
The Gulf Coast of the United States, also known as the Gulf South or the South Coast, is the coastline along the Southern United States where they meet the Gulf of Mexico. The coastal states that have a shoreline on the Gulf of Mexico are Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, and these are known as the Gulf States.
Ghana is a West African country in Africa, along the Gulf of Guinea.
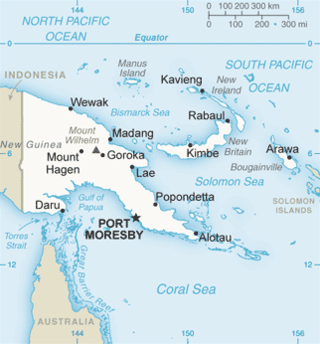
The geography of Papua New Guinea describes the eastern half of the island of New Guinea, the islands of New Ireland, New Britain and Bougainville, and smaller nearby islands. Together these make up the nation of Papua New Guinea in tropical Oceania, located in the western edge of the Pacific Ocean.

A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.

The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of 70,400 km2 (27,200 sq mi).
In West Africa, the forest zone refers to the southern part of the region once covered by tropical rainforest. Sometimes this region is referred to as Guinea to distinguish it from the grassland-covered Sudan, drier Sahel and per-arid Sahara. It is made-up of vegetation having mainly trees and consist of the following local biotic communities: -mangrove swamp forest -tropical rain forest.

Bata is a port city in the Litoral province of Equatorial Guinea. With a 2005 estimated population of 173,046, it is the most populous city in Equatorial Guinea. It lies on the Atlantic Ocean coast of Río Muni. Bata was formerly capital of Equatorial Guinea and is a transport hub and port, from which ferries sail to Malabo and Douala, while aircraft can land at Bata Airport. Bata is also known for its nightlife and market.

Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.

Gulf Province is a province of Papua New Guinea located on the southern coast. The provincial capital is Kerema. The 34,472 km2 province is dominated by mountains, lowland river deltas, and grassland flood plains. In Gulf Province, the Kikori, Turama, Purari, and Vailala rivers meet the Papuan Gulf. The province has the second-smallest population of all the provinces of Papua New Guinea with 106,898 inhabitants. The province shares land borders with Western Province to the west, Southern Highlands, Chimbu, and Eastern Highlands to the north, Morobe Province to the east, and Central Province to the southeast.

The Purari is a river that originates in the south central highlands especially in Kandep District of Enga Province of Papua New Guinea, flowing 630 kilometres (391 mi) though Gulf Province to the Gulf of Papua. The Purari has a 33,670 km2 (13,000 sq mi) drainage basin and is the third largest river in Papua New Guinea. The discharge varies through the year, averaging around 3,000 m3/s (110,000 cu ft/s)–4,000 m3/s (140,000 cu ft/s) at the delta.
Mendi, Papua New Guinea, is the provincial capital of the Southern Highlands Province. The Lai River flows by the town. It is served by Mendi Airport. The town falls under Mendi Urban LLG.

The Kikori River is a major river in southern Papua New Guinea on the island of New Guinea. The river has a total length of 445 km (277 mi) and flows southeast into the Gulf of Papua, with its delta at the head of the gulf. The settlement of Kikori lies on the delta.

Kerema is the capital of Gulf Province, Papua New Guinea. It is located on the coast of Gulf of Papua. The Gulf region is aptly named for its concave coastline with large deltas. The Gulf area is a riparian region where many rivers from the southern slopes of the highlands drain into.

Sorong is the largest city and the capital of the Indonesian province of Southwest Papua. The city is located on the western tip of the island of New Guinea with its only land borders being with Sorong Regency. It is the gateway to Indonesia's Raja Ampat Islands, species rich coral reef islands in an area considered the heart of the world's coral reef biodiversity. It also is the logistics hub for Indonesia's thriving eastern oil and gas frontier.
Mount Leonard Murray is a mountain in Papua New Guinea in central New Guinea. It is north-west of Kikori and has an elevation of 2,380 metres (7,810 ft).

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

The climate of Wales refers to the weather conditions prevailing in Wales in general or over a long period.
The Pulau River is a major river in South Papua province of Indonesia, with a total length of 403 km (250 mi).
Ipiko is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea, the most divergent of the Inland Gulf languages. Despite being spoken by only a few hundred people, language use is vigorous. It is spoken in Ipiko and Pahemuba villages, with Ipiko village being located in Amipoke ward, Baimuru Rural LLG, Kikori District, Gulf Province.
Foia Foia (Foyafoya), or Minanibai, is a Papuan language of Papua New Guinea, spoken in an area near Omati River mouth in Ikobi Kairi and Goaribari Census districts.













