
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

A recoilless rifle (rifled), recoilless launcher (smoothbore), or simply recoilless gun, sometimes abbreviated to "RR" or "RCL" is a type of lightweight artillery system or man-portable launcher that is designed to eject some form of countermass such as propellant gas from the rear of the weapon at the moment of firing, creating forward thrust that counteracts most of the weapon's recoil. This allows for the elimination of much of the heavy and bulky recoil-counteracting equipment of a conventional cannon as well as a thinner-walled barrel, and thus the launch of a relatively large projectile from a platform that would not be capable of handling the weight or recoil of a conventional gun of the same size. Technically, only devices that use spin-stabilized projectiles fired from a rifled barrel are recoilless rifles, while smoothbore variants are recoilless guns. This distinction is often lost, and both are often called recoilless rifles.

The Bazooka is a man-portable recoilless anti-tank rocket launcher weapon, widely deployed by the United States Army, especially during World War II. Also referred to as the "stovepipe", the innovative Bazooka was among the first generation of rocket-propelled anti-tank weapons used in infantry combat. Featuring a solid-propellant rocket for propulsion, it allowed for high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shaped charge warheads to be delivered against armored vehicles, machine gun nests, and fortified bunkers at ranges beyond that of a standard thrown grenade or mine. The universally applied nickname arose from the weapon's M1 variant's vague resemblance to the musical instrument called a bazooka invented and popularized by 1930s American comedian Bob Burns.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.

The Panzerfaust was a development family of single-shot man-portable anti-tank systems developed by Nazi Germany during World War II. The weapons were the first single-use light anti-tank weapons based on a pre-loaded disposable launch tube, a weapon configuration which is still used today.

Shoulder-fired missile, shoulder-launched missile or man-portable missile, among other variants, are common slang terms to describe high-caliber shoulder-mounted weapons systems; that is, weapons firing large, heavy projectiles ("missiles"), typically using the backblast principle, which are small enough to be carried by a single person and fired while held on one's shoulder. The word "missile" in this context is used in its original broad sense of a heavy projectile, and encompasses all shells and rockets, guided or unguided. A more formal variant is simply shoulder-fired weapons system and the like.

The Mk 153 Shoulder-Launched Multipurpose Assault Weapon (SMAW) is a smoothbore shoulder-fired rocket launcher. It is a portable assault weapon and has a secondary anti-armor ability. Developed from the B-300, it was introduced to the United States Armed Forces in 1984. It has a maximum effective range of 500 metres (550 yd) against a tank-sized target.

The Carl Gustaf 8.4 cm recoilless rifle is a Swedish-developed 84 mm (3.3 in) caliber shoulder-fired recoilless rifle, initially developed by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of the 1940s as a crew-served man-portable infantry support gun for close-range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battlefield illumination, smoke screening and marking fire, which has seen great export success around the globe and continues to be a popular multi-purpose support weapon in use by many nations. The Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless rifle is a lightweight, low-cost weapon that uses a wide range of ammunition, which makes it extremely flexible and suitable for a wide variety of roles.

The M72 LAW is a portable one-shot 66 mm (2.6 in) unguided anti-tank weapon.
The Panzerfaust 3 is a modern semi-disposable recoilless anti-tank weapon, which was developed between 1978 and 1985 and first entered service with the Bundeswehr in 1987. It was first ordered in 1973 to provide West German infantry with an effective weapon against contemporary Soviet armor, thereby replacing West Germany's aging PzF 44 Light Lanze launchers and the heavy Carl Gustaf 84 mm anti-tank recoilless rifle manufactured in Sweden.

The RAC 112 APILAS is a portable one-shot 112 mm recoilless anti-tank weapon, designed in France by GIAT Industries. Over 120,000 of the APILAS launchers have been produced, and they are in service with many countries.

The LRAC F1, officially called Lance-Roquettes AntiChar de 89 mm modèle F1, is a French reusable rocket launcher developed by Luchaire Défense SA, and manufactured in cooperation with Manufacture Nationale d'Armes de Saint-Étienne and was, in the 1970s, marketed by Hotchkiss-Brandt.

Alcotán-100 is a recoilless, one-man portable, single-use anti-tank rocket launcher system used by infantry, manufactured by Instalaza. The firing control unit predicts the future aiming point based on calculation before the rocket fire. It is being used as an infantry-type weapon and fireable from confined spaces. Instalaza claiming it to be, "the highest performance in unguided shoulder launched systems". It is in service with the Spanish Armed Forces and exported to other countries.

The RPG-75 is a portable, disposable, single-shot anti-tank weapon, developed in the 1970s in Czechoslovakia. It fires a 68 mm grenade with an effective range of 300 meters and maximum range of 1000 meters. It resembles the American M72 LAW rocket launcher. This recoilless rifle is recommended to be used against light tanks and armoured tracked vehicles.
The Wasp 58 is a 58-mm rocket launcher antitank weapon developed in France in the late 1980s. The weapon was, originally, privately developed by the French firm Luchaire SA, subsidiary of GIAT.
The high–low system is a design of cannon and anti-tank warfare launcher using a smaller high-pressure chamber to store propellant. It allows a much larger projectile to be launched without the heavy equipment usually needed for large caliber weapons. When the propellant is ignited, the higher pressure gases are bled out through vents at reduced pressure to a much larger low pressure chamber to push a projectile forward. The high-low system allows the weight of the weapon and its ammunition to be reduced significantly. Production cost and time are drastically lower than for standard cannon or other small-arm weapon systems firing a projectile of the same size and weight. It has a far more efficient use of the propellant, unlike earlier recoilless weapons, where most of the propellant is expended to the rear of the weapon to counter the recoil of the projectile being fired.
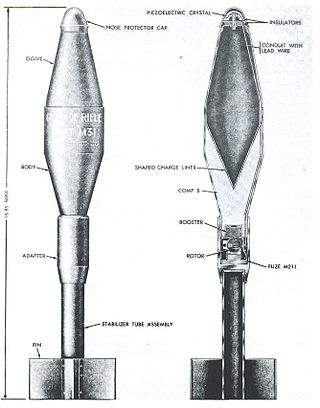
The M31 HEAT is a fin-stabilized anti-tank rifle grenade designed in the late 1950s to replace the Belgian ENERGA rifle grenade which was adopted by the US Army and US Marines as an emergency stop-gap measure during the Korean War. Like the ENERGA, it has a nose-initiated, based-detonated HEAT warhead, but unlike the ENERGA, the mechanical impact fuse system is replaced with a less complex and more reliable piezo-electric fuse system which also allows higher angles of impact, up to 65 degrees.

The AT4 is a Swedish 84 mm (3.31 in) unguided, man-portable, disposable, shoulder-fired recoilless anti-tank weapon manufactured by Saab Bofors Dynamics. The AT4 is not a rocket launcher strictly speaking, because the explosive warhead is not propelled by a rocket motor. Rather, it is a smooth-bore recoilless gun. Saab has had considerable sales success with the AT4, making it one of the most common light anti-tank weapons in the world. The M136 AT4 is a variant used by the United States Army.

The Stielgranate 41 was a German shaped charge, fin-stabilized shell, used with the 3.7 cm Pak 36 anti-tank gun to give it better anti-tank performance.
The FT5 is a shoulder-launched, unguided and portable anti-tank rocket weapon. The weapon was built in South Africa by Somchem, a division of Denel based in Somerset West, now Rheinmetall Denel Munition. The weapon was designed with the primary function to provide soldiers with a weapon capable of destroying armoured fighting vehicles and modern main battle tanks. The weapon also has a secondary function of destroying bunkers and other fortifications.

















