
Kirkcudbrightshire or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975, the area has formed part of Dumfries and Galloway for local government purposes. Kirkcudbrightshire continues to be used as a registration county for land registration. A lower-tier district called Stewartry covered the majority of the historic county from 1975 to 1996. The area of Stewartry district is still used as a lieutenancy area. Dumfries and Galloway Council also has a Stewartry area committee.

The Caledonian Railway (CR) was a major Scottish railway company. It was formed in 1845 with the objective of forming a link between English railways and Glasgow. It progressively extended its network and reached Edinburgh and Aberdeen, with a dense network of branch lines in the area surrounding Glasgow. It was absorbed into the London, Midland and Scottish Railway in 1923. Many of its principal routes are still used, and the original main line between Carlisle and Glasgow is in use as part of the West Coast Main Line railway.

The Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) was a railway company in Scotland. It served a triangular area of south-west Scotland between Glasgow, Stranraer and Carlisle. It was formed on 28 October 1850 by the merger of two earlier railways, the Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway and the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway. Already established in Ayrshire, it consolidated its position there and extended southwards, eventually reaching Stranraer. Its main business was mineral traffic, especially coal, and passengers, but its more southerly territory was very thinly populated and local traffic, passenger and goods, was limited, while operationally parts of its network were difficult.

The Portpatrick and Wigtownshire Joint Railways was a network of railway lines serving sparsely populated areas of south-west Scotland. The title appeared in 1885 when the previously independent Portpatrick Railway (PPR) and Wigtownshire Railway (WR) companies were amalgamated by the Portpatrick and Wigtownshire Railways Act 1885 into a new company jointly owned by the Caledonian Railway, Glasgow & South Western Railway, Midland Railway and the London and North Western Railway and managed by a committee called the Portpatrick and Wigtownshire Joint Committee.

The Castle Douglas and Dumfries Railway was a railway in Galloway in the south west of Scotland which linked Castle Douglas in Kirkcudbrightshire to Dumfries.
The Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway was a railway company in Scotland, which constructed the line from near Cumnock to Gretna Junction, forming the route from Glasgow to Carlisle via Dumfries, in association with other lines. Its promoters hoped it would form the only railway between central Scotland and England, but it lost out to rival companies.

The Glasgow South Western Line is a mainline railway in Scotland that runs from Glasgow to Kilmarnock, and then either Carlisle via Dumfries, or Stranraer via Ayr, with a branch to East Kilbride.

Dumfries railway station serves the town of Dumfries in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. It is located on the Glasgow South Western Line. The station is owned by Network Rail and managed by ScotRail who provide all passenger train services. It is staffed on a part-time basis throughout the week.
The Bridge of Weir Railway was an independent railway company that built a line from Johnstone to Bridge of Weir. It was taken over by the Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) in 1865 and formed the base of a line that extended to Greenock, giving the G&SWR access to the harbour facilities there, competing with the rival Caledonian Railway.

The Glasgow, Paisley, Kilmarnock and Ayr Railway (GPK&AR) was a railway in Scotland that provided train services between Glasgow, Kilmarnock and Ayr. It opened its first line, between Glasgow and Ayr, in stages from 1839 to 1840. The section between Glasgow and Paisley was made jointly with the Glasgow, Paisley and Greenock Railway. Later it built a line from Dalry via Kilmarnock to Cumnock, linking there with the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway, and together forming a through route from Glasgow to Carlisle. The two companies merged to form the Glasgow and South Western Railway.
The Ayr and Dalmellington Railway was a railway company in Scotland, which connected the growing ironworks community around Dalmellington with Ayr, in Ayrshire, Scotland. Its route was originally planned by the Ayrshire and Galloway Railway as part of a scheme to link Ayr with Castle Douglas, but lack of funds limited the construction to a very short section connecting the iron and coal pits of the Dalmellington Iron Company with its iron works, opening in 1849.
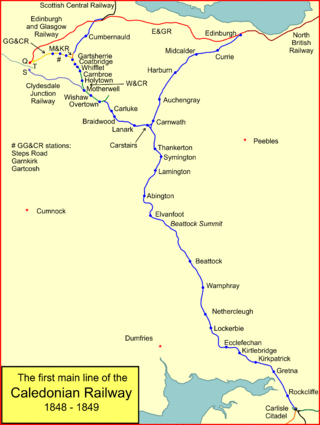
The Caledonian Railway main line in Scotland connected Glasgow and Edinburgh with Carlisle, via Carstairs and Beattock.
The Ayr and Maybole Junction Railway (A&MJR) was a railway in Ayrshire, Scotland that provided services between Ayr and Maybole. It opened in 1856 and was seen as a link in providing a through line between Glasgow and Portpatrick, then the ferry port for the north of Ireland.
The Maybole and Girvan Junction Railway was a railway company that constructed a line between Maybole and Girvan. Although promoted independently, it was supported by the Glasgow and South Western Railway, and was seen as part of a trunk line connecting Glasgow with a ferry port for the north of Ireland.
Girvan and Portpatrick Junction Railway (G&PJR) was a railway company in Scotland. It opened in 1877 between Girvan and Challoch Junction, where it joined the Portpatrick Railway, which had already reached Stranraer from Castle Douglas. Portpatrick had been an important ferry terminal for traffic to and from the north of Ireland, but its significance was waning and Stranraer assumed greater importance. The new line formed part of a route between Glasgow, Ayr and Stranraer.

Tarff railway station served the village of Ringford, in the historic county of Kirkcudbrightshire in the administrative area of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland from 1864 to 1965 on the Kirkcudbright Railway.
The Dumfries, Lochmaben and Lockerbie Railway was a railway in Dumfriesshire, Scotland. It connected Dumfries with Lockerbie via Lochmaben. Promoted independently, it was absorbed by the Caledonian Railway to give access to Dumfriesshire and later to Portpatrick for the Irish ferry service. It opened in 1863, closed to ordinary passenger services in 1952, and closed completely in 1966.
The Glasgow and South Western Railway operated a number of cross-country lines in Ayrshire.
This article traces the Caledonian Railway branches in South Lanarkshire.

Maxwelltown railway station was a station in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, located on the Dumfries-to-Stranraer direct railway line. It served the town of Maxwelltown.













