In quantum mechanics, bra–ket notation, or Dirac notation, is used ubiquitously to denote quantum states. The notation uses angle brackets, and , and a vertical bar , to construct "bras" and "kets".

The Fresnel equations describe the reflection and transmission of light when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresnel who was the first to understand that light is a transverse wave, even though no one realized that the "vibrations" of the wave were electric and magnetic fields. For the first time, polarization could be understood quantitatively, as Fresnel's equations correctly predicted the differing behaviour of waves of the s and p polarizations incident upon a material interface.
In optics, polarized light can be described using the Jones calculus, discovered by R. C. Jones in 1941. Polarized light is represented by a Jones vector, and linear optical elements are represented by Jones matrices. When light crosses an optical element the resulting polarization of the emerging light is found by taking the product of the Jones matrix of the optical element and the Jones vector of the incident light. Note that Jones calculus is only applicable to light that is already fully polarized. Light which is randomly polarized, partially polarized, or incoherent must be treated using Mueller calculus.

In mathematical physics and mathematics, the Pauli matrices are a set of three 2 × 2 complex matrices which are Hermitian, involutory and unitary. Usually indicated by the Greek letter sigma, they are occasionally denoted by tau when used in connection with isospin symmetries.
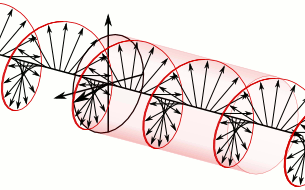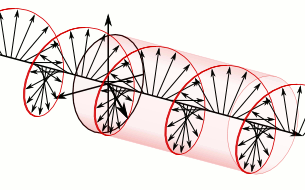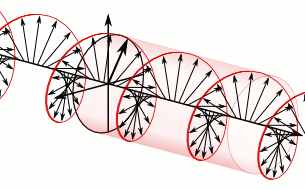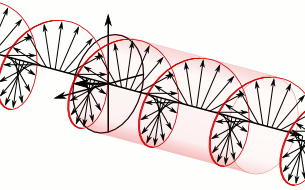
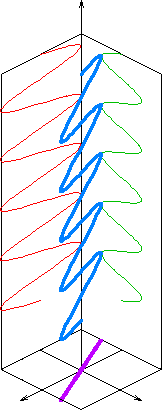
In electrodynamics, circular polarization of an electromagnetic wave is a polarization state in which, at each point, the electromagnetic field of the wave has a constant magnitude and is rotating at a constant rate in a plane perpendicular to the direction of the wave.
In electrodynamics, elliptical polarization is the polarization of electromagnetic radiation such that the tip of the electric field vector describes an ellipse in any fixed plane intersecting, and normal to, the direction of propagation. An elliptically polarized wave may be resolved into two linearly polarized waves in phase quadrature, with their polarization planes at right angles to each other. Since the electric field can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise as it propagates, elliptically polarized waves exhibit chirality.

A waveplate or retarder is an optical device that alters the polarization state of a light wave travelling through it. Two common types of waveplates are the half-wave plate, which shifts the polarization direction of linearly polarized light, and the quarter-wave plate, which converts linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light and vice versa. A quarter-wave plate can be used to produce elliptical polarization as well.
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space under the operation of composition.

In physics, the Rabi cycle is the cyclic behaviour of a two-level quantum system in the presence of an oscillatory driving field. A great variety of physical processes belonging to the areas of quantum computing, condensed matter, atomic and molecular physics, and nuclear and particle physics can be conveniently studied in terms of two-level quantum mechanical systems, and exhibit Rabi flopping when coupled to an oscillatory driving field. The effect is important in quantum optics, magnetic resonance and quantum computing, and is named after Isidor Isaac Rabi.

In quantum mechanics and computing, the Bloch sphere is a geometrical representation of the pure state space of a two-level quantum mechanical system (qubit), named after the physicist Felix Bloch.
The rigid rotor is a mechanical model of rotating systems. An arbitrary rigid rotor is a 3-dimensional rigid object, such as a top. To orient such an object in space requires three angles, known as Euler angles. A special rigid rotor is the linear rotor requiring only two angles to describe, for example of a diatomic molecule. More general molecules are 3-dimensional, such as water, ammonia, or methane.

The Stokes parameters are a set of values that describe the polarization state of electromagnetic radiation. They were defined by George Gabriel Stokes in 1852, as a mathematically convenient alternative to the more common description of incoherent or partially polarized radiation in terms of its total intensity (I), (fractional) degree of polarization (p), and the shape parameters of the polarization ellipse. The effect of an optical system on the polarization of light can be determined by constructing the Stokes vector for the input light and applying Mueller calculus, to obtain the Stokes vector of the light leaving the system. The original Stokes paper was discovered independently by Francis Perrin in 1942 and by Subrahamanyan Chandrasekhar in 1947, who named it as the Stokes parameters.

In quantum mechanics, a two-state system is a quantum system that can exist in any quantum superposition of two independent quantum states. The Hilbert space describing such a system is two-dimensional. Therefore, a complete basis spanning the space will consist of two independent states. Any two-state system can also be seen as a qubit.
Sinusoidal plane-wave solutions are particular solutions to the electromagnetic wave equation.
Photon polarization is the quantum mechanical description of the classical polarized sinusoidal plane electromagnetic wave. An individual photon can be described as having right or left circular polarization, or a superposition of the two. Equivalently, a photon can be described as having horizontal or vertical linear polarization, or a superposition of the two.
The theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation motivates the discovery of the Schrödinger equation, the equation that describes the dynamics of nonrelativistic particles. The motivation uses photons, which are relativistic particles with dynamics described by Maxwell's equations, as an analogue for all types of particles.
In geometry, various formalisms exist to express a rotation in three dimensions as a mathematical transformation. In physics, this concept is applied to classical mechanics where rotational kinematics is the science of quantitative description of a purely rotational motion. The orientation of an object at a given instant is described with the same tools, as it is defined as an imaginary rotation from a reference placement in space, rather than an actually observed rotation from a previous placement in space.
In optics, polarization mixing refers to changes in the relative strengths of the Stokes parameters caused by reflection or scattering—see vector radiative transfer—or by changes in the radial orientation of the detector.
In NMR spectroscopy, the product operator formalism is a method used to determine the outcome of pulse sequences in a rigorous but straightforward way. With this method it is possible to predict how the bulk magnetization evolves with time under the action of pulses applied in different directions. It is a net improvement from the semi-classical vector model which is not able to predict many of the results in NMR spectroscopy and is a simplification of the complete density matrix formalism.
In pure and applied mathematics, quantum mechanics and computer graphics, a tensor operator generalizes the notion of operators which are scalars and vectors. A special class of these are spherical tensor operators which apply the notion of the spherical basis and spherical harmonics. The spherical basis closely relates to the description of angular momentum in quantum mechanics and spherical harmonic functions. The coordinate-free generalization of a tensor operator is known as a representation operator.