Related Research Articles
The Pennsylvania Railroad, legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. At its peak in 1882, the Pennsylvania Railroad was the largest railroad, the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

Tower City Center is a large mixed-use facility in Downtown Cleveland, Ohio, on its Public Square. The facility is composed of a number of interconnected office buildings, including Terminal Tower, the Skylight Park mixed-use shopping center, Jack Cleveland Casino, Renaissance Cleveland Hotel, Chase Financial Plaza, and Tower City station, the main hub of Cleveland's four RTA Rapid Transit lines.

A railway roundhouse is a building with a circular or semicircular shape used by railways for servicing and storing locomotives. Traditionally, though not always the case today, these buildings surrounded or were adjacent to a turntable.

Oris Paxton Van Sweringen and Mantis James Van Sweringen were American brothers who became railroad barons in order to develop Shaker Heights, Ohio. They are better known as O. P. Van Sweringen and M. J. Van Sweringen, or by their collective nickname, the Vans. The brothers came from a farming area near Wooster, Ohio. Their father was for a time an engineer in the oil fields of Pennsylvania, fought in the Civil War and was wounded at the Battle of Gettysburg. The family moved to Cleveland, Ohio, in about 1890.

A 4-4-4-4 steam locomotive, in the Whyte notation for describing locomotive wheel arrangements, has a four-wheel leading truck, two sets of four driving wheels, and a four-wheel trailing truck. While it would be possible to make an articulated locomotive of this arrangement, the only 4-4-4-4s ever built were duplex locomotives—with two sets of cylinders driving two sets of driven wheels in one rigid frame, essentially a 4-8-4 with divided drive.

The Pennsylvania Railroad's class B6 was its most successful class of switcher locomotive, or as the PRR termed them "shifter". The PRR preferred the 0-6-0 wheel arrangement for larger switchers, whereas on other railroads the 0-8-0 gained preference. The PRR generally used 2-8-0s when larger power was required.
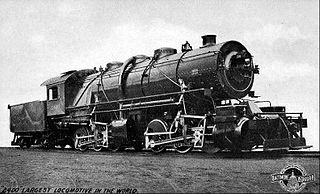
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, a 0-6-6-0 wheel arrangement refers to a locomotive with two engine units mounted under a rigid locomotive frame, with the front engine unit pivoting and each engine unit with six coupled driving wheels without any leading or trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was mostly used to describe Mallet locomotive types.

Central Station was an intercity passenger terminal in downtown Chicago, Illinois, at the southern end of Grant Park near Roosevelt Road and Michigan Avenue. Owned by the Illinois Central Railroad, it also served other companies via trackage rights. It opened in 1893, replacing Great Central Station, and closed in 1972 when Amtrak rerouted services to Union Station. The station building was demolished in 1974. It is now the site of a redevelopment called Central Station, Chicago.

The Blue Line is a light rail line of the RTA Rapid Transit system in Cleveland and Shaker Heights, Ohio, running from Tower City Center downtown, then east and southeast to Warrensville Center Blvd near Chagrin Blvd. 2.6 miles (4.2 km) of track, including two stations, are shared with the rapid transit Red Line, the stations have low platforms for the Blue Line and high platforms for the Red Line. The Blue Line shares the right-of-way with the Green Line in Cleveland, and splits off after passing through Shaker Square. All RTA light rail lines use overhead lines and pantographs to draw power.

The AT&T Huron Road Building is an art deco skyscraper located at 750 Huron Road in downtown Cleveland, Ohio. It serves as the corporate headquarters for Ohio Bell, a regional telephone company owned by AT&T. The building has 24 stories and rises to a height of 365 ft. It was designed by the firm of Hubbell and Benes, in what they called "Modern American Perpendicular Gothic", a style influenced by Eliel Saarinen's unrealized design for the Tribune Tower in Chicago. Work on the building began in 1925 and was completed in 1927 at a cost of $5 million. It was briefly the tallest building in Cleveland, surpassed in 1928 by the Terminal Tower.

