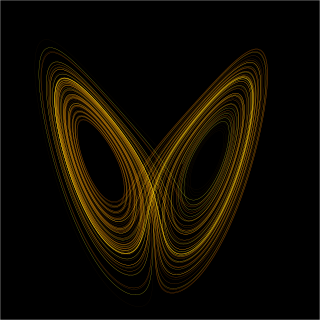
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics focused on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, and were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals, and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state. A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Texas can cause a tornado in Brazil.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. This includes

Eduardo Daniel Sontag is an American mathematician, and distinguished university professor at Northeastern University, who works in the fields control theory, dynamical systems, systems molecular biology, cancer and immunology, theoretical computer science, neural networks, and computational biology.

Dorodnitsyn Computing Centre, known as the Computing Centre of the Academy of Sciences until 2015, is a research institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. It was established in 1955.
Reservoir computing is a framework for computation derived from recurrent neural network theory that maps input signals into higher dimensional computational spaces through the dynamics of a fixed, non-linear system called a reservoir. After the input signal is fed into the reservoir, which is treated as a "black box," a simple readout mechanism is trained to read the state of the reservoir and map it to the desired output. The first key benefit of this framework is that training is performed only at the readout stage, as the reservoir dynamics are fixed. The second is that the computational power of naturally available systems, both classical and quantum mechanical, can be used to reduce the effective computational cost.
Joshua Morris Epstein is Professor of Epidemiology at the New York University College of Global Public Health. Formerly Professor of Emergency Medicine at Johns Hopkins University, with joint appointments in the departments of Applied Mathematics, Economics, Biostatistics, International Health, and Environmental Health Sciences and the Director of the JHU Center for Advanced Modeling in the Social, Behavioral, and Health Sciences. He is an External Professor at the Santa Fe Institute, a member of the New York Academy of Sciences, and a member of the Institute of Medicine's Committee on Identifying and Prioritizing New Preventive Vaccines.
Ali Hasan Nayfeh was a Palestinian-Jordanian mathematician, mechanical engineer and physicist. He is regarded as the most influential scholar and scientist in the area of applied nonlinear dynamics in mechanics and engineering. He was the inaugural winner of the Thomas K. Caughey Dynamics Award, and was awarded the Benjamin Franklin Medal in mechanical engineering. His pioneering work in nonlinear dynamics has been influential in the construction and maintenance of machines and structures that are common in daily life, such as ships, cranes, bridges, buildings, skyscrapers, jet engines, rocket engines, aircraft and spacecraft.
Stephen Ray Wiggins is a Cherokee-American applied mathematician also of British heritage best known for his contributions in nonlinear dynamics, chaos theory and nonlinear phenomena, with applications to Lagrangian aspects of fluid transport and mixing and phase space aspects of theoretical chemistry.
Satya Atluri is an American engineer, educator, researcher and scientist in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering and computational sciences, who is currently a Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Aerospace Engineering at the University of California, Irvine. Since 1966, he made fundamental contributions to the development of finite element methods, boundary element methods, Meshless Local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) methods, Fragile Points Methods (FPM), Local Variational Iteration Methods, for general problems of engineering, solid mechanics, fluid dynamics, heat transfer, flexoelectricity, ferromagnetics, gradient and nonlocal theories, nonlinear dynamics, shell theories, micromechanics of materials, structural integrity and damage tolerance, Orbital mechanics, Astrodynamics, digital Twins of Aerospace Systems, etc.
Charbel Farhat is the Vivian Church Hoff Professor of Aircraft Structures in the School of Engineering and the inaugural James and Anna Marie Spilker Chair of the Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, at Stanford University. He is also Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Professor in the Institute for Computational and Mathematical Engineering, and Director of the Stanford-King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology Center of Excellence for Aeronautics and Astronautics. He currently serves on the Space Technology Industry-Government-University Roundtable.

Nonlinear Dynamics, An International Journal of Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Engineering Systems is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all nonlinear dynamic phenomena associated with mechanical, structural, civil, aeronautical, ocean, electrical, and control systems. It is published by Springer Nature and the editor-in-chief of the journal is Walter Lacarbonara.
The Journal of Hyperbolic Differential Equations was founded in 2004 and carries papers pertaining to nonlinear hyperbolic problems and related mathematical topics, specifically on the theory and numerical analysis of hyperbolic conservation laws and of hyperbolic partial differential equations arising in mathematical physics. This includes topics such as nonlinear hyperbolic systems in continuum physics. The journal is published by World Scientific.

