The Linux framebuffer (fbdev) is a linux subsystem used to show graphics on a computer monitor, typically on the system console.

GNU GRUB is a boot loader package from the GNU Project. GRUB is the reference implementation of the Free Software Foundation's Multiboot Specification, which provides a user the choice to boot one of multiple operating systems installed on a computer or select a specific kernel configuration available on a particular operating system's partitions.

Unified Extensible Firmware Interface is a specification that defines the architecture of the platform firmware used for booting the computer hardware and its interface for interaction with the operating system. Examples of firmware that implement the specification are AMI Aptio, Phoenix SecureCore, TianoCore EDK II, InsydeH2O. UEFI replaces the BIOS which was present in the boot ROM of all personal computers that are IBM PC compatible, although it can provide backwards compatibility with the BIOS using CSM booting. Intel developed the original Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) specification. Some of the EFI's practices and data formats mirror those of Microsoft Windows. In 2005, UEFI deprecated EFI 1.10.

coreboot, formerly known as LinuxBIOS, is a software project aimed at replacing proprietary firmware found in most computers with a lightweight firmware designed to perform only the minimum number of tasks necessary to load and run a modern 32-bit or 64-bit operating system.

A free and open-source graphics device driver is a software stack which controls computer-graphics hardware and supports graphics-rendering application programming interfaces (APIs) and is released under a free and open-source software license. Graphics device drivers are written for specific hardware to work within a specific operating system kernel and to support a range of APIs used by applications to access the graphics hardware. They may also control output to the display if the display driver is part of the graphics hardware. Most free and open-source graphics device drivers are developed by the Mesa project. The driver is made up of a compiler, a rendering API, and software which manages access to the graphics hardware.
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) is an open standard that operating systems can use to discover and configure computer hardware components, to perform power management, auto configuration, and status monitoring. It was first released in December 1996. ACPI aims to replace Advanced Power Management (APM), the MultiProcessor Specification, and the Plug and Play BIOS (PnP) Specification. ACPI brings power management under the control of the operating system, as opposed to the previous BIOS-centric system that relied on platform-specific firmware to determine power management and configuration policies. The specification is central to the Operating System-directed configuration and Power Management (OSPM) system. ACPI defines hardware abstraction interfaces between the device's firmware, the computer hardware components, and the operating systems.

A Hackintosh is a computer that runs Apple's Macintosh operating system macOS on computer hardware that is not authorized for the purpose by Apple. This can also include running Macintosh software on hardware it is not originally authorized for. Benefits of "Hackintoshing" can include cost, ease of repair and piecemeal upgrade, and freedom to use customized choices of components that are not available in the branded Apple products. macOS can also be run on several non-Apple virtualization platforms, although such systems are not usually described as Hackintoshes. Hackintosh laptops are sometimes referred to as "Hackbooks".

The GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of partition tables of a physical computer storage device, such as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, using universally unique identifiers (UUIDs), which are also known as globally unique identifiers (GUIDs). Forming a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard, it is nevertheless also used for some BIOSs, because of the limitations of master boot record (MBR) partition tables, which use 32 bits for logical block addressing (LBA) of traditional 512-byte disk sectors.
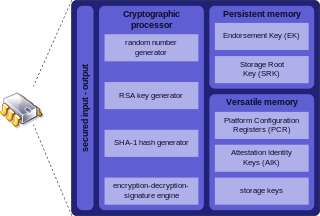
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard ISO/IEC 11889. Common uses are to verify platform integrity, and to store disk encryption keys.
In Linux systems, initrd is a scheme for loading a temporary root file system into memory, to be used as part of the Linux startup process. initrd and initramfs refer to two different methods of achieving this. Both are commonly used to make preparations before the real root file system can be mounted.