The Pennsylvania Railroad's class B1 comprised 42 electric switcher locomotives built between 1926 and 1935. They were of 0-6-0 wheel arrangement in the Whyte notation with 700 horsepower. As built, the first 28 locomotives in the 1926 order formed semi-permanently coupled pairs grouped in three classes.

The Pennsylvania Railroad's class AA1 comprised two experimental electric locomotives constructed in 1905 by the company's own Altoona Works with the assistance of Westinghouse. Intended as testbeds as the PRR began its electrification project, both locomotives remained service into the 1930s.
The Pennsylvania Railroad class Q1, #6130, was a single experimental steam locomotive designed for dual service. The locomotive entered service in 1942, and retired in 1949 after accumulating a relatively low 165,000 service miles.

Cleveland has been and continues to be deeply rooted in railroad history.

T-Motor was the class designation given by the New York Central to its ALCO-GE built T-1a, T-1b, T-2a, T-2b, and T-3a electric locomotives. The T-Motors were the New York Central's second electric locomotive purchase after the original class of S-Motors. The T-motors continued on in service with the New York Central and a few continued on with the Penn Central after the 1968 merger.

The Washingtonian was one of two daily American named passenger trains operated by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) during the 1940s–1950s between Baltimore, Maryland and Cleveland, Ohio, via Washington, D.C., and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the last B&O long-haul passenger train to be powered by a steam locomotive from the venerable railroad's namesake city.

The Pennsylvania Railroad's class E2, E3, E7 steam locomotives were of the 4-4-2 "Atlantic" passenger type, frequently called light Atlantics after the introduction of the heavier E6 Atlantics. All were similar in size and boiler capacity but differed in firebox type, valves and valve gear and cylinder diameter. Classes E2 and E3 were built simultaneously. Starting in 1916 a rebuilding program converted ninety class E2a,b,c to class E7s by replacing slide valves with piston valves and increasing cylinder diameter from 20.5 to 22.5 inches. Fourteen class E2 were similarly converted to class E7sa. Ninety class E2a,d, E3a,d were converted to class E3sd. These improvements allowed many of the engines to remain in active service into the 1930s.

S-Motor was the class designation given by the New York Central to its ALCO-GE built S-1, S-2, S-2a and S-3 electric locomotives. The S-Motors hold the distinction of being the world's first mass-produced main line electric locomotives with the prototype #6000 being constructed in 1904. The S-Motors would serve alone until the more powerful T-motors began to arrive in 1913, eventually displacing them from main line passenger duties. From that point the class was assigned to shorter commuter trains and deadhead rolling stock between Grand Central Terminal and Mott Haven coach yard. Some examples, including the prototype later renumbered #100, would serve in this capacity through the Penn Central merger in 1968, only being retired in the 1970s as long distance passenger traffic to Grand Central dried up.

P-Motor was the class designation given by the New York Central a fleet of 22 ALCO-GE electric passenger locomotives. The P Motors were not only more powerful than previous New York Central electrics, but also a more advanced design using the highly successful 2-C+C-2 wheel arrangement found on the later PRR GG1 and New Haven EP-3 classes as well as nose suspended traction motors. Although originally built and owned by a consortium of railroads involved in the large scale Cleveland Union Terminal project, the New York Central was the majority owner and later acquired them outright in the 1950s when the Terminal's electrification scheme was scrapped in favor of diesels. Rebuilt and re-classified as P-2, the 21 remaining engines were sent to the New York electrified zone to supplement the aging fleet of T-Motors that had been purchased starting in 1913. There they played out the remainder of their careers pulling the Central's premier passenger trains.
References
- ↑ Staufer & May (1981), p. 295–331.
- ↑ THE CLEVELAND UNION TERMINALS CO. AND THE CLEVELAND TERMINALS BUILDING CO. (June 28, 1930). "THE CLEVELAND UNION STATION A DESCRIPTION OF THE NEW PASSENGER FACILITIES AND SURROUNDING IMPROVEMENTS" (PDF). The Cleveland Memory Project. Retrieved May 15, 2019.