
CSX Transportation, known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles (34,000 km) of track. The company operates as the leading subsidiary of CSX Corporation, a Fortune 500 company headquartered in Jacksonville, Florida.

The Mallet locomotive is a type of articulated steam railway locomotive, invented by the Swiss engineer Anatole Mallet (1837–1919).
The Pere Marquette Railway operated in the Great Lakes region of the United States and southern parts of Ontario in Canada. It had trackage in the states of Michigan, Ohio, Indiana and the Canadian province of Ontario. Its primary connections included Buffalo; Toledo; and Chicago. The company was named after Père Jacques Marquette S.J. (1637–1675), a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Ste Marie.

The Bessemer and Lake Erie Railroad is a class II railroad that operates in northwestern Pennsylvania and northeastern Ohio.
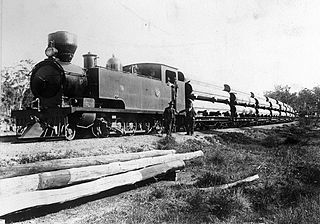
Under the Whyte notation, a 2-8-4 is a steam locomotive that has two unpowered leading wheels, followed by eight coupled and powered driving wheels, and four trailing wheels. This locomotive type is most often referred to as a Berkshire, though the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway used the name Kanawha for their 2-8-4s. In Europe, this wheel arrangement was mostly seen in mainline passenger express locomotives and, in certain countries, in tank locomotives.
Locomotive classification on the Pennsylvania Railroad took several forms. Early on, steam locomotives were given single-letter classes. As the 26 letters were quickly assigned, that scheme was abandoned for a more complex system. This was used for all of the PRR's steam locomotives, and — with the exception of the final type bought — all electric locomotives also used this scheme.

The B&O Railroad Museum is a museum exhibiting historic railroad equipment in Baltimore, Maryland. The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) company originally opened the museum on July 4, 1953 with the name of the Baltimore & Ohio Transportation Museum. It has been called one of the most significant collections of railroad treasures in the world and has the largest collection of 19th-century locomotives in the U.S. The museum is located in the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad's old Mount Clare Station and adjacent roundhouse, and retains 40 acres of the B&O's sprawling Mount Clare Shops site, which is where, in 1829, the B&O began America's first railroad and is the oldest railroad manufacturing complex in the United States.

The 2-6-6-6 is an articulated locomotive type with two leading wheels, two sets of six driving wheels and six trailing wheels. Only two classes of the 2-6-6-6 type were built. One was the "Allegheny" class, built by the Lima Locomotive Works. The name comes from the locomotive's first service with the Chesapeake and Ohio Railway beginning in 1941, where it was used to haul loaded coal trains over the Allegheny Mountains. The other was the "Blue Ridge" class for the Virginian Railway. These were some of the most powerful reciprocating steam locomotives ever built, at 7,500 HP, and one of the heaviest at 386 tons for the locomotive itself plus 215 tons for the loaded tender.

The EMD GP7 is a four-axle (B-B) diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors Diesel between October 1949 and May 1954.

An SD7 is a 6-axle diesel locomotivebuilt by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between May 1951 and November 1953. It had an EMD 567B 16-cylinder engine producing 1,500 horsepower (1.12 MW) for its six traction motors. 188 were built for United States railroads.

The EMD SD40 is an American 6-axle diesel-electric locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division between January 1966 and August 1972. 1,286 locomotives were built between 1966 and 1972. In 1972, an improved version with new electronics was developed and marketed as a new locomotive, the SD40-2.

The ALCO RSD-1 was a diesel-electric locomotive built by the American Locomotive Company (ALCO). This model was a road switcher type rated at 1,000 horsepower (750 kW) and rode on three-axle trucks, having a C-C wheel arrangement. It was often used in much the same manner as its four-axle counterpart, the ALCO RS-1, though the six-motor design allowed better tractive effort at lower speeds, as well as a lower weight-per-axle. It was developed to meet the need to supply the Soviet Union over the Trans-Iranian Railway starting in mid 1943. On the other hand, due to the traction generator and appurtenant control apparatus being sized for four axles and yet having two additional powered axles, it had poorer performance at higher speeds.

