
The Book of Exodus is the second book of the Bible. Starting with the deliverance of Moses by Pharaoh's daughter, it recounts the revelation at the Burning bush where he was called by Yahweh to deliver the Israelites from Egyptian slavery. After Pharaoh rejected his and Aaron's demands, according to the book, the Almighty inflicted ten Plagues on Egypt resulting in the Exodus. The Mosaic covenant was made at the biblical Mount Sinai, and subsequently the Tabernacle, with a "divine indwelling" of God with Israel.

The Gaza Strip, or simply Gaza, is a self-governing Palestinian territory on the eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Egypt on the southwest for 11 kilometers (6.8 mi) and Israel on the east and north along a 51 km (32 mi) border. Gaza and the West Bank are claimed by the de jure sovereign State of Palestine.
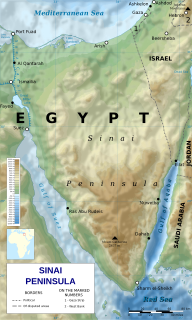
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai, is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about 60,000 km2 (23,000 sq mi) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north.

The Suez Canal is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The canal is part of the Silk Road that connects Europe with Asia.

The Six-Day War, also known as the June War, 1967 Arab–Israeli War, or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between 5 and 10 June 1967 between Israel and Jordan, Syria, and Egypt.

The Yom Kippur War, Ramadan War, or October War also known as the 1973 Arab–Israeli War, was fought from October 6 to 25, 1973, by a coalition of Arab states led by Egypt and Syria against Israel. The war took place mostly in Sinai and the Golan—occupied by Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War—with some fighting in African Egypt and northern Israel. Egypt's initial war objective was to use its military to seize a foothold on the east bank of the Suez Canal and use this to negotiate the return of the rest of Sinai.

The 1948Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1947–1949 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had been issued earlier that day, and a military coalition of Arab states entered the territory of British Palestine in the morning of 15 May.

Muhammad Anwar el-Sadat was an Egyptian politician who served as the third President of Egypt, from 15 October 1970 until his assassination by fundamentalist army officers on 6 October 1981. Sadat was a senior member of the Free Officers who overthrew King Farouk in the Egyptian Revolution of 1952, and a close confidant of President Gamal Abdel Nasser, under whom he served as Vice President twice and whom he succeeded as president in 1970. In 1978, Sadat and Menachem Begin, Prime Minister of Israel, signed a peace treaty in cooperation with United States President Jimmy Carter, for which they were recognized with the Nobel Peace Prize.

The Suez Crisis, or the Second Arab–Israeli war, also called the Tripartite Aggression in the Arab world and the Sinai War in Israel, was an invasion of Egypt in late 1956 by Israel, followed by the United Kingdom and France. The aims were to regain control of the Suez Canal for the Western powers and to remove Egyptian president Gamal Abdel Nasser, who had just nationalised the canal. After the fighting had started, political pressure from the United States, the Soviet Union and the United Nations led to a withdrawal by the three invaders. The episode humiliated the United Kingdom and France and strengthened Nasser.

The War of Attrition involved fighting between Israel and Egypt, Jordan, PLO and their allies from 1967 to 1970.

The Camp David Accords were a pair of political agreements signed by Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin on 17 September 1978, following twelve days of secret negotiations at Camp David, the country retreat of the President of the United States in Maryland. The two framework agreements were signed at the White House and were witnessed by President Jimmy Carter. The second of these frameworks led directly to the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty. Due to the agreement, Sadat and Begin received the shared 1978 Nobel Peace Prize. The first framework, which dealt with the Palestinian territories, was written without participation of the Palestinians and was condemned by the United Nations.

Taba is an Egyptian town near the northern tip of the Gulf of Aqaba. Taba is the location of Egypt's busiest border crossing with neighbouring Eilat, Israel. Taba is a frequent vacation spot for Egyptians and tourists, especially those from Israel on their way to other destinations in Egypt or as a weekend getaway. It is the northernmost resort of Egypt's Red Sea Riviera.

The Egypt–Israel peace treaty was signed in Washington, D.C., United States on 26 March 1979, following the 1978 Camp David Accords. The Egypt–Israel treaty was signed by Egyptian president Anwar Sadat and Israeli prime minister Menachem Begin, and witnessed by United States president Jimmy Carter.

Za'atar is a culinary herb or family of herbs. It is also the name of a spice mixture that includes the herb along with toasted sesame seeds, dried sumac, often salt, as well as other spices. As a family of related Middle Eastern herbs, it contains plants from the genera Origanum (oregano), Calamintha, Thymus, and Satureja (savory) plants. The name za'atar alone most properly applies to Origanum syriacum, considered in biblical scholarship to be the hyssop of the Hebrew Bible. Used in Levantine cuisine, both the herb and spice mixture are popular throughout the Mediterranean region of the Middle East.

Ficus sycomorus, called the sycamore fig or the fig-mulberry, sycamore, or sycomore, is a fig species that has been cultivated since ancient times.

Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia by a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. Egypt is a Mediterranean country bordered by the Gaza Strip (Palestine) and Israel to the northeast, the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. Across the Gulf of Aqaba lies Jordan, across the Red Sea lies Saudi Arabia, and across the Mediterranean lie Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, although none share a land border with Egypt.

Kleinmann's tortoise, also called commonly the Egyptian tortoise, Leith's tortoise, and the Negev tortoise, is a critically endangered species of neck-hiding tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species is native to Egypt, Libya, and Israel. The species was once more widespread, but its numbers are now dwindling. The species is nearly extinct in Egypt, and complete extinction in the wild is a looming threat unless more actions are taken to protect this species.

Israel, officially known as the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively, and Egypt to the southwest. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government and proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, although international recognition of the state's sovereignty over the city is limited.

The Asian barbastelle, also known as the levant barbastelle or eastern barbastelle, is a species of vesper bat. Its habitat is temperate forests and caves. It is threatened by habitat loss. It can be found in Egypt (Sinai), Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Eritrea.

The bushy-tailed jird or bushy-tailed dipodil is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is the only species in the genus Sekeetamys. It is found in Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Sudan. Its natural habitat is rocky areas.