The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America or the Laurentian Great Lakes, is a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. They are Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario and are in general on or near the Canada–United States border. Hydrologically, there are four lakes, because lakes Michigan and Huron join at the Straits of Mackinac. The Great Lakes Waterway enables travel by water among the lakes.

Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is the second-largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third-largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron. To the east, its basin is conjoined with that of Lake Huron through the narrow Straits of Mackinac, giving it the same surface elevation as its easterly counterpart; the two are technically a single lake.

The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the Straits of Mackinac. It is surrounded by water on all sides except its southern border, which it shares with Indiana and Ohio. Although the Upper Peninsula is commonly referred to as "the U.P.", it is uncommon for the Lower Peninsula to be called "the L.P."
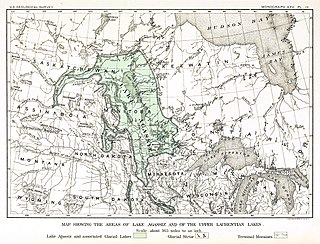
Lake Agassiz was a large glacial lake in central North America. Fed by glacial meltwater at the end of the last glacial period, its area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined.

Lake Michigan–Huron is the body of water consisting of Lake Michigan and Lake Huron, which are joined through the 5-mile-wide (8.0 km), 20-fathom-deep, open-water Straits of Mackinac. Huron and Michigan are hydrologically a single lake because the flow of water through the straits keeps their water levels in overall equilibrium. Although the flow is generally eastward, the water moves in either direction depending on local conditions. Combined, Lake Michigan–Huron is the largest freshwater lake by area in the world. However, Lake Superior is larger than either individually, and so is counted as the largest lake when Lake Huron and Lake Michigan are considered separately.

Fort Michilimackinac State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is located in Mackinaw City along the Straits of Mackinac. The park contains Fort Michilimackinac, which itself is dedicated a National Historic Landmark and Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse as well as the Old Mackinac Point Lighthouse Signal Tower which contains a foghorn.

Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing.
The Chicago Portage was an ancient portage that connected the Great Lakes waterway system with the Mississippi River waterway system. Connecting these two great water trails meant easy access from the mouth of the St Lawrence River on the Atlantic Ocean to the Rocky Mountains, and the Gulf of Mexico. The approximately six-mile link had been used by Native Americans for thousands of years during the Pre-Columbian era for travel and trade.

Lake Duluth was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior drainage basin as the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated. The oldest existing shorelines were formed after retreat from the Greatlakean advance, sometime around 11,000 years B.P. Lake Duluth formed at the western end of the Lake Superior basin. Lake Duluth overflowed south through outlets in Minnesota and Wisconsin at an elevation of around 331 m above sea level.
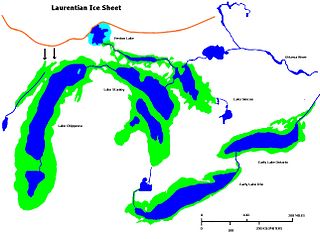
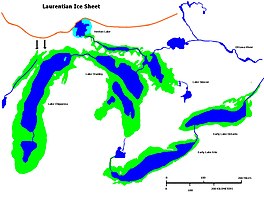
Early Lake Erie was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The early Erie fed waters to Glacial Lake Iroquois.

Lake Chicago was a prehistoric proglacial lake that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan, one of North America's five Great Lakes. Fed by retreating glaciers, it drained south through the Chicago Outlet River.

Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 Years Before Present (YBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.
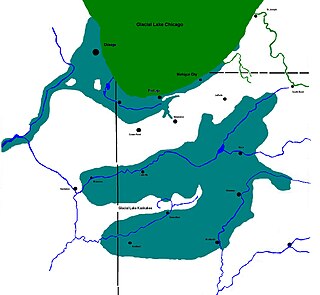
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.
Nipissing Great Lakes was a prehistoric proglacial lake. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Georgian Bay and Lake Michigan. It formed about 7,500 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the Labradorian Glacier. This body of water drained eastward from Georgian Bay to the Ottawa valley. This was a period of isostatic rebound raising the outlet over time, until it opened the outlet through the St. Clair valley.

Lake Warren was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Erie basin around 12,700 years before present (YBP) when Lake Whittlesey dropped in elevation. Lake Warren is divided into three stages: Warren I 690 feet (210 m), Warren II 680 feet (210 m), and Warren III 675 feet (206 m), each defined by the relative elevation above sea level.
Lake Wayne formed in the Lake Erie and Lake St. Clair basins around 12,500 years before present (YBP) when Lake Arkona dropped in elevation. About 20 feet (6.1 m) below the Lake Warren beaches it was early described as a lower Lake Warren level. Based on work in Wayne County, near the village of Wayne evidence was found that Lake Wayne succeeded Lake Whittlesey and preceded Lake Warren. From the Saginaw Basin the lake did not discharge water through Grand River but eastward along the edge of the ice sheet to Syracuse, New York, thence into the Mohawk valley. This shift in outlets warranted a separate from Lake Warren. The Wayne beach lies but a short distance inside the limits of the Warren beach. Its character is not greatly different when taken throughout its length in Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania and New York. At the type locality in Wayne County, Michigan, it is a sandy ridge, but farther north, and to the east through Ohio it is gravel. The results of the isostatic rebound area similar to the Lake Warren beaches.
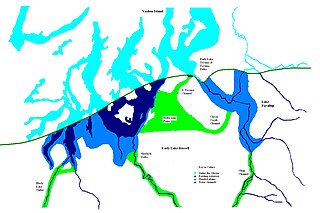
During the Vashon Glaciation a series of lakes formed along the southern margin of the Cordilleran Ice Cap. In the Puget Sound depression, a series of lakes developed, of which Lake Russell was the largest and the longest lasting. Early Lake Russell’s surface was at 160 ft (49 m) above sea level, draining across the divide at Shelton, Washington into early Glacial Lake Russell. When the ice margin receded northward, the lake expanded. When it reached the Clifton channel outlet, the water levels dropped to 120 ft (37 m) above sea level. The new longer and lower level lake is referred to as Lake Hood. The glacier continued to retreat until the northern outlet of the Hood Canal was reached as the water level equalized with Glacial Lake Russell becoming part of that body of water.

The North Bay Outlet was an outlet of a proglacial lake that preceded present day Lake Huron, where it discharged its waters near present day North Bay, rather than a more southerly route, as the Laurentian glaciation receded. Water drained down this route from approximately 10000 to 4500 bpe.

Lake Stanley, also called the Stanley unconformity, is a postglacial freshwater lake that occupied part of what is now the basin of Lake Huron during a hydrologically significant period from 10,000 years Before Present (B.P.). The lake’s surface level was approximately 70 meters below the current lake’s water surface.