
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their taxonomy, genetics, biochemical properties, and use by humans. Fungi can be a source of tinder, food, traditional medicine, as well as entheogens, poison, and infection. Mycology branches into the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases. The two disciplines are closely related, because the vast majority of plant pathogens are fungi. A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist.

Zosteraceae is a family of marine perennial flowering plants found in temperate and subtropical coastal waters, with the highest diversity located around Korea and Japan. Most seagrasses complete their entire life cycle under water, having filamentous pollen especially adapted to dispersion in an aquatic environment and ribbon-like leaves that lack stomata. Seagrasses are herbaceous and have prominent creeping rhizomes. A distinctive characteristic of the family is the presence of characteristic retinacules, which are present in all species except members of Zostera subgenus Zostera.
Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern the naming of living organisms. Standardizing the scientific names of biological organisms allows researchers to discuss findings.

Petter Adolf Karsten was a Finnish mycologist, the foremost expert on the fungi of Finland in his day, and known in consequence as the "father of Finnish mycology".

Charles Atwood Kofoid was an American zoologist known for his collection and classification of many new species of marine protozoans which established marine biology on a systematic basis.
Hyphochytrium is a genus of Hyphochytriomycetes. Hyphochytrium species occur in soil.
David Leslie Hawksworth is a British mycologist and lichenologist currently with a professorship in the Universidad Complutense de Madrid in Madrid, Spain and also a Scientific Associate of The Natural History Museum in London. In 2002, he was honoured with an Acharius Medal by the International Association for Lichenology. He married Patricia Wiltshire, a leading forensic ecologist and palynologist in 2009. As of 2022, he is the Editor-in-Chief of the journals IMA Fungus and Biodiversity and Conservation.

František Kotlaba was a Czech botanist and mycologist.

Greta Barbara Stevenson was a New Zealand botanist and mycologist. She described many new species of Agaricales.
Malajczukia is a genus of truffle-like fungi in the Mesophelliaceae family. The genus contains eight species found in Australia and New Zealand.

Albert Pilát was a Czech botanist and mycologist. He studied at the Faculty of Science at Charles University, under the guidance of Professor Josef Velenovský. In 1930, he joined the National Museum, eventually becoming head of the Mycological Department, and in 1960 a corresponding member of the academy. He was the author of many popular and scholarly publications in the field of mycology and mountain flora. He also served as the main editor of the scientific journal Czech Mycology, and described several species of fungi. His areas of particular interest include polypores and boletes. He explored the Carpathians looking for fungi and travelled widely. He was also a skilled photographer.
Roy Watling, PhD., DSc, FRSE, F.I.Biol., C.Biol., FLS is a Scottish mycologist who has made significant contributions to the study of fungi both in the identification of new species and correct taxonomic placement, as well as in fungal ecology.
Klaus Kubitzki was a German botanist. He was Emeritus professor in the University of Hamburg, at the Herbarium Hamburgense. He is known for his work on the systematics and biogeography of the angiosperms, particularly those of the Neotropics, and also the floristic record of the Tertiary era. His plant systematic work is referred to as the Kubitzki system. He was a member of the American Society of Plant Taxonomists.
David Norman Pegler is a British mycologist. Until his retirement in 1998, he served as the Head of Mycology and assistant keeper of the herbarium at the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew. Pegler received his BSc from London University in 1960, thereafter studying tropical Agaricales with R.W.G. Dennis as his graduate supervisor. He earned a master's degree in 1966, and a PhD in 1974. His graduate thesis was on agarics of east Africa, later published as A preliminary agaric flora of East Africa in 1977. In 1989, London University awarded him a DSc for his research into the Agaricales.
Robert W. Lichtwardt was a Brazilian-born American mycologist specializing in the study of arthropod-associated, gut-dwelling fungi (trichomycetes). He is known for his online monograph and interactive keys to trichomycete taxa.

David John Galloway, FRSNZ was a biochemist, botanist, and lichenologist.
Bragginsella is a monotypic genus of liverworts belonging to the family Lophocoleaceae.

The plasmodiophores are a group of obligate endoparasitic protists belonging to the subphylum Endomyxa in Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they are united under a single family Plasmodiophoridae, order Plasmodiophorida, sister to the phagomyxids.
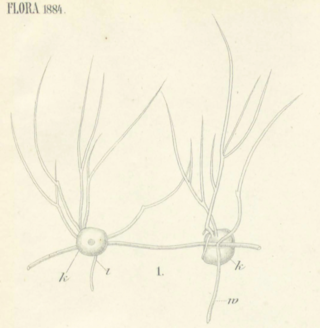
Tetramyxa is a cercozoan protist, member of the plasmodiophores, parasite of several flowering plants. It was first described by Karl von Goebel in 1884, in his work Flora. The genus is characterized by the appearance of resting spores in groups of four.

Tetramyxa parasitica is a species of parasitic cercozoan, member of the plasmodiophorids, that causes gall formation on multiple genera of aquatic plants. It was first discovered on roots of Ruppia and described by Karl von Goebel in 1884 in his work Flora, where it became the type species of the genus Tetramyxa.










