
Psoralea is a genus in the legume family (Fabaceae) with over 60 closely related species native to southern Africa. In South Africa they are commonly referred to as fountainbush (English); fonteinbos, bloukeur, or penwortel (Afrikaans); and umHlonishwa (Zulu).

Psoralea esculenta, common name prairie turnip or timpsula, is an herbaceous perennial plant native to prairies and dry woodlands of central North America, which bears a starchy tuberous root edible as a root vegetable. The plant is also known as Pediomelum esculentum. English names for the plant include tipsin, teepsenee, breadroot, breadroot scurf pea, large Indian breadroot and pomme blanche. The prairie turnip was a staple food of the Plains Indians.

Psoralea pinnata is an erect evergreen shrub or small tree that grows to a height between 1.5 metres (5 ft) and 4 metres (13 ft) tall.

Leptozestis is a genus of moths in the family Cosmopterigidae.

Psoralea corylifolia (Babchi) is a plant used in Indian and Chinese traditional medicine. The seeds of this plant contain a variety of coumarins, including psoralen.

Plicatin B is a hydroxycinnamic acid found in Psoralea plicata.
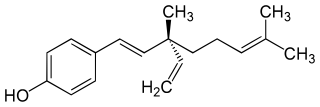
Bakuchiol is a meroterpene in the class terpenophenol.
Leptozestis polychroa is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from Victoria.
Leptozestis capnopora is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1897. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from New South Wales.
Leptozestis cataspoda is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1897. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from South Australia.
Leptozestis cyclonia is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1897. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from New South Wales.
Leptozestis psarotricha is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1897. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from New South Wales.
Leptozestis tropaea is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1897. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from South Australia.
Leptozestis argoscia is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Oswald Bertram Lower in 1904. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from Victoria.
Leptozestis autochroa is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1915. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from Victoria.
Leptozestis euryplaca is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Oswald Bertram Lower in 1893. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from South Australia and Queensland.
Leptozestis strophicodes is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1917. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from Queensland.
Agonopterix posticella is a moth in the family Depressariidae. It was described by Walsingham in 1881. It is found in North America, where it has been recorded from Washington to California and in Wyoming and Colorado.

Drupanol is a naturally occurring phenol that has been isolated from the seeds of Psoralea drupaceae. Although drupanol is sometimes said to be the same compound as bakuchiol, the two compounds are in fact distinct; they have the same molecular formula and weight but different chemical structures and hence are structural isomers. Bakuchiol has been found to possess antiandrogenic activity in vitro.







