
Zhukovskiy is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon. It forms a pair with Lebedinskiy, which is attached to the eastern rim. There are no other named craters of note in the immediate vicinity, although the immense walled plain Korolev lies farther to the southeast.

Oersted is a lunar impact crater that has been flooded by lava, leaving only a crescent-shaped rim with a gap to the southwest. The rim climbs to a maximum height of 1.7 km. This feature lies to the southeast of the crater Atlas, and southwest of Chevallier. To the south-southwest is Cepheus.

Abul Wafa is an impact crater located near the lunar equator on the far side of the Moon, named after the Persian mathematician and astronomer Abu al-Wafa' Buzjani. To the east are the crater pair Ctesibius and Heron. In the northeast lies the larger crater King, and to the southwest is Vesalius.
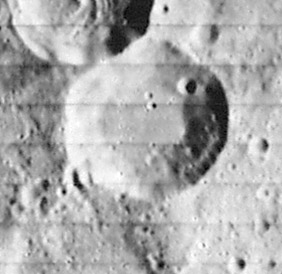
Azophi is a lunar impact crater that lies in the rugged south-central highlands of the Moon. The crater is named after the 10th-century Persian astronomer Abd Al-Rahman Al Sufi, also known by his western name, Azophi. The northwest rim is attached to the slightly smaller crater Abenezra, to the east-southeast is the large and irregular Sacrobosco, and to the west-southwest is Playfair.

Babbage is an ancient lunar impact crater that is located near the northwest limb of the Moon, named after Charles Babbage. It is attached to the southeastern rim of the prominent crater Pythagoras. The crater remnant named South intrudes into the southeastern floor of Babbage.

Blanchinus is a lunar impact crater that is situated in the rugged south-central highlands of the Moon. The crater is named after Italian astronomer Giovanni Bianchini whose Latinized name is Blanchinus. Adjacent to the south of Blanchinus is the crater Werner, and La Caille is attached to the northwest rim. West of the crater is the prominent formation Purbach.

Barringer is a lunar impact crater that is located on the southern hemisphere on the Far side of the Moon, named after geologist Daniel Barringer. It is attached to the north-northeastern rim of the walled basin named Apollo, and lies to the southeast of Plummer. South of Barringer, on the floor of the Apollo basin, is the crater Scobee.

Boussingault is a large lunar impact crater that lies near the rugged southeast limb of the Moon. Because of its location, Boussingault appears highly oblong in shape due to foreshortening. To the southwest is the crater Boguslawsky, and almost attached to the northeast rim is Helmholtz. East-southeast of Boussingault lies the crater Neumayer.

Miller is a lunar impact crater that lies amidst the rugged terrain in the southern part of the Moon. It is attached to the northern rim of the smaller crater Nasireddin, and the outer rampart of the latter reaches almost to the central peak formation at the midpoint of Miller's interior floor. Together with Huggins to the southwest and Orontius to the south-southwest, this foursome forms a chain of craters forming an arc that curves towards the north. The northwest rim of Miller in turn is attached to the satellite crater Miller C, forming the end of the arc. To the southeast lies Stöfler. The crater is named after British chemist William Allen Miller.

Chaffee is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies within the huge walled plain Apollo, and is one of several craters in that formation named for astronauts and people associated with the Apollo program. This basin is a double-ringed formation, and the crater Chaffee is situated across the southwest part of the inner ring. The ridge from this ring extends northward from the northern rim of Chaffee.

Chebyshev is a large lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. The somewhat smaller crater Langmuir is intruding into the east-southeastern rim of Chebyshev, forming a chain of large craters with Brouwer on Langmuir's eastern rim.

Chrétien is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon from the Earth. It lies due south of the Mare Ingenii, one of the few maria on the Moon's far side. The crater lies in the midpoint between the craters Garavito to the west-southwest and Oresme to the east-northeast, both of these being somewhat smaller than Chrétien.

Cajori is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the southwest of the walled plain Von Kármán, and to the east-southeast of the crater Chrétien.

Chapman is a lunar impact crater that lies just beyond the northwest rim of the Moon, on the far side as seen from the Earth. It lies to the northeast of the crater Rynin, and southward of the large walled plain Poczobutt.

Chandler is a lunar impact crater in the northern hemisphere, on the Moon's far side. It lies to the southeast of the large walled plain D'Alembert, and southeast of the slightly smaller Chernyshev crater.

Dellinger is a lunar impact crater that is located on the Moon's far side. It is attached to the southern rim of the crater Pannekoek. To the southeast lies the crater Marconi, and to the southwest is Chauvenet.

Denning is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies about midway between the craters Levi-Civita to the south and Marconi to the north-northeast. About two crater diameters to the southeast is the huge walled plain Gagarin.

Orlov is a lunar impact crater. It is located on the Moon's far side, to the northeast of the larger crater Leeuwenhoek. To the north-northwest of Orlov is De Vries, and to the east-southeast is Rumford.

Spencer Jones is a lunar impact crater on the Moon's far side. It is a roughly circular feature with a rim edge that is only moderately eroded. The inner wall of Spencer Jones is wider than elsewhere. The interior floor is relatively level with a low ridge offset to the south of the midpoint. Attached to the southwestern outer rim is the small satellite crater Spencer Jones Q.

Tsander is a large lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. Attached to the southeastern outer rim is the younger crater Kibal'chich. To the northwest lies Dirichlet, and to the northeast lies Artem'ev.






















