
The International Labour Organization (ILO) is a United Nations agency whose mandate is to advance social and economic justice by setting international labour standards. Founded in October 1919 under the League of Nations, it is one of the first and oldest specialised agencies of the UN. The ILO has 187 member states: 186 out of 193 UN member states plus the Cook Islands. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, with around 40 field offices around the world, and employs some 3,381 staff across 107 nations, of whom 1,698 work in technical cooperation programmes and projects.

The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is an international human rights treaty which sets out the civil, political, economic, social, health and cultural rights of children. The convention defines a child as any human being under the age of eighteen, unless the age of majority is attained earlier under national legislation.
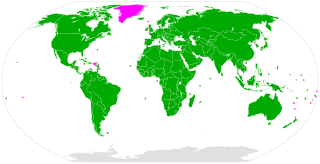
The Convention Concerning the Prohibition and Immediate Action for the Elimination of the Worst Forms of Child Labour, known in short as the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, was adopted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in 1999 as ILO Convention No 182. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions.
The Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children is a protocol to the United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime. It is one of the three Palermo protocols, the others being the Protocol Against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air and the Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms.
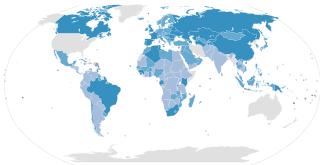
The ILO Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.

The Forced Labour Convention, the full title of which is the Convention Concerning Forced or Compulsory Labour, 1930 (No.29), is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions of the International Labour Organization. Its object and purpose is to suppress the use of forced labour in all its forms irrespective of the nature of the work or the sector of activity in which it may be performed. The Convention defines forced labour as "all work or service which is exacted from any person under the menace of any penalty and for which the said person has not offered himself voluntarily", with few exceptions like compulsory military service.
The Freedom of Association and Protection of the Right to Organise Convention (1948) No 87 is an International Labour Organization Convention, and one of eight conventions that form the core of international labour law, as interpreted by the Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work.
The Convention Concerning Statistics of Wages and Hours of Work, 1938 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Certification of Ships' Cooks Convention, 1946 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Seafarers' Identity Documents Convention, 1958 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

The Occupational Cancer Convention is an International Labour Organization Convention on workplace safety standards against occupational cancer, established in 1974 during the 59th session of the Interlnational Labour Conference. The convention entered into force in 1976 after ratification of Ecuador and Hungary.
Working Environment Convention, 1977 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Collective Bargaining Convention is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 is an International Labour Organization Convention, number 155.
Occupational Health Services Convention, 1985 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

Asbestos Convention, 1986 is an International Labour Organization Convention, adopted at the 72nd session of the International Labour Conference.
Home Work Convention, created in 1996, is an International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention, which came into force in 2000. It offers protection to workers who are employed in their own homes.
International labour law is the body of rules spanning public and private international law which concern the rights and duties of employees, employers, trade unions and governments in regulating Work and the workplace. The International Labour Organization and the World Trade Organization have been the main international bodies involved in reforming labour markets. The International Monetary Fund and the World Bank have indirectly driven changes in labour policy by demanding structural adjustment conditions for receiving loans or grants. Issues regarding Conflict of laws arise, determined by national courts, when people work in more than one country, and supra-national bodies, particularly in the law of the European Union, has a growing body of rules regarding labour rights.
The right to sit refers to laws or policies granting workers the right to be granted suitable seating at the workplace. Jurisdictions that have enshrined "right to sit" laws or policies include the United Kingdom, Jamaica, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Uganda, Lesotho, Malaysia, Brazil, Israel, Ireland, the Indian states of Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, and the British overseas territory of Gibraltar and Montserrat. Almost all states of the United States and Australia, as well as the majority of Canadian provinces passed right to sit legislation for women workers between 1881 and 1917. US states with current right to sit legislation include California, Florida, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, Oregon, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. A right to sit provision is included in the International Labour Organization's Hygiene Convention, 1964; the convention being ratified by 51 countries as of 2014. Local jurisdictions with right to sit laws include Portland, Oregon, St. Louis, Missouri and London's Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. Some jurisdictions, such as Alabama, Arkansas, Connecticut, Idaho, Kentucky, Maine, Michigan, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, Quebec, and Washington, D.C. have revoked their right to sit laws. Many right to sit laws originally contained gendered language specifying women workers only. Some jurisdictions maintain gendered laws, but many jurisdictions have amended their right to sit laws to be gender neutral.






