
The Antarctic is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other island territories located on the Antarctic Plate or south of the Antarctic Convergence. The Antarctic region includes the ice shelves, waters, and all the island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence, a zone approximately 32 to 48 km wide varying in latitude seasonally. The region covers some 20 percent of the Southern Hemisphere, of which 5.5 percent is the surface area of the Antarctica continent itself. All of the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude are administered under the Antarctic Treaty System. Biogeographically, the Antarctic realm is one of eight biogeographic realms of Earth's land surface.

Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea. Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,900 species of starfish occur on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from warm, tropical zones to frigid, polar regions. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, at 6,000 m (20,000 ft) below the surface.

The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martin in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of the mainland Antarctica.

The South Orkney Islands are a group of islands in the Southern Ocean, about 604 kilometres (375 mi) north-east of the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and 844 kilometres (524 mi) south-west of South Georgia Island. They have a total area of about 620 square kilometres (240 sq mi). The islands are claimed both by Britain, and by Argentina as part of Argentine Antarctica. Under the 1959 Antarctic Treaty, sovereignty claims are held in abeyance.

McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica. The sound, which extends about 55 kilometres long and wide, connects to the Ross Sea to the north, and to the Ross Ice Shelf cavity to the south via Haskell Strait. The strait is largely covered by the McMurdo Ice Shelf. The Royal Society Range rises from sea level to 4,205 metres on the western shoreline. Ross Island, an historic jumping-off point for polar explorers, designates the eastern boundary. The active volcano Mount Erebus at 3,794 metres dominates Ross Island. Antarctica's's largest scientific base, the United States' McMurdo Station, as well as the New Zealand Scott Base are on the southern shore of the island. Less than 10 percent of McMurdo Sound's shoreline is free of ice. It is the southernmost navigable body of water in the world.

The United States Antarctic Program is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean.

The Scotia Sea is a sea located at the northern edge of the Southern Ocean at its boundary with the South Atlantic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Drake Passage and on the north, east, and south by the Scotia Arc, an undersea ridge and island arc system supporting various islands. The sea sits atop the Scotia Plate. It is named after the expedition ship Scotia. Many icebergs melt there.

The Antarctic tern is a seabird in the family Laridae. It ranges throughout the southern oceans and is found on small islands around Antarctica as well as on the shores of the mainland. Its diet consists primarily of small fish and crustaceans. It is very similar in appearance to the closely related Arctic tern, but it is stockier, and it is in its breeding plumage in the southern summer, when the Arctic tern has shed old feathers to get its non-breeding plumage. The Antarctic tern does not migrate like the Arctic tern does, but it can still be found on a very large range. This tern species is actually more closely related to the South American tern.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost continent. It contains the geographic South Pole and is situated in the Antarctic region of the Southern Hemisphere, almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle, and is surrounded by the Southern Ocean. At 14,200,000 square kilometres, it is the fifth-largest continent and nearly twice the size of Australia. It is by far the least populated continent, with around 5,000 people in the summer and around 1,000 in the winter. About 98% of Antarctica is covered by ice that averages 1.9 km in thickness.
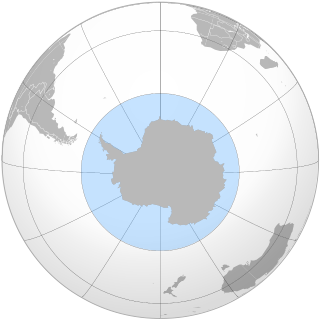
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. As such, it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem.

Dissostichus, the toothfish, is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefish. These fish are found in the Southern Hemisphere. Toothfish are marketed in the United States as Chilean sea bass or less frequently as white cod. "Chilean sea bass" is a marketing name coined in 1977 by Lee Lantz, a fish wholesaler who wanted a more attractive name for selling the Patagonian toothfish to Americans. In 1994, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accepted "Chilean sea bass" as an "alternative market name" for Patagonian toothfish. The toothfish was remarkably successful in the United States, Europe and Asia, and earned the nickname “white gold” within the market. Toothfish are vital to the ecological structure of Southern Ocean ecosystems. For this reason, on 4 September a national day is dedicated to the toothfish in South Georgia.

Acodontaster conspicuus is a species of starfish in the family Odontasteridae. It is found in the Southern Ocean, in the waters off Antarctica and the island groups nearby.
Anasterias rupicola is a species of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is found in shallow waters in the Southern Ocean and sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean.

Labidiaster annulatus, the Antarctic Sun starfish or wolftrap starfish is a species of starfish in the family Heliasteridae. It is found in the cold waters around Antarctica and has a large number of slender, flexible rays.

The wildlife of Antarctica are extremophiles, having to adapt to the dryness, low temperatures, and high exposure common in Antarctica. The extreme weather of the interior contrasts to the relatively mild conditions on the Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands, which have warmer temperatures and more liquid water. Much of the ocean around the mainland is covered by sea ice. The oceans themselves are a more stable environment for life, both in the water column and on the seabed.

Katrin Linse is a German marine biologist, best known for her work on discovering new Antarctic and deep sea species.

Diplasterias brucei is a species of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is found in the Pacific Ocean and Southern Ocean. It is a predator and scavenger and is unusual among starfish in that it broods its young.

Anasterias antarctica, commonly called the Cinderella starfish, is a species of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is found in coastal waters in the Southern Ocean and around Antarctica.

Promachocrinus is a genus of free-swimming, stemless crinoids. It is a monotypic genus, and the only species in the genus is Promachocrinus kerguelensis. This is a coldwater crinoid which is found in the seas around Antarctica and surrounding island groups, including under the sea ice.

Notocrinus virilis is a marine invertebrate, a species of crinoid or feather star in the family Notocrinidae. It is found in deep water in the Southern Ocean around the coasts of Antarctica and adjacent islands. A sea snail sometimes parasitizes it.




















