
Ammonius is a bowl-shaped lunar impact crater with a slightly raised rim. It is located on the floor of the walled plain Ptolemaeus, about 30 kilometers northeast of the crater midpoint.

Beaumont is a lava-flooded crater located on the southwestern shore of the Mare Nectaris on Earth's Moon. It lies to the northwest of the similarly flooded crater remnant Fracastorius. To the west is the prominent crater Catharina. The crater is named after French geologist Léonce Élie de Beaumont.

Winthrop is the remnant of a lunar impact crater that has been flooded by lava from the Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after American astronomer John Winthrop. It lies across the western rim of the much larger crater Letronne, a feature that has been nearly destroyed by the intruding mare lavas. All that survives of Winthrop are a few segments of the outer rim.

Chladni is a small lunar impact crater that lies near the northwest edge of Sinus Medii, in the central part of the Moon.

Cleomedes is a prominent lunar impact crater located in the northeast part of the visible Moon, to the north of Mare Crisium. It was named after Greek astronomer Cleomedes. It is surrounded by rough ground with multiple crater impacts. The irregular crater Tralles intrudes into the northwest rim. To the east is Delmotte. North of Cleomedes is a triple-crater formation with Burckhardt occupying the center.

Abenezra is a lunar impact crater located in the rugged highlands in the south-central section of the Moon. Abenezra is named after the Sephardic Jewish sage, poet, biblical commentator, and astronomer Abraham ibn Ezra. It is attached along the southeast rim to the crater Azophi. To the northeast lies the crater Geber, and further to the southeast is the larger Sacrobosco.

Doppelmayer is the remains of a lunar impact crater that lies on the southwest edge of Mare Humorum. It was named after the German mathematician and astronomer Johann Gabriel Doppelmayr. To the south-southeast is another flooded crater designated Lee, and to the southeast is Vitello. Just to the east-northeast of Doppelmayer lies the nearly submerged crater Puiseux.

Flamsteed is a small lunar impact crater located on the Oceanus Procellarum, which is named after British astronomer John Flamsteed. It lies almost due east of the dark-hued Grimaldi, and north-northwest of the flooded Letronne bay on the south edge of the mare.

Maraldi is a worn, eroded crater on the western edge of the Sinus Amoris, in the northeast part of the Moon. To the west-southwest is the crater Vitruvius, and to the northwest lies the worn Littrow crater. Just to the northeast of the crater is the dome-like Mons Maraldi rise.

Billy is a lunar impact crater that is located at the southern fringes of the Oceanus Procellarum, in the western hemisphere of the Moon. It was named after French mathematician Jacques de Billy. It lies to the southeast of the similar-sized crater Hansteen, and west-southwest of the flooded Letronne.

Biela is a lunar impact crater that is located in the rugged highlands of the southeastern Moon. It is named after Austrian astronomer Wilhelm von Biela. The crater lies to the east of Rosenberger, to the southeast of the Watt–Steinheil double crater.

Webb is a small lunar impact crater that is located near the eastern edge of the Mare Fecunditatis, in the eastern part of the Moon near the equator. It was named after British astronomer Thomas William Webb. It is to the north of the prominent crater Langrenus, and west of Maclaurin.

Banachiewicz is a largely degraded lunar impact crater that is located near the eastern limb of the Moon.

Buisson is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It is named after the French physicist Henri Buisson. Nearly attached to the southeast rim is the crater Vesalius. To the southwest is Einthoven. The rim of this crater is somewhat worn, and is lowest in the north. There is a low central ridge across the midpoint.
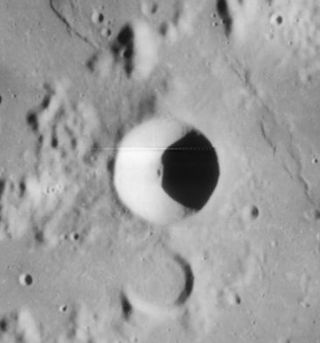
Darney is a small lunar impact crater that is located on the region of the Moon where the Mare Nubium joins the Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after French astronomer Maurice Darney. To the south is the lava-flooded crater Lubiniezky. The southern rim of Darney is attached to a series of low ridges that extend to the southwest.

Heis is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the western part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after German astronomer Eduard Heis. It is located to the northeast of the crater Delisle, and south of C. Herschel. Due east is the wrinkle ridge Dorsum Heim. Heis is a circular, symmetrical formation with an interior floor that is about half the diameter of the outer rim. The tiny satellite crater Heis A intrudes slightly into the northern rim.

Cori is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It lies less than one crater diameter to the north of the crater Baldet. To the northeast is the crater Grissom. It is named after Gerty Cori, the first American woman to win the Nobel Prize and the first woman to win the prize in the category Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.

Chevallier is a lunar impact crater that is located in the northeastern part of the Moon's near side, about a crater diameter east-southeast of the prominent crater Atlas. To the south-southeast of Chevallier is the flooded crater Shuckburgh. Chevallier was named by the IAU in 1935.

Eichstadt is a lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern section of the Montes Cordillera range that encircles the Mare Orientale impact basin. It lies toward the southwestern limb of the Moon, and so appears oblong when viewed from the Earth due to foreshortening. Over 200 kilometers to the east of Eichstadt are the craters Darwin and Lamarck, and to the south is Krasnov.

Olcott is a relatively fresh crater on the far side of the Moon. It was named after American astronomer William Tyler Olcott. It lies to the south-southeast of the craters Seyfert and Polzunov, and to the north of Kostinskiy.























