
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells either fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia.

Leptin also obese protein is a protein hormone predominantly made by adipocytes. Its primary role is likely to regulate long-term energy balance.

Adipose tissue is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular endothelial cells and a variety of immune cells such as adipose tissue macrophages. Its main role is to store energy in the form of lipids, although it also cushions and insulates the body.

Hypertriglyceridemia is the presence of high amounts of triglycerides in the blood. Triglycerides are the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. Hypertriglyceridemia occurs in various physiologic conditions and in various diseases, and high triglyceride levels are associated with atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypercholesterolemia and predispose to cardiovascular disease.

Panniculitis is a group of diseases whose hallmark is inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Symptoms include tender skin nodules, and systemic signs such as weight loss and fatigue.
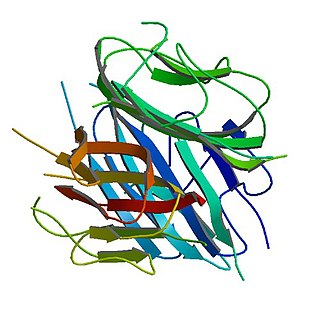
Adiponectin is a protein hormone and adipokine, which is involved in regulating glucose levels and fatty acid breakdown. In humans, it is encoded by the ADIPOQ gene and is produced primarily in adipose tissue, but also in muscle and even in the brain.
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, with the latter being the process by which fatty acids are esterified to glycerol before being packaged into very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Fatty acids are produced in the cytoplasm of cells by repeatedly adding two-carbon units to acetyl-CoA. Triacylglycerol synthesis, on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue. Nevertheless, it also occurs to some extent in other tissues such as the gut and kidney. A review on lipogenesis in the brain was published in 2008 by Lopez and Vidal-Puig. After being packaged into VLDL in the liver, the resulting lipoprotein is then secreted directly into the blood for delivery to peripheral tissues.

Lipomatosis is believed to be an autosomal dominant condition in which multiple lipomas are present on the body. Many discrete, encapsulated lipomas form on the trunk and extremities, with relatively few on the head and shoulders. In 1993, a genetic polymorphism within lipomas was localized to chromosome 12q15, where the HMGIC gene encodes the high-mobility-group protein isoform I-C. This is one of the most commonly found mutations in solitary lipomatous tumors but lipomas often have multiple mutations. Reciprocal translocations involving chromosomes 12q13 and 12q14 have also been observed within.
Lipohypertrophy is a lump under the skin caused by accumulation of extra fat at the site of many subcutaneous injections of insulin. It may be unsightly, mildly painful, and may change the timing or completeness of insulin action. It is a common, minor, chronic complication of diabetes mellitus.
Lipoatrophy is the term describing the localized loss of fat tissue. This may occur as a result of subcutaneous injections of insulin in the treatment of diabetes, from the use of human growth hormone or from subcutaneous injections of copaxone used for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. In the latter case, an injection may produce a small dent at the injection site. Lipoatrophy occurs in HIV-associated lipodystrophy, one cause of which is an adverse drug reaction that is associated with some antiretroviral medications.
Barraquer–Simons syndrome is a rare form of lipodystrophy, which usually first affects the head, and then spreads to the thorax. It is named for Luis Barraquer Roviralta (1855–1928), a Spanish physician, and Arthur Simons (1879–1942), a German physician. Some evidence links it to LMNB2.
Congenital generalized lipodystrophy is an extremely rare autosomal recessive condition, characterized by an extreme scarcity of fat in the subcutaneous tissues. It is a type of lipodystrophy disorder where the magnitude of fat loss determines the severity of metabolic complications. Only 250 cases of the condition have been reported, and it is estimated that it occurs in 1 in 10 million people worldwide.
Acquired generalized lipodystrophy (AGL), also known as Lawrence syndrome and Lawrence–Seip syndrome, is a rare skin condition that appears during childhood or adolescence, characterized by fat loss affecting large areas of the body, particularly the face, arms, and legs. There are four types of lipodystrophy based on its onset and areas affected: acquired or inherited, and generalized or partial. Both acquired or inherited lipodystrophy present as loss of adipose tissues, in the absence of nutritional deprivation. The near-total loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue is termed generalized lipodystrophy while the selective loss of adipose tissues is denoted as partial lipodystrophy. Thus, as the name suggests, AGL is a near-total deficiency of adipose tissues in the body that is developed later in life. It is an extremely rare disease with only about 100 cases reported worldwide. There are three main etiologies of AGL suspected: autoimmune, panniculitis-associated, or idiopathic. After its onset, the disease progresses over a few days, weeks, months, or even in years. Clinical presentations of AGL are similar to other lipodystrophies, including metabolic complications and hypoleptinemia. Treatments are also similar and mainly supportive for symptomatic alleviation. Although HIV- or drug-induced lipodystrophy are types of acquired lipodystrophy, their origins are very specific and distinct and hence are usually not discussed with AGL.
Familial partial lipodystrophy, also known as Köbberling–Dunnigan syndrome, is a rare genetic metabolic condition characterized by the loss of subcutaneous fat.

