
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the chest, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the chest cavity. They serve to protect the lungs, heart, and other internal organs of the thorax. In some animals, especially snakes, ribs may provide support and protection for the entire body.

In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck.

The rib cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrate animals that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protects vital organs such as the heart, lungs and great vessels. The circumferential enclosure formed by left and right rib cages, together known as the thoracic cage, is a semi-rigid bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdles to form the core part of the axial skeleton.

The sacrum, in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1–S5) between ages 18 and 30.

The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm, is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle.

The multifidusmuscle consists of a number of fleshy and tendinous fasciculi, which fill up the groove on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, from the sacrum to the axis. While very thin, the multifidus muscle plays an important role in stabilizing the joints within the spine. The multifidus is one of the transversospinales.

The quadratus lumborum muscle, informally called the QL, is a paired muscle of the left and right posterior abdominal wall. It is the deepest abdominal muscle, and commonly referred to as a back muscle. Each is irregular and quadrilateral in shape.

The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.
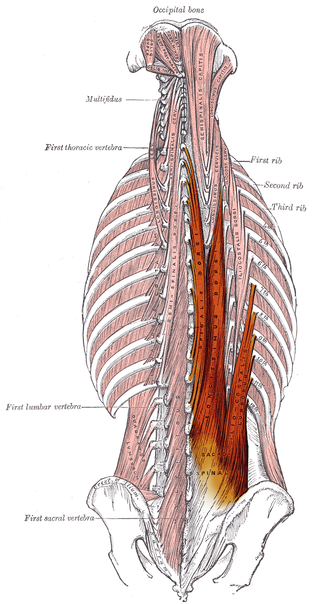
The erector spinae or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes to maintain stable posture standing or sitting.

The thoracolumbar fascia is a complex, multilayer arrangement of fascial and aponeurotic layers forming a separation between the paraspinal muscles on one hand, and the muscles of the posterior abdominal wall on the other. It spans the length of the back, extending between the neck superiorly and the sacrum inferiorly. It entails the fasciae and aponeuroses of the latissimus dorsi muscle, serratus posterior inferior muscle, abdominal internal oblique muscle, and transverse abdominal muscle.

The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals.
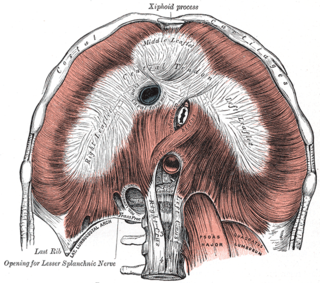
The medial arcuate ligament is a tendinous fascia that arches over the psoas major muscle as it passes posterior the diaphragm.

The iliolumbar ligament is a strong ligament which attaches medially to the transverse process of the 5th lumbar vertebra, and laterally to back of the inner lip of the iliac crest.

The lumbar triangle can refer to either the inferior lumbar (Petit) triangle, which lies superficially, or the superior lumbar (Grynfeltt) triangle, which is deep and superior to the inferior triangle. Of the two, the superior triangle is the more consistently found in cadavers and is more commonly the site of herniation; however, the inferior lumbar triangle is often simply called the lumbar triangle, perhaps owing to its more superficial location and ease in demonstration.

The crus of diaphragm, refers to one of two tendinous structures that extends below the diaphragm to the vertebral column. There is a right crus and a left crus, which together form a tether for muscular contraction. They take their name from their leg-shaped appearance – crus meaning leg in Latin.

The median arcuate ligament is a ligament under the diaphragm that connects the right and left crura of diaphragm.
The lumbar fascia is the lumbar portion of the thoracolumbar fascia. It consists of three fascial layers - posterior, middle, and anterior - that enclose two muscular compartments. The anterior and middle layers occur only in the lumbar region, whereas the posterior layer extends superiorly to the inferior part of the neck, and the inferiorly to the dorsal surface of the sacrum. The quadratus lumborum is contained in the anterior muscular compartment, and the erector spinae in the posterior compartment. Psoas major lies anterior to the anterior layer. Various superficial muscles of the posterior thorax and abdomen arise from the posterior layer - namely the latissimus dorsi, and serratus posterior inferior.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:

The pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs, together with its embedded skeleton.

The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae, each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank, and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa.
