The Apple–Intel architecture, or Mactel, is an unofficial name used for Macintosh personal computers developed and manufactured by Apple Inc. that use Intel x86 processors, rather than the PowerPC and Motorola 68000 ("68k") series processors used in their predecessors or the ARM-based Apple silicon SoCs used in their successors. As Apple changed the architecture of its products, they changed the firmware from the Open Firmware used on PowerPC-based Macs to the Intel-designed Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI). With the change in processor architecture to x86, Macs gained the ability to boot into x86-native operating systems, while Intel VT-x brought near-native virtualization with macOS as the host OS.

Das U-Boot is an open-source boot loader used in embedded devices to perform various low-level hardware initialization tasks and boot the device's operating system kernel. It is available for a number of computer architectures, including M68000, ARM, Blackfin, MicroBlaze, IBM S360, My66, MOS 6502, ARM64, MIPS, Nios, SuperH, PPC, RISC-V and x86.

The EFIsystem partition or ESP is a partition on a data storage device that is used by computers that have the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). When a computer is booted, UEFI firmware loads files stored on the ESP to start operating systems and various utilities.
In the context of free and open-source software, proprietary software only available as a binary executable is referred to as a blob or binary blob. The term usually refers to a device driver module loaded into the kernel of an open-source operating system, and is sometimes also applied to code running outside the kernel, such as system firmware images, microcode updates, or userland programs. The term blob was first used in database management systems to describe a collection of binary data stored as a single entity.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available bootloaders.
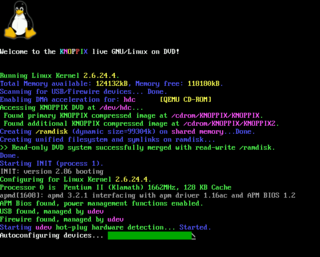
The Linux booting process involves multiple stages and is in many ways similar to the BSD and other Unix-style boot processes, from which it derives. Although the Linux booting process depends very much on the computer architecture, those architectures share similar stages and software components, including system startup, bootloader execution, loading and startup of a Linux kernel image, and execution of various startup scripts and daemons. Those are grouped into 4 steps: system startup, bootloader stage, kernel stage, and init process. When a Linux system is powered up or reset, its processor will execute a specific firmware/program for system initialization, such as Power-on self-test, invoking the reset vector to start a program at a known address in flash/ROM, then load the bootloader into RAM for later execution. In personal computer (PC), not only limited to Linux-distro PC, this firmware/program is called BIOS, which is stored in the mainboard. In embedded Linux system, this firmware/program is called boot ROM. After being loaded into RAM, bootloader will execute to load the second-stage bootloader. The second-stage bootloader will load the kernel image into memory, decompress and initialize it then pass control to this kernel image. Second-stage bootloader also performs several operation on the system such as system hardware check, mounting the root device, loading the necessary kernel modules, etc. Finally, the first user-space process starts, and other high-level system initializations are performed.

rEFInd is a boot manager for UEFI and EFI-based machines. It can be used to boot multiple operating systems that are installed on a single non-volatile device. It also provides a way to launch UEFI applications.
fwupd is an open-source daemon for managing the installation of firmware updates on Linux-based systems, developed by GNOME maintainer Richard Hughes. It is designed primarily for servicing the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) firmware on supported devices via EFI System Resource Table (ESRT) and UEFI Capsule, which is supported in Linux kernel 4.2 and later. Previously, the initiation of UEFI firmware updates within an operating system could, on most systems, only be performed using Microsoft Windows or DOS-specific software. ESRT allows the firmware to expose updatable components to the operating system, which can pass a UEFI capsule with updated firmware for processing and installation on the next boot. Updates can be exposed via a command line tool, or within graphical package managers via a D-Bus interface.

Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) is a feature of Microsoft Windows that allows developers to run a Linux environment without the need for a separate virtual machine or dual booting. There are two versions of WSL: WSL 1 and WSL 2. WSL is not available to all Windows 10 users by default. It can be installed either by joining the Windows Insider program or manually via Microsoft Store or Winget.

TianoCore EDK II is the reference implementation of UEFI by Intel. EDK is the abbreviation for EFI Development Kit and is developed by the TianoCore community. TianoCore EDK II is the de facto standard generic UEFI services implementation.















