This article is about the Transport in Zambia.

The 1,576 kilometres (979 mi) long Kafue River is the longest river lying wholly within Zambia. Its water is used for irrigation and for generating hydroelectric power. It is the largest tributary of the Zambezi, and of Zambia's principal rivers, it is the most central and the most urban. More than 50% of Zambia's population live in the Kafue River Basin and of these around 65% are urban.

Chipata is a city and administrative centre of the Eastern Province of Zambia and Chipata District. It was declared the 5th city of the country, after Lusaka, Ndola, Kitwe and Livingstone, by President Edgar Lungu on 24 February 2017. The city has undergone rapid economic and infrastructure growth in the years, leading up to city status.

Livingstone is a city in Zambia. Until 1935, it served as the capital of Northern Rhodesia. Lying 10 km (6 mi) to the north of the Zambezi River, it is a tourism attraction center for the Victoria Falls and a border town with road and rail connections to Zimbabwe on the other side of the Victoria Falls. A historic British colonial city, its present population was enumerated at 177,393 inhabitants at the 2022 census. It is named after David Livingstone, the Scottish explorer and missionary who was the first European to explore the area. Until 2011, Livingstone was the provincial capital of Zambia's Southern Province.

Victoria Falls, popularly known as Vic Falls, is a resort town and city in the province of Matabeleland North, Zimbabwe. It lies on the southern bank of the Zambezi River at the western end of Victoria Falls themselves. According to the 2022 Population Census, the town had a population of 35,199.

Mpika is a town in the Muchinga Province of Zambia, lying at the junction of the M1 Road to Kasama and Mbala and the Tanzam Highway to Dar es Salaam, Tanzania in the north-east and Lusaka in the south-west. It also has a railway station on the TAZARA Railway about 5 kilometres (3 mi) away. Mpika is situated between the Muchinga Escarpment to the east and vast miombo plains to the west. The town has an estimated population of 40,000 inhabitants (2008), while the district population is estimated at 150,000 inhabitants. Since Mpika District was the biggest district in Zambia before its division in 2017, the population density was less than 4 people per square kilometre.

The Great East Road is a major road in Zambia and the main route linking its Eastern Province with the rest of the country. It is also the major link between Zambia and Malawi and between Zambia and northern Mozambique. However, the route does not carry as much traffic as many of the other regional arterial roads and between the main cities it serves, Lusaka and Chipata, it passes through rural and wilderness areas. In Lusaka the road forms the main arterial road for the eastern suburbs. The entire route from Lusaka to Chipata and the border with Malawi is designated the T4 road on Zambia's road network.

Eastern Province is one of Zambia's ten provinces. The province lies between the Luangwa River and borders with Malawi to the east and Mozambique to the south, from Isoka in the northeast to the north of Luangwa in the south. The provincial capital is Chipata. Eastern province has an area of 51,476 km2 (19,875 sq mi), locally shares border with three other provinces of the country and is divided into fifteen districts.

Southern Province is one of Zambia's ten provinces, and home to Zambia's premier tourist attraction, Mosi-oa-Tunya, shared with Zimbabwe. The centre of the province, the Southern Plateau, has the largest area of commercial farmland of any Zambian province, and produces most of the maize crop.
This article gives lists of the National Monuments and other historic sites of Zambia, with a one- or two-line description providing links to details given on other pages.

Chadiza is a town in the Eastern Province of Zambia. Its headquarters are located in Chadiza District. It lies 35 km south of the Great East Road and about 80 km south-south-west of Chipata, on a plateau studded by isolated rocky hills, between the middle Luangwa valley and the Zambezi. It is also 35 kilometres north-north-east of the Chimefusa Border.
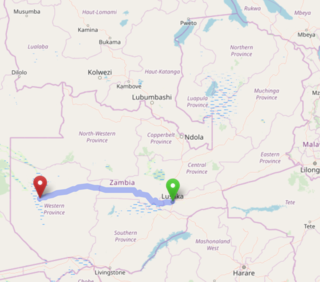
The Lusaka–Mongu Road of Zambia runs 580 km from the capital, Lusaka, to Mongu, capital of the Western Province. It connects that province to the rest of the country, as well as being one of two routes to the south-west extremity of North-Western Province. It also serves as the main highway of the western half of Central Province. The entire route from Lusaka to Mongu is designated as the M9 road.

The T1 or Lusaka–Livingstone Road is the main highway of the Southern Province of Zambia. It begins 55 kilometres south of the city of Lusaka and heads south-west to the principal tourist destination, Victoria Falls in Livingstone, via Mazabuka, Monze, Choma and Kalomo, measuring approximately 430 kilometres (267 mi). The entire route is part of Trans-African Highway network number 4 or Cairo-Cape Town Highway between Cairo and Cape Town.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Zambia:
Zambia, officially known as the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. The neighbouring countries are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique, Zimbabwe, Botswana, and Namibia to the south, and Angola to the west. The capital city is Lusaka, located in the southeast of the country. The population is concentrated mainly around the capital and the Copperbelt to the northwest.

Lusaka is the capital and largest city of Zambia. It is one of the fastest-developing cities in southern Africa. Lusaka is in the southern part of the central plateau at an elevation of about 1,279 metres (4,196 ft). As of 2019, the city's population was about 3.3 million, while the urban population is estimated at 2.5 million in 2018. Lusaka is the centre of both commerce and government in Zambia and connects to the country's four main highways heading north, south, east, and west. English is the official language of the city administration, while Bemba and Nyanja are the commonly spoken street languages.

Chipata District is a district of Zambia, located in Eastern Province. The capital lies at Chipata. As of the 2010 Zambian Census, the district had a population of 455,783 people.

The T2 is a trunk road in Zambia. The road runs from the Tunduma border with Tanzania via Mpika, Kabwe and Lusaka to the Chirundu border with Zimbabwe. The road is the longest route of the country, as it is approximately 1,155 kilometres (718 mi). The route from Mpika to Kafue is a toll road. The route from Tanzania to Lusaka is Zambia's Great North Road and is part of the Tanzam Highway.
The T6 road is a road in the Eastern Province of Zambia. It is a branch of the Great East Road and it is the primary road used to access Northern Mozambique from Zambia. It connects Katete with the Chanida Border with Mozambique.

Sena railway, also called Shire Highlands railway, Dondo-Malawi railway and North-South Malawi railway, is a railway that connects Dondo, Mozambique, to Chipata, in Zambia. It is c. 1000 km long, in a 1067 mm gauge.


















