
Urban forestry is the care and management of single trees and tree populations in urban settings for the purpose of improving the urban environment. Urban forestry involves both planning and management, including the programming of care and maintenance operations of the urban forest. Urban forestry advocates the role of trees as a critical part of the urban infrastructure. Urban foresters plant and maintain trees, support appropriate tree and forest preservation, conduct research and promote the many benefits trees provide. Urban forestry is practiced by municipal and commercial arborists, municipal and utility foresters, environmental policymakers, city planners, consultants, educators, researchers and community activists.

Lorentz National Park is a national park located in Central Papua, Indonesia, in the southwest of western New Guinea. With an area of 25,056 km2 (9,674 mi2), it is the largest national park in Southeast Asia. In 1999 Lorentz was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.

Taï National Park is a national park in Côte d'Ivoire that contains one of the last areas of primary rainforest in West Africa. It was inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1982 due to the diversity of its flora and fauna. Five mammal species of the Taï National Park are on the Red List of Threatened Species: pygmy hippopotamus, olive colobus monkeys, leopards, chimpanzees, and Jentink's duiker.
Royal Botanical Gardens (RBG) is headquartered in Burlington owning extensive environmental protection areas, historic sites and culturally relevant gardens in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the major tourist attractions between Niagara Falls and Toronto, as well as a significant local and regional horticultural, education, conservation, and scientific resource. The mandate is derived by a Provincial Act of 1941 centred on human interaction with the natural world and protection of environmentally significant lands that form the western tip of Lake Ontario. Royal Botanical Gardens spans an area of about 10 km by 4 km, dominated by two coastal wetlands, and glacial-carved landscapes that extend from the lake up to the Niagara Escarpment plateau. The various gardens and natural areas are accessed through nine public entrance locations. It is one of several Prescribed Public Bodies listed under the Ontario Heritage Act.
La Selva Biological Station is a protected area encompassing 1,536 ha of low-land tropical rain forest in northeastern Costa Rica. It is owned and operated by the Organization for Tropical Studies, a consortium of universities and research institutions from the United States, Costa Rica, and Puerto Rico. Recognized internationally as one of the most productive field stations in the world for tropical forest research and peer-reviewed publications, La Selva hosts approximately 300 scientists and 100 university courses every year. The primary goal of La Selva Biological Station is to preserve and protect an intact forest, as well as providing laboratory facilities for tropical research and education. The research potential of the area is not only vital to tropical ecology, but it is also an important location in the effort to study relations between local communities and protected areas. In addition, its high diversity and ease of access to the Puerto Viejo-Horquetas highway makes La Selva an important ecotourism destination and environmental education center for tourists and the local community.

Huascarán National Park is a Peruvian national park that comprises most of the mountain range known as Cordillera Blanca which is part of the central Andes, in the region of Ancash. The park covers an area of 340,000 hectares and is managed by the Peruvian Network of Protected Natural Areas, or SERNANP. It was designated as a World Heritage Site in 1985 by UNESCO, is also a well-known mountaineering spot, and harbors a unique biodiversity with plant species such as the Queen of the Andes, trees of the genera Polylepis and Buddleja, and animals such as spectacled bears, condors, vicunas, and tarucas.

The Korea Forest Service is a central administrative agency under the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFR), responsible for protecting and nurturing forests, increasing forest resources, developing forest products, conducting research on forest management and improvement, and is located in Daejeon Government Complex. In the past, during the national forestation campaign from 1973 to 1986, it was temporarily under the Ministry of Home Affairs, but returned to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in 1987. However, as the agency's work was focused solely on maintaining and managing successful national forestation policies, questions were raised about its necessity for a period of time. Currently, the agency has transformed its identity into one that strives to generate continuous income through forest resources.

Guanacaste Conservation Area is an administrative area which is managed by the Sistema Nacional de Areas de Conservacion (SINAC) of Costa Rica for conservation in the northwestern part of Costa Rica. It contains three national parks, as well as wildlife refuges and other nature reserves. The area contains the Area de Conservación Guanacaste World Heritage Site, which comprises four areas.

Sierra de Guadarrama National Park is a national park in Spain, covering nearly 34,000 hectares, the fifth largest in Spain's national parks system. The Guadarrama mountain range contains some ecologically valuable areas, located in the Community of Madrid and Castile and León. The law that regulates the recently approved national park was published in the BOE in June 26, 2013.

Papua New Guinea together with the West Papua region of Indonesia make up a major tropical wilderness area that still contains 5% of the original and untouched tropical high-biodiversity terrestrial ecosystems. PNG in itself contains over 5% of the world's biodiversity in less than 1% of the world's total land area. The flora of New Guinea is unique because it has two sources of origin; the Gondwana flora from the south and flora with Asian origin from the west. As a result, New Guinea shares major family and genera with Australia and the East Asia, but is rich in local endemic species. The endemicity is a result of mountainous isolation, topographic and soil habitat heterogeneity, high forest disturbance rates and abundant aseasonal rainfall year round. PNG boasts some 15–21,000 higher plants, 3,000 species of orchids, 800 species of coral, 600 species of fish, 250 species of mammals and 760 species of birds and 8 species of tree-kangaroos out of which 84 genera of animals are endemic. Ecosystems range from lowland forests to montane forests, alpine flora down to coastal areas which contains some of the most extensive pristine mangrove areas in the world. Much of this biodiversity has remained intact for thousands of years because the ruggedness of the terrain made the interior lands inaccessible; furthermore low population density and restrictions on the effectiveness of traditional tools, ensured that these biodiversity was never overexploited.

