
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.

An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit. Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery.

An electrochemical cell is a device that generates electrical energy from chemical reactions. Electrical energy can also be applied to these cells to cause chemical reactions to occur.

A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. The anode of a conventional lithium-ion cell is typically graphite made from carbon. The cathode is typically a metal oxide. The electrolyte is typically a lithium salt in an organic solvent.

An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that utilizes an external source of electrical energy to force a chemical reaction that would otherwise not occur. The external energy source is a voltage applied between the cell′s two electrodes; an anode and a cathode, which are immersed in an electrolyte solution. This is in contrast to a galvanic cell, which itself is a source of electrical energy and the foundation of a battery. The net reaction taking place in a galvanic cell is a spontaneous reaction, i.e, the Gibbs free energy remains -ve, while the net reaction taking place in an electrolytic cell is the reverse of this spontaneous reaction, i.e, the Gibbs free energy is +ve.
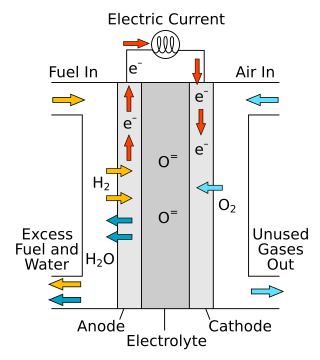
A solid oxide fuel cell is an electrochemical conversion device that produces electricity directly from oxidizing a fuel. Fuel cells are characterized by their electrolyte material; the SOFC has a solid oxide or ceramic electrolyte.
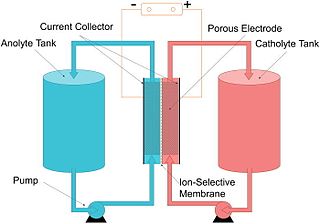
A flow battery, or redox flow battery, is a type of electrochemical cell where chemical energy is provided by two chemical components dissolved in liquids that are pumped through the system on separate sides of a membrane. Ion transfer inside the cell occurs through the membrane while both liquids circulate in their own respective space. Cell voltage is chemically determined by the Nernst equation and ranges, in practical applications, from 1.0 to 2.43 volts. The energy capacity is a function of the electrolyte volume and the power is a function of the surface area of the electrodes.

Aluminium hydride (also known as alane and alumane) is an inorganic compound with the formula AlH3. Alane and its derivatives are common reducing (hydride addition) reagents in organic synthesis that are used in solution at both laboratory and industrial scales. In solution—typically in etherial solvents such tetrahydrofuran or diethyl ether—aluminium hydride forms complexes with Lewis bases, and reacts selectively with particular organic functional groups (e.g., with carboxylic acids and esters over organic halides and nitro groups), and although it is not a reagent of choice, it can react with carbon-carbon multiple bonds (i.e., through hydroalumination). Given its density, and with hydrogen content on the order of 10% by weight, some forms of alane are, as of 2016, active candidates for storing hydrogen and so for power generation in fuel cell applications, including electric vehicles. As of 2006 it was noted that further research was required to identify an efficient, economical way to reverse the process, regenerating alane from spent aluminium product.

Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula LiFePO
4. It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosphate batteries, a type of Li-ion battery. This battery chemistry is targeted for use in power tools, electric vehicles, solar energy installations and more recently large grid-scale energy storage.
Renal reabsorption of sodium (Na+) is a part of renal physiology. It uses Na-H antiport, Na-glucose symport, sodium ion channels (minor). It is stimulated by angiotensin II and aldosterone, and inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide.
A Direct Carbon Fuel Cell (DCFC) is a fuel cell that uses a carbon rich material as a fuel such as bio-mass or coal. The cell produces energy by combining carbon and oxygen, which releases carbon dioxide as a by-product. It is also called coal fuel cells (CFCs), carbon-air fuel cells (CAFCs), direct carbon/coal fuel cells (DCFCs), and DC-SOFC.

A membrane electrode assembly (MEA) is an assembled stack of proton-exchange membranes (PEM) or alkali anion exchange membrane (AAEM), catalyst and flat plate electrode used in fuel cells and electrolyzers.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal in the field of biochemistry and biophysics that was established in 1947. The journal is published by Elsevier with a total of 100 annual issues in ten specialised sections.

A microbial electrolysis cell (MEC) is a technology related to Microbial fuel cells (MFC). Whilst MFCs produce an electric current from the microbial decomposition of organic compounds, MECs partially reverse the process to generate hydrogen or methane from organic material by applying an electric current. The electric current would ideally be produced by a renewable source of power. The hydrogen or methane produced can be used to produce electricity by means of an additional PEM fuel cell or internal combustion engine.
The lithium–air battery (Li–air) is a metal–air electrochemical cell or battery chemistry that uses oxidation of lithium at the anode and reduction of oxygen at the cathode to induce a current flow.
A metal–air electrochemical cell is an electrochemical cell that uses an anode made from pure metal and an external cathode of ambient air, typically with an aqueous or aprotic electrolyte.
Electrochemical engineering is the branch of chemical engineering dealing with the technological applications of electrochemical phenomena, such as electrosynthesis of chemicals, electrowinning and refining of metals, flow batteries and fuel cells, surface modification by electrodeposition, electrochemical separations and corrosion.

Andrzej Wieckowski was an Emeritus Professor of Chemistry at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign and the North American Editor of Electrochimica Acta. He is known for his spectroscopic investigations of electrocatalysis in fuel cells and co-inventing of the direct formic acid fuel cell (DFAFC). He authored more than 300 publications, has been cited over 13,000 times and has an h-index 60. He was appointed fellow of the Electrochemical Society in 2007 and fellow of the International Society of Electrochemistry in 2009. He was awarded the US Department of Energy Prize for outstanding Scientific Accomplishment in Materials Chemistry in 1992, the ISE Jacques Tacussel Prize in 1998, the ECS David. C. Graham Award in 2003, and the ISE Gold Medal in 2007.

In electrochemistry, a thermogalvanic cell is a kind of galvanic cell in which heat is employed to provide electrical power directly. These cells are electrochemical cells in which the two electrodes are deliberately maintained at different temperatures. This temperature difference generates a potential difference between the electrodes. The electrodes can be of identical composition and the electrolyte solution homogeneous. This is usually the case in these cells. This is in contrast to galvanic cells in which electrodes and/or solutions of different composition provide the electromotive potential. As long as there is a difference in temperature between the electrodes a current will flow through the circuit. A thermogalvanic cell can be seen as analogous to a concentration cell but instead of running on differences in the concentration/pressure of the reactants they make use of differences in the "concentrations" of thermal energy. The principal application of thermogalvanic cells is the production of electricity from low-temperature heat sources. Their energetic efficiency is low, in the range of 0.1% to 1% for conversion of heat into electricity.
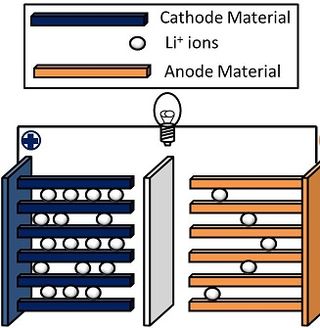
Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (abbreviated NMC, Li-NMC, LNMC, or NCM) are mixed metal oxides of lithium, nickel, manganese and cobalt with the general formula LiNixMnyCo1-x-yO2. These materials are commonly used in lithium-ion batteries for mobile devices and electric vehicles, acting as the positively charged cathode.












