Lipin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPIN1 gene. [5] [6] [7] [8]
Lipin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LPIN1 gene. [5] [6] [7] [8]
Lipin-1 has phosphatidate phosphatase activity. [9] [10] [11] The nuclear localization of Lipin 1 is regulated by the mammalian Target Of Rapamycin protein kinase and links mTORC1 activity to the regulation of Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBP)-dependent gene transcription. [12] [13] [14]
Homozygous mutations in LPIN1 gene in humans cause recurrent rhabdomyolysis and exercise-induced myalgia while carrier state may predispose for statin-induced myopathy. [15] [16]
This gene also represents a candidate gene for human lipodystrophy, characterized by loss of body fat, fatty liver, hypertriglyceridemia, and insulin resistance. Mouse studies suggest that this gene functions during normal adipose tissue development and may also play a role in human triglyceride metabolism. [8] [12]

The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), also referred to as the mechanistic target of rapamycin, and sometimes called FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the MTOR gene. mTOR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family of protein kinases.

The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) is a receptor protein found on beta cells of the pancreas and on neurons of the brain. It is involved in the control of blood sugar level by enhancing insulin secretion. In humans it is synthesised by the gene GLP1R, which is present on chromosome 6. It is a member of the glucagon receptor family of G protein-coupled receptors. GLP1R is composed of two domains, one extracellular (ECD) that binds the C-terminal helix of GLP-1, and one transmembrane (TMD) domain that binds the N-terminal region of GLP-1. In the TMD domain there is a fulcrum of polar residues that regulates the biased signaling of the receptor while the transmembrane helical boundaries and extracellular surface are a trigger for biased agonism.

Pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase catalytic subunit 1, also known as protein phosphatase 2C, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDP1 gene. PDPC 1 is an enzyme which serves to reverse the effects of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase upon pyruvate dehydrogenase, activating pyruvate dehydrogenase.

Protein kinase C delta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCD gene.

Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP1CA gene.
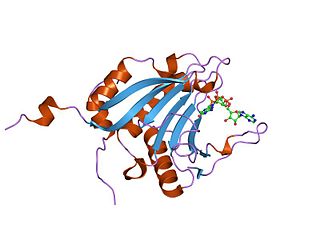
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4EBP1 gene.

SH2-domain containing Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 5-phosphatase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the INPPL1 gene.

Free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFA3) is a G-protein coupled receptor that in humans is encoded by the FFAR3 gene.

The enzyme phosphatidate phosphatase (PAP, EC 3.1.3.4) is a key regulatory enzyme in lipid metabolism, catalyzing the conversion of phosphatidate to diacylglycerol:

Src homology 2 (SH2) domain containing inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase 1(SHIP1) is an enzyme with phosphatase activity. SHIP1 is structured by multiple domain and is encoded by the INPP5D gene in humans. SHIP1 is expressed predominantly by hematopoietic cells but also, for example, by osteoblasts and endothelial cells. This phosphatase is important for the regulation of cellular activation. Not only catalytic but also adaptor activities of this protein are involved in this process. Its movement from the cytosol to the cytoplasmic membrane, where predominantly performs its function, is mediated by tyrosine phosphorylation of the intracellular chains of cell surface receptors that SHIP1 binds. Insufficient regulation of SHIP1 leads to different pathologies.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRA gene.

Protein phosphatase inhibitor 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R2 gene.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit B (eIF3b) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF3B gene.

For the SSH-1 protocol, see Secure Shell#Version 1

Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 4 catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP4C gene.

Krueppel-like factor 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF11 gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase delta is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the PTPRD gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase N2 (R-PTP-N2) also known as islet cell autoantigen-related protein (ICAAR) and phogrin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRN2 gene. PTPRN and PTPRN2 are both found to be major autoantigens associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF4EBP2 gene.

Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1), also known as forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma (FKHR), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXO1 gene. FOXO1 is a transcription factor that plays important roles in regulation of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by insulin signaling, and is also central to the decision for a preadipocyte to commit to adipogenesis. It is primarily regulated through phosphorylation on multiple residues; its transcriptional activity is dependent on its phosphorylation state.