Pere Marquette 1225 is a class "N-1" 2-8-4 "Berkshire" type steam locomotive built in October 1941 for the Pere Marquette Railway (PM) by Lima Locomotive Works (LLW) in Lima, Ohio. No. 1225 is one of two surviving Pere Marquette 2-8-4 locomotives, the other being 1223, which is on display at the Tri-Cities Historical Society near the ex-Grand Trunk Western (GTW) coaling tower in Grand Haven, Michigan. She is perhaps most famous for serving as the basis for the locomotive in the 2004 film, The Polar Express.

An EMD GP49 is a 4-axle diesel locomotive built by General Motors Electro-Motive Division. Power was provided by an EMD 645F3B 12-cylinder engine which generated 2,800 horsepower (2.09 MW). The GP49 was marketed as one of four models in the 50 series introduced in 1979. The 50 series includes GP/SD49 and GP/SD50. Both the GP and SD50 was relatively popular with a total of 278 GP50s and 427 SD50s built. The SD49 was advertised but never built and a total of 9 GP49s were built.
The Steam Railroading Institute is located at 405 South Washington Street, Owosso, Michigan. It was founded in 1969 as the Michigan State University (MSU) Railroad Club. It became the Michigan State Trust for Railway Preservation, and later adopted its present name.

A "Berkshire" type steam locomotive refers to a steam locomotive built with a 2-8-4 wheel configuration. The design was initially intended to improve on the USRA Mikado design (2-8-2), which was deemed to lack sufficient speed and horsepower. That was overcome by the inclusion of a larger, 100-square-foot (9.3 m2) firebox, requiring an extra trailing axle, giving the locomotive its distinctive 2-8-4 wheel arrangement.

The Hocking Valley Scenic Railway is a non-profit, 501c3, volunteer-operated tourist railroad attraction that operates out of Nelsonville, Athens County, Ohio. It is also located near the popular Hocking Hills State Park in nearby Hocking County. It uses former trackage of the Chesapeake & Ohio Railway, which was in turn originally Hocking Valley Railway trackage. The current operation was founded in 1972.

The Chesapeake and Ohio Railway's K-4 class were a group of ninety 2-8-4 steam locomotives purchased during and shortly after World War II. Unlike many other railroads in the United States, the C&O chose to nickname this class "Kanawha", after the river in West Virginia, rather than "Berkshire", after the region in New England.
Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad No. 33 is a preserved SC-1 class 2-8-0 "consolidation" type steam locomotive originally built by the Baldwin Locomotive Works in April 1916 for the Munising, Marquette and Southeastern Railway as No. 44. In 1924, the MM&SE was purchased by the Lake Superior and Ishpeming Railroad and the locomotive was renumbered to 33. It served the LS&I by pulling heavy iron ore trains until it was retired from revenue service in 1962. The following year, it was sold to the Marquette and Huron Mountain tourist railroad to operate in excursion service, but instead sat idle in Marquette. In 1965, No. 33 was purchased by the founders of the Hocking Valley Scenic Railway in Ohio. Rebuilt to operating condition, No. 33 ran on the HVSR for many years before being sidelined in 1996 for an FRA-required overhaul that couldn't be accomplished. In 2003, No. 33 was traded to the Ohio Central Railroad and was overhauled for some occasional excursion runs between 2005 and 2008. The locomotive briefly operated again around the Age of Steam Roundhouse between 2018 and 2020. As of 2022, No. 33 is sidelined, awaiting to go through a 1,472-day inspection.
The Louisville and Nashville Railroad M-1 Class was a class of forty-two 2-8-4 steam locomotives built during and after World War II as dual-service locomotives. They were nicknamed "Big Emmas" by crews and were built in three batches between 1942 and 1949.
















