
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear in human beings may occur in response to a certain stimulus occurring in the present, or in anticipation or expectation of a future threat perceived as a risk to oneself. The fear response arises from the perception of danger leading to confrontation with or escape from/avoiding the threat, which in extreme cases of fear can be a freeze response or paralysis.

A pheromone is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to impact the behavior of the receiving individuals. There are alarm pheromones, food trail pheromones, sex pheromones, and many others that affect behavior or physiology. Pheromones are used by many organisms, from basic unicellular prokaryotes to complex multicellular eukaryotes. Their use among insects has been particularly well documented. In addition, some vertebrates, plants and ciliates communicate by using pheromones. The ecological functions and evolution of pheromones are a major topic of research in the field of chemical ecology.

The vomeronasal organ (VNO), or Jacobson's organ, is the paired auxiliary olfactory (smell) sense organ located in the soft tissue of the nasal septum, in the nasal cavity just above the roof of the mouth. The name is derived from the fact that it lies adjacent to the unpaired vomer bone in the nasal septum. It is present and functional in all snakes and lizards, and in many mammals, including cats, dogs, cattle, pigs, and some primates. Some humans may have physical remnants of a VNO, but it is vestigial and non-functional.

Lavender oil is an essential oil obtained by distillation from the flower spikes of certain species of lavender. There are over 400 types of lavender species worldwide with different scents and qualities. Two forms are distinguished, lavender flower oil, a colorless oil, insoluble in water, having a density of 0.885 g/mL; and lavender spike oil, a distillate from the herb Lavandula latifolia, having density 0.905 g/mL. Like all essential oils, it is not a pure compound; it is a complex mixture of phytochemicals, including linalool and linalyl acetate.

Androsterone, or 3α-hydroxy-5α-androstan-17-one, is an endogenous steroid hormone, neurosteroid, and putative pheromone. It is a weak androgen with a potency that is approximately 1/7 that of testosterone. Androsterone is a metabolite of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In addition, it can be converted back into DHT via 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, bypassing conventional intermediates such as androstanedione and testosterone, and as such, can be considered to be a metabolic intermediate in its own right.
Skatole or 3-methylindole is an organic compound belonging to the indole family. It occurs naturally in the feces of mammals and birds and is the primary contributor to fecal odor. In low concentrations, it has a flowery smell and is found in several flowers and essential oils, including those of orange blossoms, jasmine, and Ziziphus mauritiana.
Body odor is present in all animals, including humans, and its intensity can be influenced by many factors. Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various diseases and physiological conditions. Though body odor has played an important role in early humankind, it is generally considered to be an unpleasant odor amongst many human cultures.

Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer, but often associatively called "minty", as it is an ingredient in mint candies. It is produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. It is also produced synthetically, used as a fragrance and as a flavoring agent.

In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality. The terms are derived from Ancient Greek χείρ (cheir), meaning "hand"; which is the canonical example of an object with this property.
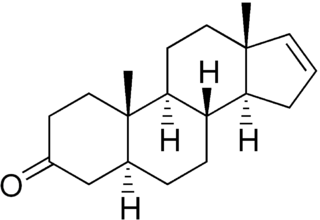
Androstenone (5α-androst-16-en-3-one) is a steroidal pheromone. It is found in boar's saliva, celery cytoplasm, and truffle fungus. Androstenone was the first mammalian pheromone to be identified. It is found in high concentrations in the saliva of male pigs, and, when inhaled by a female pig that is in heat, results in the female assuming the mating stance. Androstenone is the active ingredient in 'Boarmate', a commercial product made by DuPont sold to pig farmers to test sows for timing of artificial insemination.

Linalool refers to two enantiomers of a naturally occurring terpene alcohol found in many flowers and spice plants. Linalool has multiple commercial applications, the majority of which are based on its pleasant scent. A colorless oil, linalool is classified as an acyclic monoterpenoid. In plants, it is a metabolite, a volatile oil component, an antimicrobial agent, and an aroma compound. Linalool has uses in manufacturing of soaps, fragrances, food additives as flavors, household products, and insecticides.

Citral is an acyclic monoterpene aldehyde, and being a monoterpene, it is made of two isoprene units. Citral is a collective term which covers two geometric isomers that have their own separate names; the E-isomer is named Geranial (trans-Citral) or Citral A. The Z-isomer is named Neral (cis-Citral) or Citral B. These enantiomers occur as a mixture, not necessarily racemic; e.g. in essential oil of Australian ginger, the Neral to Geranial ratio is 0.61.

Limonene is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the oil of citrus fruit peels. The D-isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, is a flavoring agent in food manufacturing. It is also used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewables-based solvent in cleaning products. The less common L-isomer has a piny, turpentine-like odor, and is found in the edible parts of such plants as caraway, dill, and bergamot orange plants.

The cabbage looper is a medium-sized moth in the family Noctuidae, a family commonly referred to as owlet moths. Its common name comes from its preferred host plants and distinctive crawling behavior. Cruciferous vegetables, such as cabbage, bok choy, and broccoli, are its main host plant; hence, the reference to cabbage in its common name. The larva is called a looper because it arches its back into a loop when it crawls.

Eucalyptol is a monoterpenoid. A colorless liquid, it is a bicyclic ether. Eucalyptol has a fresh mint-like smell and a spicy, cooling taste. It is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents. Eucalyptol makes up 90% of eucalyptus oil. Eucalyptol forms crystalline adducts with hydrohalic acids, o-cresol, resorcinol, and phosphoric acid. Formation of these adducts is useful for purification.

Androstenol, also known as 5α-androst-16-en-3α-ol, is a steroidal pheromone and neurosteroid in humans and other mammals, notably pigs. It possesses a characteristic musk-like odor.

An odor or odour is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive by their sense of smell. An odor is also called a "smell" or a "scent", which can refer to either a pleasant or an unpleasant odor.
cis-7,8-Epoxy-2-methyloctadecane (also known as disparlure) is the chemical compound with formula C19H38O. It is a sex pheromone found in moths, such as the Gypsy moth, and used to attract a mate. It is also a harmful pesticide for many tree species.
The lateral horn is one of the two areas of the insect brain where projection neurons of the antennal lobe send their axons. The other area is the mushroom body. Several morphological classes of neurons in the lateral horn receive olfactory information through the projection neurons.
Verbenol (2-pine-4-ol) is a group of stereoisomeric bicyclic monoterpene alcohols. These compounds have been found to be active components of insect pheromones and essential oils.














