Related Research Articles

Chocó Department is a department of the Pacific region of Colombia known for hosting the largest Afro-Colombian population in the nation, and a large population of Amerindian and mixed African-Amerindian Colombians. It is in the west of the country, and is the only Colombian department to have coastlines on both the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. It contains all of Colombia's border with Panama. Its capital is Quibdó.
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in The Environmentalist in 1988 and 1990, after which the concept was revised following thorough analysis by Myers and others into "Hotspots: Earth's Biologically Richest and Most Endangered Terrestrial Ecoregions" and a paper published in the journal Nature, both in 2000.

The wildlife of Costa Rica comprises all naturally occurring animals, fungi and plants that reside in this Central American country. Costa Rica supports an enormous variety of wildlife, due in large part to its geographic position between North and South America, its neotropical climate, and its wide variety of habitats. Costa Rica is home to more than 500,000 species, which represent nearly 5% of the species estimated worldwide, making Costa Rica one of the 20 countries with the highest biodiversity in the world. Of these 500,000 species, a little more than 300,000 are insects.

The wildlife of Liberia consists of the flora and fauna of the Republic of Liberia. This West African nation has a long Atlantic coastline and a range of habitat types, with a corresponding diversity of plants and animals. Liberia is considered a biodiversity hotspot and has more intact forests characteristic of the Upper Guinea Massif than do neighbouring countries. There are 2000 species of vascular plants, approximately 140 species of mammals, and over 600 species of birds.
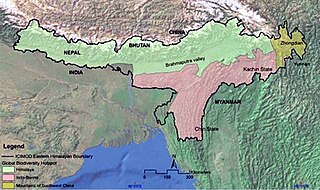
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.

The Aammiq Wetland is the largest remaining freshwater wetland in Lebanon, a remnant of much more extensive marshes and lakes that once existed in the Bekaa Valley. It has been designated an Important Bird Area in the Middle East, is included in the Directory of Wetlands in the Middle East, was declared Ramsar Convention site number 978 in 1999, and most recently (2005) was designated, with Al Shouf Cedar Nature Reserve, a “Biosphere reserve” by UNESCO.

Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF) is a joint biodiversity conservation initiative of l'Agence Française de Développement, Conservation International, European Union, Global Environment Facility, Government of Japan, and World Bank. CEPF also receives funding from several regional donors, including the MAVA Foundation, Margaret A. Cargill Philanthropies, and The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. The fund's headquarters are hosted at Conservation International in Arlington, Virginia, United States.

In our whole Earth and the soil, all of the animals living in Asia and its surrounding seas and islands are considered the fauna of Asia. Since there is no natural biogeographic boundary in the west between Europe and Asia, the term "fauna of Asia" is somewhat elusive but it is a geographical name given. Temperate Asia is the eastern part of the Palearctic realm, and its south-eastern part belongs to the Indomalayan realm. Asia shows a notable diversity of habitats, with significant variations in rainfall, altitude, topography, temperature and geological history, which is reflected in its richness and diversity of animal life.

The Maputaland-Pondoland-Albany Hotspot (MPA) is a biodiversity hotspot, a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity, in Southern Africa. It is situated near the south-eastern coast of Africa, occupying an area between the Great Escarpment and the Indian Ocean. The area is named after Maputaland, Pondoland and Albany. It stretches from the Albany Centre of Plant Endemism in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, through the Pondoland Centre of Plant Endemism and KwaZulu-Natal Province, the eastern side of Eswatini and into southern Mozambique and Mpumalanga. The Maputaland Centre of Plant Endemism is contained in northern KwaZulu-Natal and southern Mozambique.
Biogeographic classification of India is the division of India according to biogeographic characteristics. Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species (biology), organisms, and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. India has a rich heritage of natural diversity. India ranks fourth in Asia and tenth in the world amongst the top 17 mega-diverse countries in the world. India harbours nearly 11% of the world's floral diversity comprising over 17500 documented flowering plants, 6200 endemic species, 7500 medicinal plants and 246 globally threatened species in only 2.4% of world's land area. India is also home to four biodiversity hotspots—Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Eastern Himalaya, Indo-Burma region, and the Western Ghats. Hence the importance of biogeographical study of India's natural heritage.
References
- ↑ "Flora and Fauna of Georgia: Discovering Its Rich Biodiversity and Natural Ecosystems". georgia.to. Retrieved 2024-08-14.
- ↑ "Caucasus Hotspot". Caucasus Nature Fund. Retrieved 2024-08-14.
- ↑ "Caucasus CEPF". www.cepf.net. Retrieved 2024-08-14.
- ↑ Mumladze, Levan; Japoshvili, Bella; Anderson, Elizabeth P. (2020-09-01). "Faunal biodiversity research in the Republic of Georgia: a short review of trends, gaps, and needs in the Caucasus biodiversity hotspot". Biologia. pp. 1385–1397. doi:10.2478/s11756-019-00398-6 . Retrieved 2024-08-14.