Mikhail Izrailevich Rabinovich (MIR) is a Russian influential physicist and neuroscientist working in the field of nonlinear dynamics and its applications. His work helped shape the understanding of dynamical systems.
In the bifurcation theory, a bounded oscillation that is born without loss of stability of stationary set is called a hidden oscillation. In nonlinear control theory, the birth of a hidden oscillation in a time-invariant control system with bounded states means crossing a boundary, in the domain of the parameters, where local stability of the stationary states implies global stability. If a hidden oscillation attracts all nearby oscillations, then it is called a hidden attractor. For a dynamical system with a unique equilibrium point that is globally attractive, the birth of a hidden attractor corresponds to a qualitative change in behaviour from monostability to bi-stability. In the general case, a dynamical system may turn out to be multistable and have coexisting local attractors in the phase space. While trivial attractors, i.e. stable equilibrium points, can be easily found analytically or numerically, the search of periodic and chaotic attractors can turn out to be a challenging problem.
Gábor Stépán, Hungarian professor of applied mechanics, member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, fellow of the International Academy for Production Engineering (CIRP), fellow of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), former dean of the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering in the Budapest University of Technology and Economics. Won the Széchenyi Prize in 2011, the Thomas K. Caughey Dynamics Award in 2015, and the Delay Systems Lifetime Achievements Award in 2021. His research fields include nonlinear vibrations, delay-differential equations, and stability theory. He was elected as a fellow of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics in 2017, "for contributions to the theory and analysis of delayed dynamical systems and their applications".
Ioannis George (Yannís) Kevrekidis is currently the Bloomberg Distinguished Professor in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering within the Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University. He holds secondary appointments in the Whiting School's Department of Applied Mathematics & Statistics and the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine's Department of Urology.
Panayotis G. Kevrekidis is a professor in the Department of Mathematics and Statistics at the University of Massachusetts Amherst. Kevrekidis earned his B.Sc. in physics in 1996 from the University of Athens. He obtained his M.S. in 1998 and Ph.D. in 2000 from Rutgers University, the latter under the joint supervision of Joel Lebowitz and Panos G. Georgopoulos. His thesis was entitled “Lattice Dynamics of Solitary Wave Excitations”. He then assumed a post-doctoral position split between the Program in Applied and Computational Mathematics of Princeton University (10/2000–02/2001) and the Theoretical Division and the Center for Nonlinear Studies of Los Alamos National Laboratory (03/2001–08/2001). From 09/2001, he joined the Department of Mathematics and Statistics of the University of Massachusetts Amherst as an assistant professor. He was awarded tenure and promotion to associate professor in 06/2005. As of 09/2010, he is a full professor at the same institution. He is presently the Stanislaw M. Ulam Scholar at the Center for Nonlinear Studies at Los Alamos National Laboratory.

Soumitro Banerjee is an Indian electrical engineer and a professor at the Department of Physical Sciences of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata. He is known for his studies on bifurcation phenomena in power electronic circuits and is an elected fellow of all three major Indian science academies: the National Academy of Sciences, India, Indian Academy of Sciences, and Indian National Science Academy. He is also a fellow of The World Academy of Sciences, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, West Bengal Academy of Sciences and the Indian National Academy of Engineering. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 2003.
Muthusamy Lakshmanan is an Indian theoretical physicist currently working as Professor of Eminence at the Department of Nonlinear Dynamics of Bharathidasan University. Presently he is the DST-SERB National Science Chair awarded by Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology. He has held several research fellowships which included Raja Rammanna fellowship of Department of Atomic Energy, Alexander von Humboldt fellowship, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science fellowship, Royal Society Nuffield Foundation fellowship, and NASI-Senior Scientist Platinum Jubilee Fellowship. In the year 2021, on August 15, he was conferred with Dr. A. P. J Abdul Kalam Award by the Government of Tamil Nadu.





