
Cabannes is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. The rim has been worn by subsequent impacts, with a smaller crater overlying the southern rim. However the formation has not been significantly reshaped by nearby craters.

Ammonius is a bowl-shaped lunar impact crater with a slightly raised rim. It is located on the floor of the walled plain Ptolemaeus, about 30 kilometers northeast of the crater midpoint.
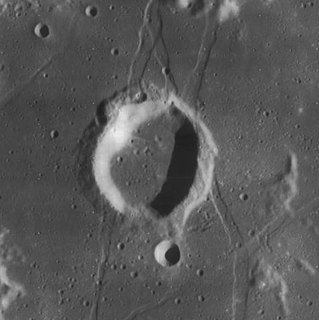
Ramsden is a lunar impact crater located on the western stretch of the Palus Epidemiarum. It was named after British instrument maker Jesse Ramsden. To the east-southeast is the crater Capuanus, and to the north lies Dunthorne.

Aryabhata, named after Indian astronomer Aryabhata, is the remnant of a lunar impact crater located in the eastern Mare Tranquillitatis. The crater has been almost submerged by lava-flow, and now only an arc-shaped ridge formed from the eastern half of the rim remains above the lunar mare. This crater was previously identified as Maskelyne E before being named by the IAU in 1979. Maskelyne itself is to the southwest.

Bessarion is a lunar impact crater located near the southwest edge of Mare Imbrium. It is named after Greek scholar Bessarion. Some distance to the east is the crater T. Mayer. Bessarion is a bowl-shaped crater with a low central rise and a higher albedo than the maria, making it a brighter feature when the sun is overhead.

Brayley is a lunar impact crater located in the southwest part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after British geographer Edward W. Brayley. It has a circular rim and a low rise in the center. There are no notable craters overlapping the rim or interior. The sinuous rille Rima Brayley passes to the north of Brayley.

Draper is a small lunar impact crater in the southern part of the Mare Imbrium. It is a circular, cup-shaped formation, with a tiny craterlet intruding into the northeastern rim. To the north-northeast is the crater Pytheas, and to the south lies the Montes Carpatus range. Just to the southeast is the slightly smaller crater identified as Draper C. The crater is named after American astronomer Henry Draper.

Marth is a small lunar impact crater located in the northwest part of the Palus Epidemiarum. It was named after German astronomer Albert Marth. To the northwest is the crater Dunthorne, and to the southwest lies Ramsden. This feature lies in a system of rilles named the Rimae Ramsden, and an interrupted branch passes only a few kilometers to the south of the rim.

Beketov is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern reaches of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after Russian chemist Nikolay Beketov. To the south is the ghost crater Jansen R. Northeast of Beketov, along the edge of the mare, is the crater Vitruvius. Beketov was previously designated Jansen C before being named by the IAU. The flooded crater Jansen itself lies to the south.

Brewster is a small lunar impact crater in the northern fringes of Sinus Amoris. It was named after the Scottish scientist, Sir David Brewster. Its diameter is 9.8 km. It lies to the southwest of the larger crater Römer. To the southeast of Brewster is the similar-sized Franck. This crater is cup-shaped and symmetrical, with no overlapping craters of note. A low ridge is attached to the northern rim. The crater interior has a relatively high interior albedo compared to the surrounding terrain.

Boscovich is a lunar impact crater that has been almost completely eroded away by subsequent impacts. It is located west-northwest of the crater Julius Caesar, and south-southeast of the prominent Manilius. The crater floor has a low albedo, and the dark hue makes it relatively easy to recognize. The surface is crossed by the rille system designated Rimae Boscovich that extends for a diameter of 40 kilometres. The crater is named after Croatian physicist Roger Joseph Boscovich.
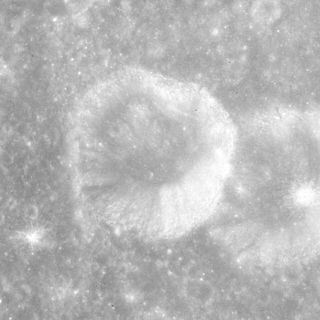
Daly is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon, to the northwest of the crater Apollonius. This formation is relatively circular, with a slight inward bulge along the northern rim. The inner wall is wider in the southern half than in the north. The crater intrudes into the comparably sized crater Apollonius F to the east-southeast.

Bjerknes is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the rugged far side of the Moon. The crater lies behind the southeastern limb, and beyond the region that is sometimes brought into sight through libration. Thus this crater can not be viewed from Earth, and has only been seen from orbit. Nearby named craters are Clark to the east, and Pogson to the south-southwest.

Capuanus is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of the Palus Epidemiarum. It was named after Italian astronomer F. Capuano di Manfredonia. The outer rim is eroded and indented by lesser crater impacts, with notches in the north, west, and southern parts of the rim. The interior floor has been resurfaced by basaltic lava, which is connected to the surrounding lunar mare by a narrow, crater-formed gap in the northern rim. The floor is particularly notable for the hosting a number of domes, which are believed to have formed through volcanic activity.

Cook is a lunar impact crater that lies in the western part of the Mare Fecunditatis, just to the southeast of the prominent crater Colombo. To the southwest is Monge.

Feuillée is a small lunar impact crater in the eastern part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after French natural scientist Louis Feuillée. It lies less than a half crater diameter to the northwest of Beer, and the two formations form a nearly matched pair. To the west is the small but prominent crater Timocharis.

Elger is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of Palus Epidemiarum, the Marsh of Epidemics, in the southwest part of the Moon's near side. To the northeast is the flooded crater Capuanus, and farther to the northwest is Ramsden.

Dunthorne is a small lunar impact crater that is located to the northwest of the small lunar mare called Palus Epidemiarum, in the southwest part of the Moon's near side. It was named after British astronomer Richard Dunthorne. It lies to the southwest of the crater Campanus, east of Vitello. Due south is Ramsden.
Fibiger is a lunar impact crater located on the lunar near side near the northern pole. The nearest major feature is the Byrd crater. The crater was adopted and named after Danish pathologist Johannes Andreas Grib Fibiger in 2009 by the IAU. Located just north of Fibiger are craters Erlanger and Peary, which are 9.9 km and 73 km in diameter, respectively.

Florey is a lunar impact crater on the lunar near side near the northern pole. Florey is directly adjacent to Byrd crater to the Southeast and Peary crater to the North. The crater is named after Australian scientist Howard Florey. The crater was named by the IAU in 2009.




















