This article needs additional citations for verification .(December 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| King Salmon River | |
|---|---|
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Alaska |
| Borough | Lake and Peninsula |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Mother Goose Lake |
| - location | Alaska Peninsula National Wildlife Refuge |
| - coordinates | 57°13′02″N157°22′59″W / 57.21722°N 157.38306°W [1] |
| - elevation | 76 ft (23 m) [2] |
| River mouth | Ugashik River |
| - location | 7 miles (11 km) south of Bristol Bay and 8 miles (13 km) southwest of Ugashik, Alaska Peninsula |
| - coordinates | 57°29′50″N157°38′30″W / 57.49722°N 157.64167°W Coordinates: 57°29′50″N157°38′30″W / 57.49722°N 157.64167°W [1] |
| - elevation | 0 ft (0 m) [1] |
| Length | 35 mi (56 km) [1] |
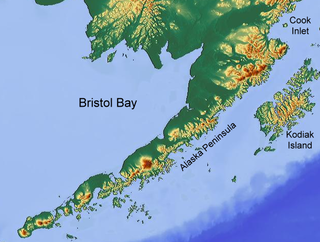
The King Salmon River is a 35-mile (56 km) tributary of the Ugashik River in the U.S. state of Alaska. [1] Beginning at Mother Goose Lake in the Aleutian Range, it flows northwest to meet the larger river near the upper reaches of Ugashik Bay. [3] The lake and the upper course of the King Salmon lie within the Alaska Peninsula National Wildlife Refuge. [3] The river's gravel bottom and braided channels are ideal for the many king salmon that spawn in its waters, but they limit navigation to small skiff.

The Ugashik River is a stream, 43 miles (69 km) long, on the Alaska Peninsula of the U.S. state of Alaska. It flows from headwaters near Lower Ugashik Lake and empties into Ugashik Bay, an estuary of the Bering Sea's Bristol Bay.

In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are currently 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory and shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Due to this shared sovereignty, Americans are citizens both of the federal republic and of the state in which they reside. State citizenship and residency are flexible, and no government approval is required to move between states, except for persons restricted by certain types of court orders. Four states use the term commonwealth rather than state in their full official names.

Alaska is a U.S. state in the northwest extremity of North America, just across the Bering Strait from Asia. The Canadian province of British Columbia and territory of Yukon border the state to the east and southeast. Its most extreme western part is Attu Island, and it has a maritime border with Russia to the west across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort seas—southern parts of the Arctic Ocean. The Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. It is the largest U.S. state by area and the seventh largest subnational division in the world. In addition, it is the 3rd least populous and the most sparsely populated of the 50 United States; nevertheless, it is by far the most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel in North America: its population—estimated at 738,432 by the United States Census Bureau in 2015— is more than quadruple the combined populations of Northern Canada and Greenland. Approximately half of Alaska's residents live within the Anchorage metropolitan area. Alaska's economy is dominated by the fishing, natural gas, and oil industries, resources which it has in abundance. Military bases and tourism are also a significant part of the economy.
There are many rivers in Alaska bearing the name King Salmon River, including tributaries to the Egegik River and Nushagak River systems in southwest Alaska, alone. The name is also occasionally confused with a nickname given the Kenai River, a popular fishing stream located in the Cook Inlet drainage of southcentral Alaska.

The Egegik River is a waterway in the U.S. state of Alaska. A biological survey was conducted at the base of the Alaska Peninsula in 1902 by Wilfred Hudson Osgood, which included the Egegik River.

The Nushagak River is a river in southwest Alaska, United States. It begins in the Alaska Range and flows southwest 450 km (280 mi) to Nushagak Bay, an inlet of Bristol Bay, east of Dillingham, Alaska.

The Kenai River called Kahtnu in the Dena'ina language, is the longest river in the Kenai Peninsula of south central Alaska. It runs 82 miles (132 km) westward from Kenai Lake in the Kenai Mountains, through the Kenai National Wildlife Refuge and Skilak Lake to its outlet into the Cook Inlet of the Pacific Ocean near Kenai and Soldotna.
Besides the large numbers of king salmon, the river also hosts large numbers of sea-run Dolly Varden, Chum Salmon and a small run of Pink Salmon.

The Dolly Varden trout is a species of salmonid native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. It is in the genus Salvelinus of true chars, which includes 51 recognized species, the most prominent being the brook, lake and bull trout, as well as Arctic char. Although many populations are semi-anadromous, fluvial and lacustrine populations occur throughout its range. It is considered by taxonomists as part of the Salvelinus alpinus or Arctic char complex, as many populations of bull trout, Dolly Varden trout and Arctic char overlap.