
Lidar is a method for determining ranges by targeting an object with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar can also be used to make digital 3-D representations of areas on the earth's surface and ocean bottom, due to differences in laser return times, and by varying laser wavelengths. It has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications.
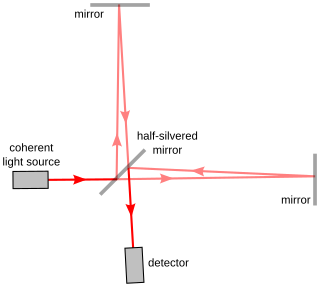
Interferometry is a technique which uses the interference of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall will measure zero.

Time of flight (ToF) is the measurement of the time taken by an object, particle or wave to travel a distance through a medium. This information can then be used to measure velocity or path length, or as a way to learn about the particle or medium's properties. The traveling object may be detected directly or indirectly.

Laser Doppler velocimetry, also known as laser Doppler anemometry, is the technique of using the Doppler shift in a laser beam to measure the velocity in transparent or semi-transparent fluid flows or the linear or vibratory motion of opaque, reflecting surfaces. The measurement with laser Doppler anemometry is absolute and linear with velocity and requires no pre-calibration.

Satellite geodesy is geodesy by means of artificial satellites—the measurement of the form and dimensions of Earth, the location of objects on its surface and the figure of the Earth's gravity field by means of artificial satellite techniques. It belongs to the broader field of space geodesy. Traditional astronomical geodesy is not commonly considered a part of satellite geodesy, although there is considerable overlap between the techniques.
Distributed temperature sensing systems (DTS) are optoelectronic devices which measure temperatures by means of optical fibres functioning as linear sensors. Temperatures are recorded along the optical sensor cable, thus not at points, but as a continuous profile. A high accuracy of temperature determination is achieved over great distances. Typically the DTS systems can locate the temperature to a spatial resolution of 1 m with accuracy to within ±1°C at a resolution of 0.01°C. Measurement distances of greater than 30 km can be monitored and some specialised systems can provide even tighter spatial resolutions.

Modal analysis is the study of the dynamic properties of systems in the frequency domain. Examples would include measuring the vibration of a car's body when it is attached to a shaker, or the noise pattern in a room when excited by a loudspeaker.
Noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), also known as noise and vibration (N&V), is the study and modification of the noise and vibration characteristics of vehicles, particularly cars and trucks. While noise and vibration can be readily measured, harshness is a subjective quality, and is measured either via jury evaluations, or with analytical tools that can provide results reflecting human subjective impressions. The latter tools belong to the field psychoacoustics.
A laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) is a scientific instrument that is used to make non-contact vibration measurements of a surface. The laser beam from the LDV is directed at the surface of interest, and the vibration amplitude and frequency are extracted from the Doppler shift of the reflected laser beam frequency due to the motion of the surface. The output of an LDV is generally a continuous analog voltage that is directly proportional to the target velocity component along the direction of the laser beam.
The photoacoustic Doppler effect, as its name implies, is one specific kind of Doppler effect, which occurs when an intensely modulated light wave induces a photoacoustic wave on moving particles with a specific frequency. The observed frequency shift is a good indicator of the velocity of the illuminated moving particles. A potential biomedical application is measuring blood flow.

A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments.

Continuous-scan laser Doppler vibrometry (CSLDV) is a method of using a laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) in which the laser beam is swept across the surface of a test subject to capture the motion of a surface at many points simultaneously. This is different from scanning laser vibrometry (SLDV) in which the laser beam is kept at a fixed point during each measurement and quickly moved to a new position before acquiring the next measurement.
Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is one of the major causes of secondary brain ischemia that accompanies a variety of pathological conditions, most notably traumatic brain injury (TBI), strokes, and intracranial hemorrhages. It can cause complications such as vision impairment due to intracranial pressure (VIIP), permanent neurological problems, reversible neurological problems, seizures, stroke, and death. However, aside from a few Level I trauma centers, ICP monitoring is rarely a part of the clinical management of patients with these conditions. The infrequency of ICP can be attributed to the invasive nature of the standard monitoring methods. Additional risks presented to patients can include high costs associated with an ICP sensor's implantation procedure, and the limited access to trained personnel, e.g. a neurosurgeon. Alternative, non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure, non-invasive methods for estimating ICP have, as a result, been sought.
A laser surface velocimeter (LSV) is a non-contact optical speed sensor measuring velocity and length on moving surfaces. Laser surface velocimeters use the laser Doppler principle to evaluate the laser light scattered back from a moving object. They are widely used for process and quality control in industrial production processes.

Atomic force acoustic microscopy (AFAM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM). It is a combination of acoustics and atomic force microscopy. The principal difference between AFAM and other forms of SPM is the addition of a transducer at the bottom of the sample which induces longitudinal out-of-plane vibrations in the specimen. These vibrations are sensed by a cantilever and tip called a probe. The figure shown here is the clear schematic of AFAM principle here B is the magnified version of the tip and sample placed on the transducer and tip having some optical coating generally gold coating to reflect the laser light on to the photodiode.

As described here, white light interferometry is a non-contact optical method for surface height measurement on 3-D structures with surface profiles varying between tens of nanometers and a few centimeters. It is often used as an alternative name for coherence scanning interferometry in the context of areal surface topography instrumentation that relies on spectrally-broadband, visible-wavelength light.
Sensors for arc welding are devices which – as a part of a fully mechanised welding equipment – are capable to acquire information about position and, if possible, about the geometry of the intended weld at the workpiece and to provide respective data in a suitable form for the control of the weld torch position and, if possible, for the arc welding process parameters.

A high performance positioning system (HPPS) is a type of positioning system consisting of a piece of electromechanics equipment that is capable of moving an object in a three-dimensional space within a work envelope. Positioning could be done point to point or along a desired path of motion. Position is typically defined in six degrees of freedom, including linear, in an x,y,z cartesian coordinate system, and angular orientation of yaw, pitch, roll. HPPS are used in many manufacturing processes to move an object smoothly and accurately in six degrees of freedom, along a desired path, at a desired orientation, with high acceleration, high deceleration, high velocity and low settling time. It is designed to quickly stop its motion and accurately place the moving object at its desired final position and orientation with minimal jittering.












