
Sir Samuel White Baker was an English explorer, officer, naturalist, big game hunter, engineer, writer and abolitionist. He also held the titles of Pasha and Major-General in the Ottoman Empire and Egypt. He served as the Governor-General of the Equatorial Nile Basin between April 1869 and August 1873, which he established as the Province of Equatoria. He is mostly remembered as the first European to visit Lake Albert, as an explorer of the Nile and interior of central Africa, and for his exploits as a big game hunter in Asia, Africa, Europe and North America. Baker wrote a considerable number of books and published articles. He was a friend of King Edward VII, who as Prince of Wales, visited Baker with Queen Alexandra in Egypt. Other friendships were with explorers Henry Morton Stanley, Roderick Murchison, John H. Speke and James A. Grant, with the ruler of Egypt Pasha Ismail The Magnificent, Major-General Charles George Gordon and Maharaja Duleep Singh.

Mehmed Emin Pasha was an Ottoman physician of German Jewish origin, naturalist, and governor of the Egyptian province of Equatoria on the upper Nile. The Ottoman Empire conferred the title "Pasha" on him in 1886, and thereafter he was referred to as "Emin Pasha".

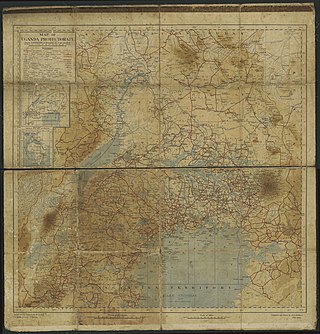
Equatoria is the southernmost region of South Sudan, along the upper reaches of the White Nile and the border between South Sudan and Uganda. Juba, the national capital and the largest city in South Sudan, is located in Equatoria. Originally a province of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, it also contained most of northern parts of present-day Uganda, including Lake Albert and West Nile. It was an idealistic effort to create a model state in the interior of Africa that never consisted of more than a handful of adventurers and soldiers in isolated outposts.

Gondokoro island is located in Central Equatoria. The island was a trading-station on the east bank of the White Nile in Southern Sudan, 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) south of Khartoum. Its importance lay in the fact that it was within a few kilometres of the limit of navigability of the Nile from Khartoum upstream. From this point the journey south to Uganda was continued overland.

The Emin Pasha Relief Expedition of 1887 to 1889 was one of the last major European expeditions into the interior of Africa in the nineteenth century. Led by Henry Morton Stanley, its goal was ostensibly the relief of Emin Pasha, the besieged Egyptian governor of Equatoria, who was threatened by Mahdist forces.

The Lado Enclave was a leased territory administered by the Congo Free State and later by the Belgian Congo that existed from 1894 until 1910, situated on the west bank of the Upper Nile in what is now South Sudan and northwest Uganda. Its capital was the town of Lado.

Dufile was originally a fort built by Emin Pasha, the Governor of Equatoria, in 1879; it is located on the Albert Nile just inside Uganda, close to a site chosen in 1874 by then-Colonel Charles George Gordon to assemble steamers that were carried there overland. Abandoned by Emin's people in January 1889, Dufile being within the Lado Enclave was reoccupied and reconstructed by Belgian forces from 1902 to 1907.

Juba is the capital and largest city of South Sudan. The city is situated on the White Nile and also serves as the capital of the Central Equatoria State. It is the most recently declared national capital and had a population of 525,953 in 2017. It has an area of 52 km2 (20 sq mi), with the metropolitan area covering 336 km2 (130 sq mi).
Wadelai was a boma at a narrow point on the Albert Nile in what is now northern Uganda. There were several shortlived colonial stations there, the first being the final chief station of Emin Pasha when Governor of Equatoria. Wadelai gives its name to a current Ugandan sub-county.

Belgium controlled several territories and concessions during the colonial era, principally the Belgian Congo from 1908 to 1960, Ruanda-Urundi from 1922 to 1962, and Lado Enclave from 1884 to 1910. It also had small concessions in Guatemala (1843–1854) and Belgian concession of Tianjin in China (1902–1931) and was a co-administrator of the Tangier International Zone in Morocco.

Richard Buchta(Austrian German pronunciation: [ˈrɪçart ˈbuxtɐ], 19 January 1845 – 29 July 1894) was an Austrian explorer in East Africa, travel writer, painter and photographer. Born in Radlow, Galicia, Austrian Empire, he traveled widely, first to Germany, France, the Balkans, and Turkey, Egypt and the Sudan. Upon his return to Germany and later to Austria, he published several books on the geography, ethnic groups and political conditions of the historic Sudan in the 1870s and 1880s. His historical photographs, taken mainly in southern Sudan, are regarded as the earliest photographs of ethnic people living along the White Nile and beyond.

Southern Sudan was an autonomous region consisting of the ten southern states of Sudan between its formation in July 2005 and independence as the Republic of South Sudan in July 2011. The autonomous government was initially established in Rumbek and later moved to Juba. It was bordered by Ethiopia to the east; Kenya, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south; and the Central African Republic to the west. To the north lies the predominantly Arab and Muslim region directly under the control of the central government. The region's autonomous status was a condition of a peace agreement between the Sudan People's Liberation Army/Movement (SPLA/M) and the Government of Sudan represented by the National Congress Party ending the Second Sudanese Civil War. The conflict was Africa's longest running civil war.
The history of South Sudan comprises the history of the territory of present-day South Sudan and the peoples inhabiting the region.

Mongalla or Mangalla is a Payam in Juba County, Central Equatoria State in South Sudan, on the east side of the Bahr al Jebel or White Nile river. It lies about 75 km by road northeast of Juba. The towns of Terekeka and Bor lie downstream, north of Mongalla.

Chauncey Hugh Stigand (1877–1919) was a British army officer, colonial administrator, and big game hunter. He was killed in action while attempting to suppress a rebellion of Aliab Dinka.
Kiro was a colonial post in what is now the Central Equatoria State of South Sudan on the west side of the Bahr al Jebel or White Nile river. It was in part of the Lado enclave.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Khartoum, Sudan.

The Turco-Egyptian conquest of Sudan was a major military and technical feat. Fewer than 10,000 men set off from Egypt, but, with some local assistance, they were able to penetrate 1,500 km up the Nile River to the frontiers of Ethiopia, giving Egypt an empire as large as Western Europe.
Mount Lado or Jebel Lado is an isolated hillock in Central Equatoria, South Sudan, about 13 km northwest of the White Nile and 28 km due north of the national capital Juba. The mountain was also called Mount Nyerkenyi.

Equatoria was a Mudiriyah of the Khedivate of Egypt in the late 19th century. It was located in modern-day South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Uganda. Equatoria, as an Egyptian province, was created on the 26th of May, 1871, following the formal annexation of Gondokoro by Egypt, which was organized by Samuel Baker. Throughout its early existence, the provincial administration in Gondokoro was plagued by instability, as conflict with slave traders and the native Bari tribes meant that the governor only controlled the areas around the capital and the forts. However, during its later existence, Equatoria experienced a “golden period”, where the province was self-sufficient, prosperous, and the Egyptians under Emin Pasha maintained positive relations with both the interlacustrine kingdoms, and the surrounding tribes. Ultimately however, the outbreak of the Mahdist War in the Sudan which severed communications with Khartoum and Cairo, led to the fall of Equatoria, as Mahdist offensives led by Karam Allāh Muḥammad Kurkusāwī surrounded the Egyptian forts, which forced Emin to withdraw south to Wadelai, until he finally abandoned the province in early 1889, following an expedition sent to relieve his forces.



















