
The Jumo 210 was Junkers Motoren's first production inverted V12 gasoline aircraft engine, first produced in the early 1930s. Depending on the version it produced between 610 and 730 PS and can be considered a counterpart of the Rolls-Royce Kestrel in many ways. Although originally intended to be used in almost all pre-war designs, rapid progress in aircraft design quickly relegated it to the small end of the power scale by the late 1930s. Almost all aircraft designs switched to the much larger Daimler-Benz DB 600, so the 210 was produced only for a short time before Junkers responded with a larger engine of their own, the Junkers Jumo 211.

The Delta was a 12-cylinder inverted-V aircraft engine built by Isotta Fraschini prior to and during World War II.
The Benz Bz.III was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, inline engine developed in Germany for use in aircraft in 1914. Developing 112 kW (150 hp) at 1,400 rpm from 14.3 L, it powered many German military aircraft during World War I. It was replaced in production by the unrelated Benz Bz.IIIa. and eventually the V-8 Benz Bz.IIIb. The Benz Bz.III was built under licence in Sweden by AB Thulinverken, known as the Thulin E.

The Junkers L 5 was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, inline engine for aircraft built in Germany during the 1920s. First run in 1925, it was a much enlarged development of the Junkers L2.
The Benz Bz.II was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, inline engine developed in Germany for use in aircraft in 1913. With a displacement of 10.15 L (619.4 cu in) it developed about 75–82 kW (100–110 hp). It had cast-iron cylinders with sheet metal cooling jackets welded to them. The two overhead valves per cylinder were operated via pushrods and rocker arms by a single camshaft embedded in the engine block on the right-hand side.

The Wright R-2160 Tornado was an experimental 42-cylinder, 7-cylinder per row, 6-row liquid-cooled inline radial aircraft engine. It was proposed in 1940 with 2,350 hp (1,752 kW) for experimental aircraft such as the Lockheed XP-58 Chain Lightning, Vultee XP-68 Tornado, and the Republic XP-69.

The Armstrong Siddeley Deerhound was a large aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley between 1935 and 1941. An increased capacity variant known as the Boarhound was never flown, and a related, much larger, design known as the Wolfhound existed on paper only. Development of these engines was interrupted in April 1941, when the company's factory was bombed, and on 3 October 1941 the project was cancelled by the Air Ministry.

The Beardmore Tornado is an eight-cylinder inline diesel aircraft engine built in 1927 by William Beardmore and Company of Glasgow, Scotland, and used in the British R101 airship when petrol engines were thought unsafe in the tropics. The model is given as Tornado IIIA or Tornado III C.I. The fuel is described as Diesel heavy-oil.

The Beardmore 120 hp was a British six-cylinder, water-cooled aero engine that first ran in 1914, it was built by William Beardmore and Company as a licensed-built version of the Austro-Daimler 6. The engine featured cast iron cylinders and mild steel concave pistons. Produced between August 1914 and December 1918, the design powered many World War I aircraft types.
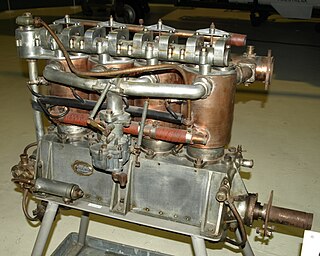
The Green C.4 was a British four-cylinder, water-cooled aero engine that first ran in 1908, it was designed by Gustavus Green and built by the Green Engine Co and Aster Engineering. The engine was one of two Green designs to win a government prize.

The Beardmore 160 hp is a British six-cylinder, water-cooled aero engine that first ran in 1916. It was built by Arrol-Johnston and Crossley Motors for William Beardmore and Company as a development of the Beardmore 120 hp, itself a licensed-built version of the Austro-Daimler 6.

The Green E.6 was a British six-cylinder, water-cooled aero engine that first ran in 1911, it was designed by Gustavus Green and built by the Green Engine Co and Mirlees, Bickerton & Day of Stockport between August 1914 and December 1918.

The Green D.4 was a four-cylinder watercooled inline piston engine produced by the Green Engine Co in the UK in 1909. It produced about 60 hp (45 kW) and played an important role in the development of British aviation before World War I.
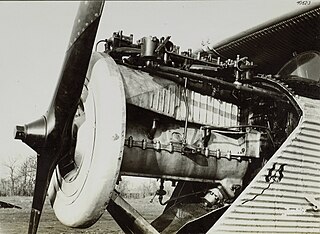
The Junkers L1 was the first engine manufactured by Junkers to fly. It was an air-cooled, upright six-cylinder inline four-stroke petrol engine only produced in small numbers and largely used for research, but led to the successful L5 and its V-12 development, the L55.
The Junkers L55 was Junkers' first V-12 engine, appearing in 1927 and based on a pair of six-cylinder L5s. In 1928 a supercharger was added. It was used in one or two Junkers aircraft in their early development but was replaced by the geared L88 geared V-12 of 1929.
The Junkers L88 was Junkers' first geared V-12 engine, appearing c.1930 and based on a pair of 6-cylinder L8s. In 1932 a supercharger was added. It was used in the world's second working pressurised aircraft, the Junkers Ju 49 and, for a while, in the large G 38 airliner and its Japanese built military version.
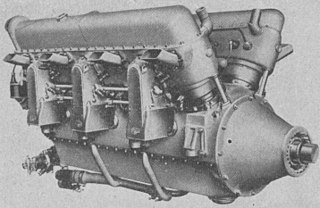
The Lorraine 12H Pétrel was a French V-12 supercharged, geared piston aeroengine initially rated at 370 kW (500 hp), but later developed to give 640 kW (860 hp). It powered a variety of mostly French aircraft in the mid-1930s, several on an experimental basis.

The Fiat AN.1 was an experimental Italian water-cooled diesel straight six cylinder aircraft engine from the late 1920s.

The Potez 6D is a French six cylinder inverted inline aircraft engine put into production after World War II in normal and supercharged versions. Unsupercharged, it produced a take-off power of 179 kW (240 hp) at 2,530 rpm.

The Isotta Fraschini Gamma was an air cooled aircraft engine developed by the Italian engineering company Isotta Fraschini in the 1930s. It was an inverted V12 rated at over 500 hp (373 kW). Produced in small numbers for one-off aircraft, including the Ambrosini SAI.107 and Caproni Vizzola F.5 Gamma fighter trainer prototypes, it was developed into the more powerful and more numerous Delta.
















