A princely state was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown.

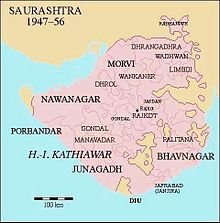
Nawanagar was an Indian princely state in the historical Halar region, located on the southern shores of the Gulf of Kutch. It was ruled by the Jadeja Rajput dynasty and became a part of newly formed India. Its capital city was Nawanagar city, now known as Jamnagar. It had an area of 3,791 square miles (9,820 km2) and a population estimated at 336,779 in 1901. Its rulers, who use the title of "Jam Saheb" are of the same clan as the Rao of Kutch. They were entitled to a 13-gun salute. The state flag was a rectangular red flag with a white elephant, near and facing the hoist. During the British, the state was part of the Kathiawar Agency, within the Gujarat Division of Bombay Presidency.
In India, a privy purse was a payment made to the ruling families of erstwhile princely states as part of their agreements to first integrate with India in 1947 after the independence of India, and later to merge their states in 1949, thereby ending their ruling rights.

Jadeja is a Samma Rajput clan that inhabits the Indian state of Gujarat and the Tharparkar district of Sindh, Pakistan. They originated from Sammas of Sindh, a pastoral group, and laid a claim on the Rajput identity after marriages with Sodha Rajput women by adopting a process called Rajputisation.

Major General Maharaja Sawai Governor Sir Man Singh II GCSI GCIE was an Indian prince, government official, diplomat and sportsman.

Rajkot State was one of the princely states of India during the period of British rule. It was a 9-gun salute state belonging to the Kathiawar Agency of the Bombay Presidency. Its capital was in Rajkot, located in the historical Halar region of Kathiawar on the banks of the Aji River. Nowadays, Rajkot is the fourth largest city of Gujarat state.
Maharajadhiraj Mirza Maharao Sri Madansinhji Vijayaraji Sawai Bahadur was the last official ruler of the Princely State of Cutch, from 26 February 1948 to 1 June 1948.

Bikaner State was the Princely State in the north-western most part of the Rajputana province of imperial British India from 1465 to 1947. The founder of the state Rao Bika was a younger son of Rao Jodha ruler of and founder of the city of Jodhpur in Marwar. Rao Bika chose to establish his own kingdom instead of inheriting his father's. Bika defeated the Jat clans of Jangladesh which today refers to the north and north-western Rajasthan along with his uncle Rao Kandhal and his adviser Vikramji Rajpurohit and founded his own kingdom. Its capital was the city of Bikaner.

Pradyumansinhji Lakhajirajsinhji, the 14th Thakore Saheb of Rajkot, was an Indian nobleman and ruler of the princely state of Rajkot from June 1940 until the abolition of princely titles in 1971. The third son of Lakhajirajsinhji II Bavajirajsinhji, the 12th Thakore Saheb, Pradyumansinhji succeeded to the title after the death of his older brother, Dharmendrasinhji, on 11 June 1940.
Vala State or Vallabhipura was a non-salute princely state in India during the British Raj until 1948. The centre was the city of Vallabhi. The last ruler of the state signed the state's accession to the Indian Union on 15 February 1948.

The Ranasan State was a small princely state belonging to the Mahi Kantha Agency of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It had its capital in Ranasan village, Talod municipality, Sabarkantha district of present-day Gujarat State.

The Vadagam State was a 5th Class princely state belonging to the Mahi Kantha Agency of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It had its capital in Vadgam taluk, Banaskantha district of present-day Gujarat State. Wadagam State's last ruler signed the accession to join the Indian Union in 1948.

Kharsawan State, also spelt Kharsua or kharaswan, (Odia:ଖରସୁଆଁ)was a princely state in India during the British Raj. The state had a privy purse of 33,000 rupees. It was one of the Odia Princely states of India during the period of the British Raj and the major language spoken in the area is Odia.

Morvi State, also spelled as Morvee State or Morbi State, was a princely salute state in the historical Halar prant (district) of Kathiawar during the British Raj.

Dhrol State was one of the 562 princely states of British India. It was a 9 gun salute state belonging to the Kathiawar Agency of the Bombay Presidency. Its capital was in the town of Dhrol, located in the historical Halar region of Kathiawar.
Mohanpur State was a small princely state belonging to the Mahi Kantha Agency of the Bombay Presidency during the era of the British Raj. It was centered on Mohanpur town, in present-day Sabarkantha district of Gujarat State, and included 52 villages.
Chuda is a town and Taluka headquarter of Chuda Taluka in Surendranagar district, Gujarat, India. It was formerly a Jhala Rajput princely state.
Gadhka is a village and formerly the seat of a Rajput taluka and minor princely state, named after the village, in Western Saurashtra, presently in western India's state Gujarat.
Jethwa dynasty was a dynasty that ruled over present day Gujarat region of India from 7th century AD till middle of 20th century, when India became independent. It was a Rajput dynasty ruled by Jethwa clan of Rajputs.
Kathiwara State or Kathiwada State was a princely state ruled by the Jadon dynasty that encompassed about 181 square kilometres (70 sq mi) of the territory immediately surrounding the city of Kathiwara. The princely state acceded to India in 1947. Upon accession to the Indian Union, it was absorbed into the province of Madhya Bharat.