions, most-notably obsessive–compulsive disorder but also many other disorders, including panic disorder, major depressive disorder, trichotilomania, body dysmorphic disorder and chronic pain. It has also been notably used to treat premature ejaculation and the cataplexy associated with narcolepsy.

Tiagabine is an anticonvulsant medication produced by Cephalon that is used in the treatment of epilepsy. The drug is also used off-label in the treatment of anxiety disorders and panic disorder.

Psychotic depression, also known as depressive psychosis, is a major depressive episode that is accompanied by psychotic symptoms. It can occur in the context of bipolar disorder or major depressive disorder. It can be difficult to distinguish from schizoaffective disorder, a diagnosis that requires the presence of psychotic symptoms for at least two weeks without any mood symptoms present. Unipolar psychotic depression requires that psychotic symptoms occur during severe depressive episodes, although residual psychotic symptoms may also be present in between episodes. Diagnosis using the DSM-5 involves meeting the criteria for a major depressive episode, along with the criteria for "mood-congruent or mood-incongruent psychotic features" specifier.
The clinical global impression (CGI) rating scales are measures of symptom severity, treatment response and the efficacy of treatments in treatment studies of patients with mental disorders. It is a brief 3-item observer-rated scale that can be used in clinical practice as well as in researches to track symptom changes. It was developed by Early Clinical Drug Evaluation Program (ECDEU) team of researchers for use in NIMH-led clinical trials that could provide clinical judgment based assessment for determining the severity of symptoms and the treatment progress. This was meant to assess the patient's functioning prior to and after initiating medication in trials which is an important part of study process. Its 3 items assess, 1) Severity of Illness (CGI-S), 2) Global Improvement (CGI-I), and 3) Efficacy Index. Many researchers, while recognizing the validity of the scale, consider it to be subjective as it requires the user of the scale to compare the subjects to typical patients in the clinician experience.
The emphasis of the treatment of bipolar disorder is on effective management of the long-term course of the illness, which can involve treatment of emergent symptoms. Treatment methods include pharmacological and psychological techniques.
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) is an American imprint of the American Dutch publishing conglomerate Wolters Kluwer. It was established by the acquisition of Williams & Wilkins and its merger with J.B. Lippincott Company in 1998. Under the LWW brand, Wolters Kluwer, through its Health Division, publishes scientific, technical, and medical content such as textbooks, reference works, and over 275 scientific journals. Publications are aimed at physicians, nurses, clinicians, and students.
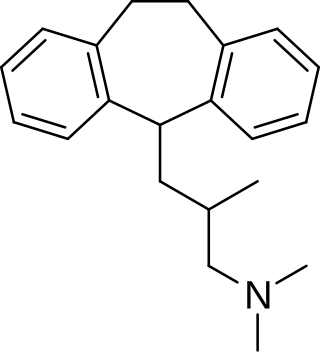
Butriptyline, sold under the brand name Evadyne among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and several other European countries for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. Along with trimipramine, iprindole, and amoxapine, it has been described as an "atypical" or "second-generation" TCA due to its relatively late introduction and atypical pharmacology. It was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Neurosurgery is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal of neurosurgery and the official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. It is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. The journal publishes original research, reviews, and editorials.

Certain lithium compounds, also known as lithium salts, are used as psychiatric medication, primarily for bipolar disorder and for major depressive disorder. In lower doses, other salts such as lithium citrate are known as nutritional lithium and have occasionally been used to treat ADHD. Lithium is taken orally.
Joanna Moncrieff is a British psychiatrist and academic. She is Professor of Critical and Social Psychiatry at University College London and a leading figure in the Critical Psychiatry Network. She is a prominent critic of the modern 'psychopharmacological' model of mental disorder and drug treatment, and the role of the pharmaceutical industry. She has written papers, books and blogs on the use and over-use of drug treatment for mental health problems, the mechanism of action of psychiatric drugs, their subjective and psychoactive effects, the history of drug treatment, and the evidence for its benefits and harms. She also writes on the history and politics of psychiatry more generally. Her best known books are The Myth of the Chemical Cure and The Bitterest Pills.

Prof. Robert Haim Belmaker, is an Israeli psychiatrist who has had major academic positions in Israeli psychiatry since 1974. He had a formative influence on biological directions in Israeli psychiatry. He was Hoffer-Vickar Professor of Psychiatry at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheva Israel until his retirement and is now Emeritus.
Irvin M. Cohen, M.D. (1922–2019) was a psychiatrist specializing in psychopharmacology, recognized for his role in the early use of chlorpromazine in the treatment of schizophrenia, the development of the first benzodiazepine (Librium) treatments in depressive patients, and in the adoption of lithium to treat bipolar disorder.

Thomas A. Ban was a Hungarian-born Canadian psychiatrist, psychopharmacologist, academic, researcher and theorist.













