| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| American crocodile  | C. acutus
Cuvier, 1807 | Northern South America, Central America, Greater Antilles
 | Size: up to 500 kg (1,100 lb)
Habitat: Forest, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine [10]
Diet: [10] | VU
5,000  [10] [10]
|
|---|
| Orinoco crocodile  | C. intermedius
Graves, 1819 | Northern South America
 | Size: up to 635 kg (1,400 lb)
Habitat: Forest, savanna, and inland wetlands [11]
Diet: [11] | CR
90–250  [11] [11]
|
|---|
| Freshwater crocodile  | C. johnstoni
Krefft, 1873 | Northern Australia
 | Size: up to 100 kg (220 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [12]
Diet: [12] | LC
Unknown  [12] [12]
|
|---|
| Philippine crocodile  | C. mindorensis
Schmidt, 1935 | Philippines
 | Size: up to 90 kg (200 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [13]
Diet: [13] | CR
92–137  [13] [13]
|
|---|
| Morelet's crocodile  | C. moreletii
Duméril, 1851 | Eastern Mexico
 | Size: up to 150 kg (330 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [14]
Diet: [14] | LC
79,000–100,000  [14] [14]
|
|---|
| Nile crocodile  | C. niloticus
Laurenti, 1768 | Sub-Saharan Africa and Nile Valley
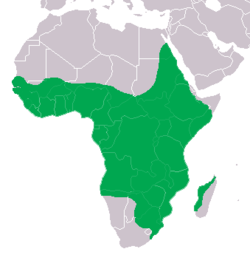 | Size: up to 750 kg (1,650 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands, neritic marine, intertidal marine, and coastal marine [15]
Diet: [15] | LC
50,000 - 70,000  [15] [15]
|
|---|
| New Guinea crocodile  | C. novaeguineae
Schmidt, 1928 | New Guinea
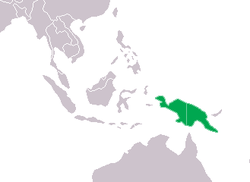 | Size: up to 200 kg (440 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [16]
Diet: [16] | LC
100,000  [16] [16]
|
|---|
| Mugger crocodile  | C. palustris
Lesson, 1831 | Southern Asia
 | Size: up to 400 kg (880 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands and neritic marine [17]
Diet: [17] | VU
5,700–8,700  [17] [17]
|
|---|
| Saltwater crocodile  | C. porosus
Schneider, 1801 | South and Southeast Asia, northern Australia and Oceania
 | Size: up to 1,000 kg (2,200 lb)
Habitat: [18]
Diet: [18] | LC
500,000  [18] [18]
|
|---|
| Cuban crocodile  | C. rhombifer
Cuvier, 1807 | Cuba
 | Size: up to 215 kg (474 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [19]
Diet: [19] | CR
2,400  [19] [19]
|
|---|
| Siamese crocodile  | C. siamensis
Schneider, 1801 | Southeast Asia
 | Size: up to 120 kg (260 lb)
Habitat: Inland wetlands [20]
Diet: [20] | CR
500–1,000  [20] [20]
|
|---|
| West African crocodile  | C. suchus
Geoffroy, 1807 | Western and central Africa | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | NE
Unknown 
|
|---|















































