The Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the state organisation responsible for defending the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The FARDC was rebuilt patchily as part of the peace process which followed the end of the Second Congo War in July 2003.

South Kivu is one of 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Its capital is Bukavu.

The Ituri conflict is an ongoing low intensity asymmetrical conflict between the agriculturalist Lendu and pastoralist Hema ethnic groups in the Ituri region of the north-eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). While the two groups had fought since as early as 1972, the name 'Ituri conflict' refers to the period of intense violence between 1999 and 2003. Armed conflict continues to the present day.

The Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda is an armed rebel group active in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. As an ethnic Hutu group opposed to the ethnic Tutsi influence, the FDLR is one of the last factions of Rwandan rebels active in the Congo. It was founded through an amalgamation of other groups of Rwandan refugees in September 2000, including the former Army for the Liberation of Rwanda (ALiR), under the leadership of Paul Rwarakabije. It was active during the latter phases of the Second Congo War and the subsequent insurgencies in Kivu.
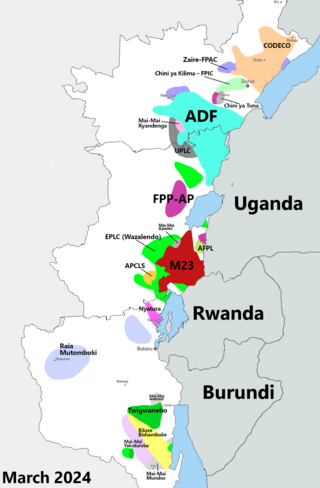
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

The March 23 Movement, often abbreviated as M23 and also known as the Congolese Revolutionary Army, is a Congolese rebel military group that is for the most part formed of ethnic Tutsi. Based in eastern areas of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), it operates mainly in the province of North Kivu, which borders both Uganda and Rwanda. The M23 rebellion of 2012 to 2013 against the DRC government led to the displacement of large numbers of people. On 20 November 2012, M23 took control of Goma, a provincial capital with a population of a million people, but it was requested to evacuate it by the International Conference on the Great Lakes Region because the DRC government had finally agreed to negotiate. In late 2012, Congolese troops, along with UN troops, retook control of Goma, and M23 announced a ceasefire and said that it wanted to resume peace talks.

Bunyakiri is a town located in the high plateau of Kalehe Territory in the South Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Bunyakiri is nearby the Bulehe and Mulamba villages. It is mainly inhabited by Tembo, Havu, Twa and Hunde ethnic groups.

The Allied Democratic Forces insurgency is an ongoing conflict waged by the Allied Democratic Forces in Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, against the governments of those two countries and the MONUSCO. The insurgency began in 1996, intensifying in 2013, resulting in hundreds of deaths. The ADF is known to currently control a number of hidden camps which are home to about 2,000 people; in these camps, the ADF operates as a proto-state with "an internal security service, a prison, health clinics, and an orphanage" as well as schools for boys and girls.
The Land Forces, also called the Congolese Army, are the land warfare component and the largest branch of the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC).

The 2017 Semuliki attack was an attack carried out by elements of the Allied Democratic Forces on a United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO) operating base in the Beni Territory, North Kivu region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo on December 7, 2017. The attack was highly coordinated and resulted in the deaths of fifteen U.N. peacekeeping personnel and wounds to 53 others making it the deadliest incident for the U.N. since the deaths of twenty-four Pakistani peacekeepers in an ambush in Somalia in 1993. The attack was among many of the latest flare-ups in violence in the North Kivu region which borders Uganda and Rwanda and one of the ADF's deadliest attacks in recent history. U.N. Secretary-General António Guterres labeled the attack, "the worst attack on UN peacekeepers in the organization's recent history."

Raïa Mutomboki or Raiya Mutomboki are a Mai-Mai militia operating in the South Kivu region in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. The group formed in 2005 to fight against Rwandan Hutu groups such as the Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR) as part of the Kivu conflict.

The National Coalition of the People for the Sovereignty of Congo, and also known as the Alliance of Article 64, is an armed rebel coalition in the east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The group is a coalition of around 12 different Mai-Mai groups in and around South Kivu province. It was formed on 30 June 2017, symbolically Congolese Independence Day.

Nduma Defense of Congo—Renovated is an armed militia group operating in north-east of the Democratic Republic of the Congo which controls large parts of North Kivu province. It has been a major participant of the Kivu conflict since its 2014 split from the Nduma Defense of Congo.
The 2020 Democratic Republic of the Congo attacks were a series of attacks which took place in 2020. The attacks were mostly carried out by the Allied Democratic Forces (ADF), a radical Islamist rebel group and the Cooperative for the Development of Congo (CODECO), an agricultural and religious group made up of ethnic Lendu people. The attacks left at least 1,316 people dead and 132 injured.
The Kipupu massacre occurred on 16 July 2020 in the South Kivu village of Kipupu in the Mwenga Territory in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Gunmen belonging to the Ngumino and Twiganeho militias of the Banyamulenge community attacked the village and reportedly killed 220 people according to provincial lawmakers, while independent analysts state only 18 people were killed.
The 2017 CNPSC offensive was a military offensive launched by rebels of the National Coalition of the People for the Sovereignty of Congo (CNPSC) on 30 June 2017 against security forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and MONUSCO. The goal of the offensive was to capture major settlements, mainly in South Kivu province in order to raise support for a popular uprising against then-president Joseph Kabila, who the coalition had deemed as an illegitimate president.
This a timeline of the Kivu conflict during 2020.
In late March 2022, the March 23 Movement (M23) launched an offensive in North Kivu, clashing with the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC) and MONUSCO. The fighting displaced hundreds of thousands of civilians and caused renewed tensions between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda, as the latter was proved of supporting the rebel offensive.

Lulenge constitutes one of the four sectors within the Fizi Territory of South Kivu Province, situated in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Geographically positioned adjacent to the Kiloba and Makena villages at an elevation of 943 meters, the sector's administrative center is Kilembwe. Lulenge is delineated to the north by the Itombwe sector and Mwenga Territory, to the east by Lake Tanganyika and the Mutambala sector, to the south by the N'gangya sector, and to the west by Shabunda Territory.
Bibogobogo, also known as Bibokoboko in Kibembe, is a village in the middle plateaus of the Mutambala Sector in the Fizi Territory in the South Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is situated in the forested mountains and middle plateaus, overlooking Baraka in the south-west, near Kisombe and Bibokoboko II villages. Bibogobogo shares the borders with Uvira Territory in the North, the Mwenga Territory and Shabunda Territory in the West, the Kalemie Territory in the South, and Lake Tanganyika in the East. Geologically, the regional soil is composed of metals, including sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, aluminium and mercury, making it suitable for gold plating, mercury pollution, pollution index and agriculture.












