Related Research Articles
The Convention on the Unification of Certain Points of Substantive Law on Patents for Invention, also called Strasbourg Convention or Strasbourg Patent Convention, is a multilateral treaty signed by Member States of the Council of Europe on November 27, 1963 in Strasbourg, France. It entered into force on August 1, 1980 and led to a significant harmonization of patent laws across European countries.
The International Labour Organization Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention calls for time-bound programmes for the eradication of the worst forms of child labour. Countries ratifying this Convention must take immediate and effective measures to secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour (WFCL) as a matter of urgency.
White Lead (Painting) Convention, 1921 is an International Labour Organization Convention established in 1921 to advance the prohibition of using white lead in paint.
Underground Work (Women) Convention, 1935 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

Indigenous and Tribal Populations Convention, 1957 is an International Labour Organization Convention within the United Nations that was established in 1957. Its primary focus is to recognize and protect the cultural, religious, civil and social rights of indigenous and tribal populations within an independent country, and to provide a standard framework for addressing the economic issues that many of these groups face.
The Indigenous and Tribal Peoples Convention, 1989 is an International Labour Organization Convention, also known as ILO Convention 169, or C169. It is the major binding international convention concerning indigenous peoples and tribal peoples, and a forerunner of the Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples.
Human Resources Development Convention, 1975 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Employment Promotion and Protection against Unemployment Convention, 1988 is an International Labour Organization Convention to promote employment especially vocational guidance, training and rehabilitation, offer the best protection against the adverse effects of involuntary unemployment, but that involuntary unemployment nevertheless exists and that it is therefore important to ensure the social security systems should promote employment assistance and economic support to those who are involuntary unemployed.

The International Convention for the Protection of All Persons from Enforced Disappearance (ICPPED) is an international human rights instrument of the United Nations intended to prevent forced disappearance, which, as defined in international law, is part of crimes against humanity. The text was adopted by the United Nations General Assembly on 20 December 2006 and opened for signature on 6 February 2007. It entered into force on 23 December 2010. As of April 2023, 98 states have signed the convention and 71 have ratified it.
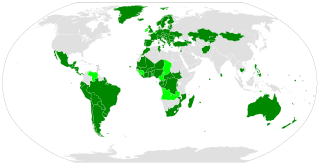
The Optional Protocol to the Convention Against Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman or Degrading Treatment or Punishment is a treaty that supplements to the 1984 United Nations Convention Against Torture. It establishes an international inspection system for places of detention modeled on the system that has existed in Europe since 1987.
The Convention on the Non-Applicability of Statutory Limitations to War Crimes and Crimes Against Humanity was adopted and opened for signature, ratification and accession by United Nations General Assembly resolution 2391 (XXIII) of 26 November 1968. Pursuant to the provisions of its Article VIII, it came into force on 11 November 1970.

The Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is an international human rights treaty of the United Nations intended to protect the rights and dignity of persons with disabilities. Parties to the convention are required to promote, protect, and ensure the full enjoyment of human rights by persons with disabilities and ensure that persons with disabilities enjoy full equality under the law. The Convention serves as a major catalyst in the global disability rights movement enabling a shift from viewing persons with disabilities as objects of charity, medical treatment and social protection towards viewing them as full and equal members of society, with human rights. The convention was the first U.N. human rights treaty of the twenty-first century.

Vocational rehabilitation, also abbreviated VR or voc rehab, is a process which enables persons with functional, psychological, developmental, cognitive, and emotional disabilities, impairments or health disabilities to overcome barriers to accessing, maintaining, or returning to employment or other useful occupations.

The Council of Europe Convention on Preventing and Combating Violence Against Women and Domestic Violence, better known as the Istanbul Convention, is a human rights treaty of the Council of Europe opposing violence against women and domestic violence which was opened for signature on 11 May 2011, in Istanbul, Turkey. The convention aims at prevention of violence, victim protection and to end the impunity of perpetrators. As of March 2019, it has been signed by 45 countries and the European Union. On 12 March 2012, Turkey became the first country to ratify the convention, followed by 37 other countries from 2013 to 2022. The Convention came into force on 1 August 2014. In 2021, Turkey became the first and only country to withdraw from the convention, after denouncing it on 20 March 2021. The convention ceased to be effective in Turkey on 1 July 2021, following its denunciation. On 1 June 2023 the Council of the European Union approved the EU’s accession to the Istanbul Convention.

The Hague Convention on the International Recovery of Child Support and Other Forms of Family Maintenance, also referred to as the Hague Maintenance Convention or the Hague Child Support Convention is a multilateral treaty governing the enforcement of judicial decisions regarding child support extraterritorially. It is one of a number of conventions in the area of private international law of the Hague Conference on Private International Law in 2007. The convention is open to all states as well as to Regional Economic Integration Organizations as long as they are composed of sovereign states only and have sovereignty in the content of the convention. The convention entered into force on 1 January 2013 between Norway and Albania, with Bosnia-Herzegovina (2013), Ukraine (2013), the European Union, Montenegro (2017), United States (2017), Turkey (2017), Kazakhstan (2017), Brazil (2017), Honduras (2017), Belarus (2018), Guyana (2020), Nicaragua (2020), United Kingdom (2021), Serbia (2021), New Zealand (2021), Ecuador (2022), Botswana (2022) and Azerbaijan (2023) following suit. Because the EU acceptance of the convention applies in 27 EU countries, the convention applies in 45 countries worldwide.
The Convention on the Transfer of Sentenced Persons is an international treaty regulating the extradition and social rehabilitation of imprisoned persons. The Convention was concluded in Strasbourg on 21 March 1983 and entered into force on 1 July 1985. It has been ratified by 66 countries, including every country of the Council of Europe except Monaco. It has also been ratified by 19 states outside the Council of Europe, including Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, the United States and India. The latest accession to the Convention was India in January 2018.
The Council of Europe Convention on the Protection of Children Against Sexual Exploitation and Sexual Abuse, also known as the Lanzarote Convention, is a Council of Europe multilateral treaty whereby states agree to criminalise certain forms of sexual abuse against children. It is the first international treaty that addresses child sexual abuse that occurs within the home or family.

The Hague Judgments Convention, formally the Convention of 2 July 2019 on the Recognition and Enforcement of Foreign Judgments in Civil or Commercial Matters is an international treaty concluded within the Hague Conference on Private International Law. It was concluded in 2019, and will enter into force on 1 September 2023 for the European Union and Ukraine. The convention governs the recognition of judgements in civil and commercial matters.
Estimates of the prevalence of disability in Egypt have ranged from 1.8% to 11%. Egypt ratified the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities on 10 April 2008. The Egyptian constitution of 2014 guarantees a range of rights for people with disabilities, and Egypt passed legislation entitled the Law on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities in February 2018.
References
- ↑ Referred to by the United Nations as "The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" due to the Macedonia naming dispute.