
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods. In addition, some non-arthropods such as mollusks possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system.
Barry Bolton is an English myrmecologist, an expert on the classification, systematics, and taxonomy of ants, who long worked at the Natural History Museum, London. He is known especially for monographs on African and Asian ants, and for encyclopaedic global works, including the Identification Guide to Ant Genera (1994), A New General Catalogue of Ants of the World, Synopsis and Classification of Formicidae (2003), and Bolton's Catalogue of Ants of the World: 1758-2005 (2007). Now retired, Bolton is a Fellow of the Royal Entomological Society and Myrmecologist, Biodiversity Division, Department of Entomology, Natural History Museum, London.

Leptanilla is a genus of ant in the subfamily Leptanillinae. Like other genera in this subfamily, the queen is fed by the hemolymph of their own larvae, which have specialized processes for this purpose.

Angustalius is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.
Larval hemolymph feeding is a behaviour trait found in the queens of some species of ant. This is found mainly in the ants of the subfamily Amblyoponinae and give them the other name of Dracula ant. In colonies of the Amblyopone silvestrii the queens feed on the hemolymph of their larvae when food is not available. In one species, Myopopone castanea, worker ants consume larval hemolymph. This is said to be a precursor to trophallaxis in other ant families. The larvae themselves are not killed by this process. This behaviour is also seen in Proceratium and in Leptanilla the larvae have special organs that exude the haemolymph. On the other hand, the foundresses suppress larval hemolymph feeding (LHF) when prey is available, allowing them to rear the first workers more swiftly. The nondestructive form of cannibalism can be regarded as a nutritive adaptation related to: (1) the lack of social food transfer in this species, and (2) its specialized predation on large sporadic prey (centipedes). LHF similar to that in Amblyopone was found in Proceratium and another type of LHF, with a larval specialized exudatory organ, in Leptanilla.
L. japonica may refer to:
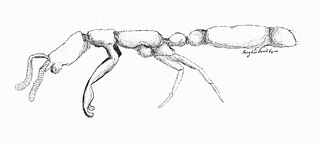
Leptanilla japonica is an uncommon highly migratory, subterranean ant found in Japan. They are tiny insects, with workers measuring about 1.2 mm and queens reaching to about 1.8 mm, and live in very small colonies of only a few hundred individuals at a time Its sexual development follows a seasonal cycle that affects the colony's migration and feeding habits, and vice versa. L. japonica exhibits specialized predation, with prey consisting mainly of geophilomorph centipedes, a less reliable food source that also contributes to their high rate of nest migration. Like ants of genera Amblyopone and Proceratium, the genus Leptanilla engages in larval hemolymph feeding (LHF), with the queen using no other form of sustenance. LHF is an advantageous alternative to the more costly cannibalism. Unlike any other ant, however, members of Leptanilla, including L. japonica, have evolved a specialized organ dubbed the “larval hemolymph tap” that reduces the damage LHF inflicts on the larvae. LHF has become this species' main form of nutrition.

Reddyanus besucheti is a species of scorpion in the family Buthidae endemic to Sri Lanka.

Stigmatomma is a genus of ants in the subfamily Amblyoponinae. The genus has a worldwide distribution, and like most other amblyoponines, Stigmatomma species are specialized predators. First described by Roger (1859), it was for a long time considered to be a synonym of Amblyopone until it was revived as an independent genus by Yoshimura & Fisher (2012) based on worker mandible morphology.

Yavnella is a genus of ants in the subfamily Leptanillinae. Its two species are distributed in India and Israel. The genus is known only from male specimens.

Phaulomyrma is a genus of ants in the subfamily Leptanillinae containing a single species, Phaulomyrma javana.

Leptanillini is a tribe of Leptanillinae ants with three extant genera.

Rogeria is a genus of ant in the subfamily Myrmicinae. The genus is known from the Americas, Pacific, and Caribbean. Little is known about their biology.

Ooceraea is a genus of ants in the subfamily Dorylinae containing approximately 16 described species. The genus is distributed across the Australasia, Indomalaya, Malagasy, Neotropical, Oceania, and Palearctic bioregions. Ooceraea was described by Roger (1862) and later placed as a junior synonym of Cerapachys by Brown (1973). Ooceraea was resurrected as a valid genus by Borowiec (2016) during redescription of the doryline genera.

Noonilla is a genus of ants of uncertain placement in the family Formicidae. It contains the single species Noonilla copiosa, first described by Petersen in 1968 based on male specimen from the Philippines. Noonilla was initially placed in the subfamily Leptanillinae, but was later removed from the subfamily when Ogata, Terayama & Masuko (1995) reviewed the genus, leaving the genus incertae sedis in the family.

Leptanilla swani is a species of ant in the genus Leptanilla. Described by William Morton Wheeler in 1932, the species is endemic to Australia, and the only species of the genus Leptanilla to be found there. Workers are pale in colour, measuring 1.3 to 5 millimetres while queens are larger at 2 millimetres (0.079 in) long.

Leptanilla macauensis is a species of ant in the genus Leptanilla. Chi-Man Leong, an undergraduate student at National Taiwan University at the time, first collected specimens of this species. The species was subsequently formally described by Leong, Yamane & Guénard in 2018, the species is only known from specimens collected from Macau by means of a Winkler extractor. Workers are yellowish brown in colour, measuring 1.12 to 1.14 millimetres. The queen has yet to be described.
Alissonotum piceum, is a species of dung beetle found in India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Réunion island and Mauritius.

Leptanilla havilandi is a species of ant in the subfamily Leptanillinae. The species can be found in Singapore and Malaysia.