Lipotoxicity is a metabolic syndrome that results from the accumulation of lipid intermediates in non-adipose tissue, leading to cellular dysfunction and death. The tissues normally affected include the kidneys, liver, heart and skeletal muscle. Lipotoxicity is believed to have a role in heart failure, obesity, and diabetes, and is estimated to affect approximately 25% of the adult American population.
Metreleptin, sold under the brand name Myalept among others, is a synthetic analog of the hormone leptin used to treat various forms of dyslipidemia. It has been approved in Japan for metabolic disorders including lipodystrophy and in the United States as replacement therapy to treat the complications of leptin deficiency, in addition to diet, in patients with congenital generalized or acquired generalized lipodystrophy.
Asprosin is a protein hormone produced by mammals in tissues that stimulates the liver to release glucose into the blood stream. Asprosin is encoded by the gene FBN1 as part of the protein profibrillin and is released from the C-terminus of the latter by specific proteolysis. In the liver, asprosin activates rapid glucose release via a cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent pathway.

Christos Socrates Mantzoros is a Greek American physician-scientist, practicing internist-endocrinologist, teacher and researcher. He is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and an adjunct professor at Boston University School of Medicine. He currently serves as the chief of endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism at the VA Boston Healthcare System, where he created de novo a leading academic division true to its tripartite mission and as the founding director of human nutrition at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Harvard Medical School. Finally, he holds the editor-in-chief position of the journal Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental.

Steven Grinspoon is an American physician who is a Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, Chief of the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) Metabolism Unit, and Director of the Nutrition Obesity Research Center at Harvard. In addition, he is the MGH Endowed Chair in Neuroendocrinology and Metabolism. His work investigates the neuroendocrine regulation of body composition, and physiologic consequences of fat distribution on cardiovascular disease and inflammation. He has investigated the effects of reduced growth hormone on metabolic dysregulation in obesity and was the first to propose the use of a Growth Hormone-releasing Hormone (GHRH) analogue to increase endogenous GH secretion on lipodystrophy and generalized obesity, which led to the FDA approval of Tesamorelin for excess visceral fat accumulation in HIV-infected patients. This work has now been extended to show effects on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). More recently, his research focuses on the inflammatory mechanisms by which ectopic fat and other metabolic perturbations contribute to HIV-Cardiovascular disease (CVD), and in this regard, he led the AHA State of the Science Conference on CVD in HIV. Additionally, he is leading the multicenter REPRIEVE study, the first study of a primary prevention strategy for CVD in people living with HIV. He has also investigated increased Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) activation and immune activation in relationship to visceral fat accumulation, and the mechanisms of subcutaneous adipose dysfunction involving DICER. Grinspoon has served on the Harvard faculty since 1995 and has been selected by the American Society for Clinical Investigation and the Association of American Physicians for his scientific contributions. He received the American Federation of Medical Research Investigator of the Year Award in 2005 and the Edward H. Ahrens Jr. Award for Patient Oriented Research in 2014 as well as the Endocrine Society Laureate Award for Translational Research in 2016. He has published over 330 articles and mentored over 40 trainees in his career. He was elected as a Member of the American Clinical and Climatological Association for his achievements in 2017. His work demonstrating the effects of Tesamorelin to reduce hepatic fat and fibrosis progression in NAFLD, published in Lancet HIV, was a finalist for the Clinical Research Forum’s top 10 Clinical Research Achievement Awards in 2020. In 2015, he became the Principal Investigator of the NIH-funded Nutrition Obesity Research Center at Harvard.