Social forestry is the management and protection of forests and afforestation of barren and deforested lands with the purpose of helping environmental, social and rural development. The term social forestry was first used in 1976 by The National Commission on Agriculture, when the government of India aimed to reduce pressure on forests by planting trees on all unused and fallow lands. It was intended as a democratic approach to forest conservation and usage, maximizing land utilization for multiple purposes.

Celaque National Park is a national park in Lempira Ocotepeque and Copán, western Honduras. It was established on 5 August 1987 and covers an area of 266.31 square kilometres. It includes Honduras’ tallest peak, called Cerro Las Minas or Pico Celaque, which reaches approximately 2,870 metres (9,416 ft) above mean sea level. It has an elevation ranging from 975 to 2,870 metres. Celaque's terrain is very rugged, two-thirds of the area has a slope greater than 60 degrees. The park is classified as a cloud forest with a mean precipitation of 1,600 mm at lower altitudes and a mean of 2,400 mm at higher altitudes. The word celaque is reputed to mean caja de aguas in the local, but now extinct, indigenous Lenca language. Celaque's nine rivers supplies water to 120 villages nearby including the district capital of Gracias. Celaque is high in biodiversity and is home to pumas, ocelots and Bolitoglossa celaque, an endangered plethodontid salamander found only in the mountains of Celaque.

Since declaring independence in 1981, Belize has enacted many environmental protection laws aimed at the preservation of the country's natural and cultural heritage, as well as its wealth of natural resources. These acts have established a number of different types of protected areas, with each category having its own set of regulations dictating public access, resource extraction, land use and ownership.
The Massif de la Hotte is a mountain range in southwestern Haiti, on the Tiburon Peninsula. About 2.5 million years ago, Massif de la Hotte was separated from the Massif de la Selle by a deep, wide sea channel, and formed a separate island. This resulted in a hotbed of endemism in la Hottes bird, plant, and reptile communities. The Massif de la Hotte is subdivided into the Oriental la Hotte in the East, the central la Hotte and the Occidental la Hotte on the Western tip of the Tiburon peninsula. The Occidental la Hotte is relatively remote and is one of the most biologically diverse and significant areas of all of Hispaniola. It also supports some of the last stands of Haiti's dense cloud forest on its peaks.

The Instituto Nacional de Biodiversidad (INBio) is the national institute for biodiversity and conservation in Costa Rica. Created at the end of the 1980s, and despite having national status, it is a privately run institution that works closely with various government agencies, universities, business sector and other public and private entities inside and outside of the country. The goals of the institute are to complete an inventory of the natural heritage of Costa Rica, promote conservation and identify chemical compounds and genetic material present in living organisms that could be used by industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics or others.

Karimunjawa National Park, also Crimon Java National Park, is a national marine park designated in the Karimun Java archipelago, Jepara Regency, Central Java, Indonesia. It lies 80 km north west of Jepara, Central Java in the Java Sea. The national park was formally declared as Marine Protection Area in 2001. Based on popular local myth, this archipelago was discovered by Sunan Nyamplungan, the nephew of Sunan Kudus who is one of the Wali Sanga.

Wakatobi National Park is a marine national park in Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. The name of Wakatobi is a portmanteau of the four main Tukangbesi Islands: Wangi-wangi, Kaledupa, Tomia, and Binongko. Since 2005 the park is listed as a tentative World Heritage Site.
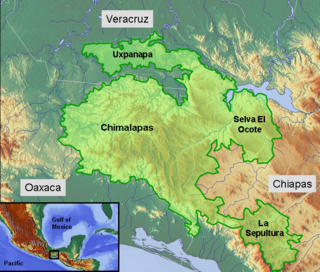
The Selva Zoque, which includes the Chimalapas rain forest, is an area of great ecological importance in Mexico. Most of the forest lies in the state of Oaxaca but parts are in Chiapas and Veracruz. It is the largest tract of tropical rainforest in Mexico, and contains the majority of terrestrial biodiversity in the country. The forest includes the Selva El Ocote, a federally-protected biosphere reserve, but is otherwise not yet protected. Despite the rich ecology of the region, a 2003 study that focused on bird populations stated that "the fauna of the heart of the Chimalapas, including its vast rainforests, have seen little or no study". As it is an impoverished region, efforts to preserve the ecology are often at odds with demands to improve the economy.

The forests of Mexico cover a surface area of about 64 million hectares, or 34.5% of the country. These forests are categorized by the type of tree and biome: tropical forests, temperate forests, cloud forests, riparian forests, deciduous, evergreen, dry, moist, etc.. The agency in charge of Mexico's forests is the Comisión Nacional Forestal. Despite major reforms to the Mexican Constitution in 1992 regarding private land, Mexico would later enact major forest regulation laws in 1998 and 2003. Though no longer required to enforce land regulation in Mexico, Article 27 of the Mexican Constitution also still permits the Mexican Government to enact land regulation.
Rwoho Forest Reserve is a protected area located to the south of Bugamba Central Forest Reserve in Rwampara and Isingiro districts in south western Uganda. The reserve covers extensive high ground and numerous valleys, including the majority of the Kyezo valley's western watershed. Rwoho Forest Reserve has an area of 91 square kilometers and is maintained on behalf of the Government of Uganda by the National Forestry Authority (NFA) under the National Forestry Authority and Tree Planting Act 8/2003.
















