
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.

Cruentarens are a group of macrolides secreted by the myxobacteria Byssovorax cruenta. There are two isomers (cruentaren A and B) have been isolated. They each have a molecular formula of C33H51NO8 and molecular weight 589 g/mol. Cruentaren A strongly inhibits the growth of yeasts and filamentous fungi, and inhibits the proliferation of different cancer cell lines in vitro, including a multidrug-resistant KB line. Cruentaren B shows only marginal cytotoxicity and no antifungal activity.
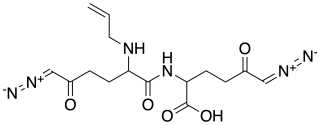
Alazopeptin is an antibiotic, with moderate anti-trypanosomal and antitumor activity. It was originally isolated from Streptacidiphilus griseoplanus, sourced from soil near Williamsburg, Iowa. It is also isolated from Kitasatospora azatica. It is still largely produced via fermentation broths of that organism. Structurally, alazopeptin is a tripeptide and contains 2 molecules of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine and one molecule of L-alanine. In 2021 the biosynthetic pathway of alazopeptin was elucidated.
Streptomyces avermitilis is a species of bacteria in the genus Streptomyces. This bacterium was discovered by Satoshi Ōmura in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan.
Venturicidins are a group of antifungal compounds. The first member of this class was isolated from Streptomyces bacteria in 1961. Additional members of this class were subsequently isolated and characterized. An antifungal substance "aabomycin A" was isolated from Streptomyces in 1969. However, in 1990 it was reported that aabomycin A is actually a 3:1 mixture of two related components, which were then named aabomycin A1 and aabomycin A2. The structures of these were shown to be identical with those of the previously characterized compounds venturicidin A and venturicidin B, respectively. A new analog, venturicidin C, was recently reported from a Streptomyces isolated from thermal vents associated with the Ruth Mullins coal fire in Kentucky.

Carbomycin, also known as magnamycin, is a colorless, optically active crystalline macrolide antibiotic with the molecular formula C42H67NO16. It is derived from the bacterium Streptomyces halstedii and active in inhibiting the growth of Gram-positive bacteria and "certain Mycoplasma strains." Its structure was first proposed by Robert Woodward in 1957 and was subsequently corrected in 1965.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT52.
Streptomyces thermocarboxydus is a streptomycete bacterium species. It is moderately thermophilic and carboxydotrophic, with type strain AT37.
Naphthomycins are a group of closely related antimicrobial chemical compounds isolated from Streptomyces. They are considered a subclass of ansamycins.
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of Actinomycetota, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Streptomyces aculeolatus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Tottori prefecture in Japan. Streptomyces aculeolatus produces naphthablin.
Streptomyces aurantiacus is a bacterium species from the genus Streptomyces which produces aurantin, pamamycin-621, aurantimycin A, aurantimycin B, aurantimycin C, aurantimycin D, dihydronancimycin and ancimycin.
Streptomyces diastaticus is an alkaliphilic and thermophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces diastaticus produces oligomycin A, oligomycin C, rimocidin and the leukotriene-A4 hydrolase-inhibitor 8(S)-amino-2(R)-methyl-7-oxononanoic acid. Streptomyces diastaticus also produces gougerotin and diastaphenazine and the antibiotic ruticin.
Streptomyces halstedii is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from deeper soil layers. Streptomyces halstedii produces magnamycin B, vicenistatin deltamycin A2, deltamycin A3, bafilomycin B1 and bafilomycin C1. Streptomyces halstedii also produces complex antifungal antibiotics like oligomycins and the antibiotics anisomycin and sinefungin.
Streptomyces hundungensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from a quarry in Tangkhul Hundung in Manipur in India Streptomyces hundungensis has antifungal activity.
Streptomyces microflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces microflavus produces nemadectin, fattiviracin A1, milbemycin and deoxyuridines. Streptomyces microflavus also produces the ionophore valinomycin. Streptomyces microflavus is also known to cause potato common scab disease in Korea.
Streptomyces rochei is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Russia. Streptomyces rochei produces borrelidin, butyrolactol A, butyrolactol B, uricase and streptothricin. Streptomyces rochei has antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici and Aspergillus fumigatus. Streptomyces rochei produces moenomycin and bambermycin. Streptomyces rochei produces amicetin A, amicetin B, amicetin C and streptolin. Streptomyces rochei produces endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase mithramycin, amicetin, bamicetin, and plicacetin.
Streptomyces specialis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Germany.
Streptomyces violaceusniger is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceusniger has antifungal activity. Streptomyces violaceusniger produces isoafricanol and spirofungin.

The arylomycins are a class of antibiotics initially isolated from a soil sample obtained in Cape Coast, Ghana. In this initial isolation, two families of closely related arylomycins, A and B, were identified. The family of glycosylated arylomycin C lipopeptides were subsequently isolated from a Streptomyces culture in a screen for inhibitors of bacterial signal peptidase. The initially isolated arylomycins have a limited spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. The only activity against Gram-negative bacteria was seen in strains with a compromised outer membrane.





