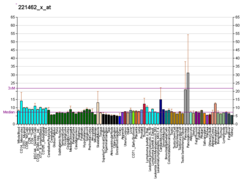
| KLK15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | KLK15 , ACO, HSRNASPH, kallikrein related peptidase 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 610601; MGI: 2447533; HomoloGene: 77571; GeneCards: KLK15; OMA:KLK15 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kallikrein-15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLK15 gene. [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
Contents
Kallikreins are a subgroup of serine proteases having diverse physiological functions. Growing evidence suggests that many kallikreins are implicated in carcinogenesis and some have potential as novel cancer and other disease biomarkers. This gene is one of the fifteen kallikrein subfamily members located in a cluster on chromosome 19. In prostate cancer, this gene has increased expression, which indicates its possible use as a diagnostic or prognostic marker for prostate cancer. The gene contains multiple polyadenylation sites and alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [9]